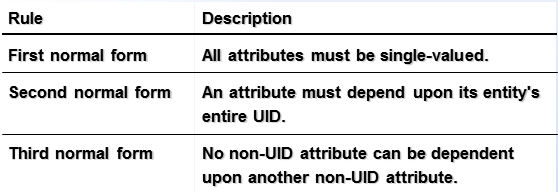
三大范式:
第一范式:如大小不能作为属性,因为大小有长宽高三个方面,不是单值的; 第二范式:所有属性必须依赖于主键,否则另外的那些属性可以拆分作为另外的一张表;
第三范式:所有的非主属性之间不依赖于任何一个其他属性,仅仅单一的地只依赖与主键,如成绩除了关联学号,还依赖于具体学科;这样就不符合第三范式;
DDL语句:
1: 建立数据库
CREATE DATABASE student
ON PRIMARY
(
NAME = student,
FILENAME = 'D:\Data\student.mdf',
SIZE = 4MB,
MAXSIZE = 6MB,
FILEGROWTH = 20%
)2: 定义表
CREATE TABAL Stu
(
Sno CHAR(5) PRIMARY KEY,
Sname VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE,
Sex CHAR(1) NOT NULL,
Sdept VARCHAR(15),
Smon CHAR(5),
SBirthday SMALLDATIME
)约束
非空约束/not null字段约束
create table stu_uu(
// 默认值,自己命名的非空约束
id number(5) default 1 constraint nul_1 not null,
name varchar2(30) constraint nul_2 not null,
// 可省constraint xxx,即可省略约束命名,系统自动命名
score number(5,2) not null
remark varchar2(30)
)
// 注意not null约束不允许用于表约束中,如:
// constraint nul_3 not null(remark) 是错误的;主键约束
create table stu_uu(
id number(5) constraint nul_1 not null constraint pk_id primary key, // 默认值,自己命名的非空约束
name varchar2(30) constraint nul_2 not null,
// 可省constraint xxx,即可省略约束命名,系统自动命名
score number(5,2) not null
remark varchar2(30)
)
/*
constraint pk_id primary key(id) 若是使用表级约束进行
定义主键,则主键约束名不可省略,列级中的主键约束的约束名可省略
*/外键约束
create table score_uu
(
id number(5) not null primary key,
score float default 0 not null
)
create table stu_uu
(
id number(5) not null primary key,
name varchar2(30) not null,
score_id number(5) not null constraint pk_fk_001
references score_uu(id) // 列级约束
// constraint pk_fk_001 foreign key (score_id) //references score_uu(id) on delete cascade//表级约束
)注:
外键约束时加上:
on delete cascade - 表示删除主表的记录时,其对应的关联表记录也会被删除,删除关联表则删除不了,报错违反一致性约束
on delete set null - 表示删除主表的记录时,其对应的关联表记录也会被删除,删除关联表时关联表的记录能够删除,记录中主表对应的外键这时值自动改为NULL值;
唯一约束
CHECK约束
create table str_uu
(
id integer not null primary key,
name varchar2(30) not null check (length(name) <= 10)
) 注:对于列级约束的约束名都可以省略,用系统自动的命名也行,但是对于表级约束则不能省略约束名;
其中,非空约束是不能作为表级约束的,其它约束都可以作为表级约束或列级约束;
check约束的规则:
Expressions not allowed
1 References to pseudocolumns CURRVAL, NEXTVAL, LEVEL, or ROWNUM
2 Calls to SYSDATE, UID, USER, or USERENV functions
3 Queries that refer to other values in other rows注意创建表时使用以下这种方式:
Create a table containing all employees in department number 41 in the S_EMP table.CREATE TABLE emp_41
AS
SELECT id, last_name, userid, start_date
FROM s_emp
WHERE dept_id = 41; 数据会被正常拷贝,但是:
Do not forget that only the NOT NULL constraint is copied.其它的约束全部丢失;
DML语句
1. insert
insert into 表名(字段1,字段2,....) values(值1,值2,....);
insert into 表名 values(值1,值2,....);--必须是全部字段2.update
update 表名 set 字段1=值1/表达式,字段2=值2,.... [where 条件]
// 不带where子句时,会出现全部记录被修改的情况
update s_emp set salary = salary+50;3.delete
// 删除记录,与删除表的drop指令区分
delete from 表名 [where ...]
// 不带上where条件的会删除所有记录4.alter
ALTER TABLE <表名>
[ADD <新列名> <数据类型> [完整性约束]]
[DROP <完整性约束>]
[MODIFY <列名> <数据类型>]举例:
ALTER TABLE Stu ADD Scome DATETIME;
ALTER TABLE SC DROP SCORE_CHK;
ALTER TABLE Stu MODIFY COLUMN Sname VARCHAR(28);删除基本表
DROP TABLE Stu建立索引
create index idx_test
on stu_uu( name, birth );
// SC表按照学好升序,课程号降序建唯一索引
create UNIQUE INDEX SCno ON SC
(Sno ASC, Cno DESC);删除索引
DROP INDEX 数据表名.索引名;l Automatically(自动索引)
A unique index is created automatically when you define a PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE constraint in a table definition.
ll Manually(自定义索引)
Users can create non-unique indexes on columns to speed up access time to the rows.
提倡使用索引的原因:
1 Used by the Oracle Server to speed up the retrieval of rows by using a pointer
2 Reduces disk I/O by using rapid path access method to locate the data quickly
3 Automatically used and maintained by the Oracle Server, and no interaction is required from the user.
视图
视图view(“管中窥豹”,类似一个表中的小窗口,对数据库的限制访问)
1 Restrict database access
2 Simplify queries
3 Data independence(数据独立无关)
4 Different appearances for the same data
创建视图
create view 视图名
(字段名)
as
select子查询
[with check 选项]
[with read only]
// 这里的as后的select子查询不能使用order by例子:
create view vw_test001 as
select id, firsr_name, salary+nvl(commissiom_pct,0) as sal
// 对于视图中的表达式作为列名必须用as其别名
from s_emp;或者方式二:
create or replace view vw_test001(id,name,sal)
as
select id,first_name,salary+nvl(commission_pct,0) from s_emp;3.2.使用视图
与表的使用一样;
select * from vw_test001; // 一个视图可以看作一张表
3.3.视图的作用:
通过视图可以对同一张表进行不同角度的查询。
3.4.视图的本质:
查询模版
3.5.删除视图
DROP VIEW viewname; 注意:
1: 视图中不能使用order by,但视图创建好后,使用时可以使用order by;
2: 索引能提高查询速度。但假如不必要的索引会影响插入删除等的性能问题;






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








