LRU算法(最近最久未使用算法)
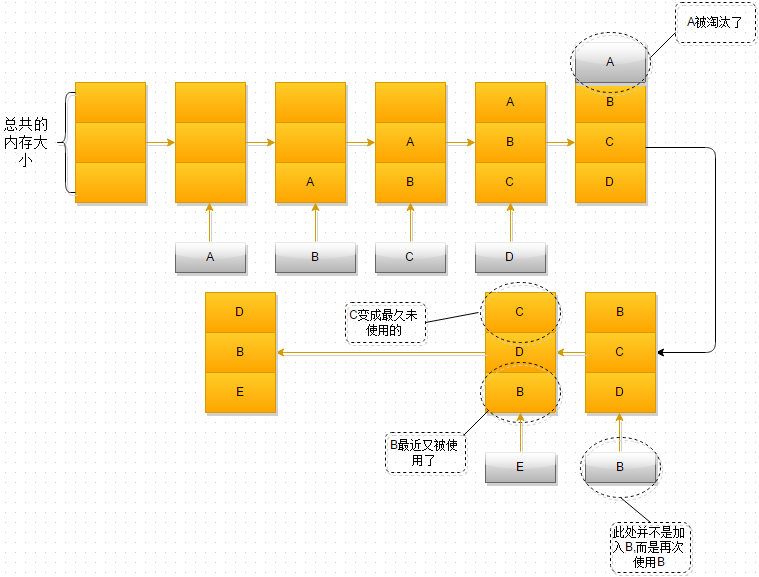
LRU算法作为内存管理的一种有效算法,其含义是在内存有限的情况下,当内存容量不足时,为了保证程序的运行,这时就不得不淘汰内存中的一些对象,释放这些对象占用的空间,那么选择淘汰哪些对象呢?LRU算法就提供了一种策略,告诉我们选择最近一段时间内,最久未使用的对象将其淘汰,至于为什么要选择最久未使用的,可以想想,最近一段时间内使用的东西,我们是不是可能一会又要用到呢~,而很长一段时间内都没有使用过的东西,也许永远都不会再使用
在操作系统中LRU算法淘汰的不是内存中的对象,而是页,当内存中数据不足时,通过LRU算法,选择一页(一般是4KB)将其交换到虚拟内存区(Swap区)
LRU算法演示
算法实现应该采用怎样的数据结构
队列,FIFO,LRU算法最为精典的实现,HashMap+Double LinkedList,时间复杂度为O(1)
struct Node
{
Node(int _key,int _value){key = _key;value = _value;pre = next = NULL;}
int key;
int value;
Node*pre;
Node*next;
};
class LRUCache{
public:
// @param capacity, an integer
LRUCache(int capacity) {
// write your code here
this->capacity = capacity;
size = 0;
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
}
// @return an integer
int get(int key) {
// write your code here
if(m.find(key)==m.end())
{
return -1;
}
else
{
Node* n = m[key];
int ret = n->value;
if(head!=n)
{
if(n==tail)
tail = tail->pre;
Node*pre = n->pre;
if(n->next!=NULL)
n->next->pre = pre;
pre->next = n->next;
n->next = head;
head->pre = n;
head = n;
}
return ret;
}
}
// @param key, an integer
// @param value, an integer
// @return nothing
void set(int key, int value) {
// write your code here
if(head==NULL)
{
head = new Node(key,value);
tail = head;
size++;
m[key] = head;
return;
}
if(m.find(key)==m.end())
{
Node*n = new Node(key,value);
n->next = head;
head->pre = n;
head = n;
m[key] = n;
size++;
}
else
{
Node*n = m[key];
if(head!=n)
{
if(n==tail)
tail = tail->pre;
Node*pre = n->pre;
pre->next = n->next;
if(n->next!=NULL)
n->next->pre = pre;
n->next = head;
head->pre = n;
head = n;
m[key] = n;
}
head->value = value;
}
if(size>capacity)
{
Node*todel = tail;
int keyToDel = todel->key;
tail = tail->pre;
tail->next = NULL;
delete todel;
m.erase(m.find(keyToDel));
size--;
}
}
private:
int capacity;
int size;
Node*head;
Node*tail;
unordered_map<int,Node*> m;
};





















 607
607

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








