LeetCode Weekly Contest 32解题思路
详细代码可以fork下Github上leetcode项目,不定期更新。
赛题
本次周赛主要分为以下4道题:
- 581 Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray (4分)
- 582 Kill Process (6分)
- 583 Delete Operation for Two Strings (7分)
- 587 Erect the Fence (9分)
581 Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray (4分)
Problem:
Given an integer array, you need to find one continuous subarray that if you only sort this subarray in ascending order, then the whole array will be sorted in ascending order, too.
You need to find the shortest such subarray and output its length.
Example 1:
Input: [2, 6, 4, 8, 10, 9, 15]
Output: 5
Explanation: You need to sort [6, 4, 8, 10, 9] in ascending order to make the whole array sorted in ascending order.
Note:
- Then length of the input array is in range [1, 10,000].
- The input array may contain duplicates, so ascending order here means <=.
我的思路:
分别找寻数组中的最大值和最小值,然后递归,分为四种情况:
a. 首元素 == 最小值 && 尾元素 == 最大值;
b. 首元素 != 最小值 && 尾元素 == 最大值;
c. 首元素 == 最小值 && 尾元素 != 最大值;
d. 首元素 != 最小值 && 尾元素 != 最大值;public int findUnsortedSubarray(int[] nums) {
return helper(nums, 0, nums.length-1);
}
private int helper(int[] nums, int start, int end){
if (start > end){
return 0;
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++){
min = Math.min(min, nums[i]);
max = Math.max(max, nums[i]);
}
if (min == nums[start] && max == nums[end]){
return helper(nums, start+1, end-1);
}
if (min == nums[start]){
return helper(nums, start+1, end);
}
if (max == nums[end]){
return helper(nums, start, end-1);
}
return end-start+1;
}优化思路:
对数组进行排序,然后直接进行比较,数组排序的时间复杂度为
O(nlogn)
,所以整个时间复杂度为
O(nlogn)
代码如下:
public int findUnsortedSubarray(int[] nums) {
int[] sorted = nums.clone();
Arrays.sort(sorted);
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if (nums[i] == sorted[i]) len++;
else break;
}
for (int j = nums.length-1; j >=0; j--){
if (nums[j] == sorted[j]) len++;
else break;
}
return Math.max(0, nums.length-len);
}582 Kill Process (6分)
Problem:
Given n processes, each process has a unique PID (process id) and its PPID (parent process id).
Each process only has one parent process, but may have one or more children processes. This is just like a tree structure. Only one process has PPID that is 0, which means this process has no parent process. All the PIDs will be distinct positive integers.
We use two list of integers to represent a list of processes, where the first list contains PID for each process and the second list contains the corresponding PPID.
Now given the two lists, and a PID representing a process you want to kill, return a list of PIDs of processes that will be killed in the end. You should assume that when a process is killed, all its children processes will be killed. No order is required for the final answer.
Example 1:
Input:
pid = [1, 3, 10, 5]
ppid = [3, 0, 5, 3]
kill = 5
Output: [5,10]
Explanation:
Kill 5 will also kill 10.
Note:
- The given kill id is guaranteed to be one of the given PIDs.
- n >= 1.
我的思路:
map+队列,因为PID的父类不会继承多个PPID,所以我们可以用PPID作为键值,把PPID的孩子们都找到存在Map中,KILL某个进程时,依次把它的孩子进程也杀死即可,因此存在队列中。代码如下:
public List<Integer> killProcess(List<Integer> pid, List<Integer> ppid, int kill) {
Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < ppid.size(); i++){
map.computeIfAbsent(ppid.get(i), k -> new ArrayList<Integer>()).add(pid.get(i));
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(kill);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int target = queue.poll();
ans.add(target);
if (map.containsKey(target)){
List<Integer> tmp = map.get(target);
for (int num : tmp){
queue.offer(num);
}
}
}
return ans;
}583 Delete Operation for Two Strings (7分)
Problem:
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of steps required to make word1 and word2 the same, where in each step you can delete one character in either string.
Example 1:
Input: “sea”, “eat”
Output: 2
Explanation: You need one step to make “sea” to “ea” and another step to make “eat” to “ea”.
Note:
- The length of given words won’t exceed 500.
- Characters in given words can only be lower-case letters.
最小编辑距离的简单版本,直接用DP解决即可。
思路:
dp[i][j]:表示word1[0,i)和word2[0,j)的最小编辑距离。
两种情况:
if word1[i] == word2[j]; dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j];
if word2[i] != word2[j]; dp[i+1][j+1] = 1 + max{dp[i][j+1],dp[i+1][j]}
代码如下:
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int n = word1.length();
int m = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][m+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
Arrays.fill(dp[i], 1<<30);
}
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
dp[i+1][0] = i+1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++){
dp[0][j+1] = j+1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if (word1.charAt(i) == word2.charAt(j)){
dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j];
}else{
dp[i+1][j+1] = Math.min(dp[i][j+1]+1, Math.min(dp[i+1][j]+1, dp[i][j]+2));
}
}
}
return dp[n][m];
}可优化的地方:
- dp初始化为INF可以去除,只要把min中的+1提取出来即可。
- dp[0][j]和dp[i][0]的更新可以合并到双重循环中。
优化代码如下:
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int n = word1.length();
int m = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][m+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++){
if (i == 0 || j == 0){
dp[i][j] = i + j;
continue;
}
if (word1.charAt(i-1) == word2.charAt(j-1)){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1];
}else{
dp[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return dp[n][m];
}587 Erect the Fence (9分)
Problem:
There are some trees, where each tree is represented by (x,y) coordinate in a two-dimensional garden. Your job is to fence the entire garden using the minimum length of rope as it is expensive. The garden is well fenced only if all the trees are enclosed. Your task is to help find the coordinates of trees which are exactly located on the fence perimeter.
Example 1:
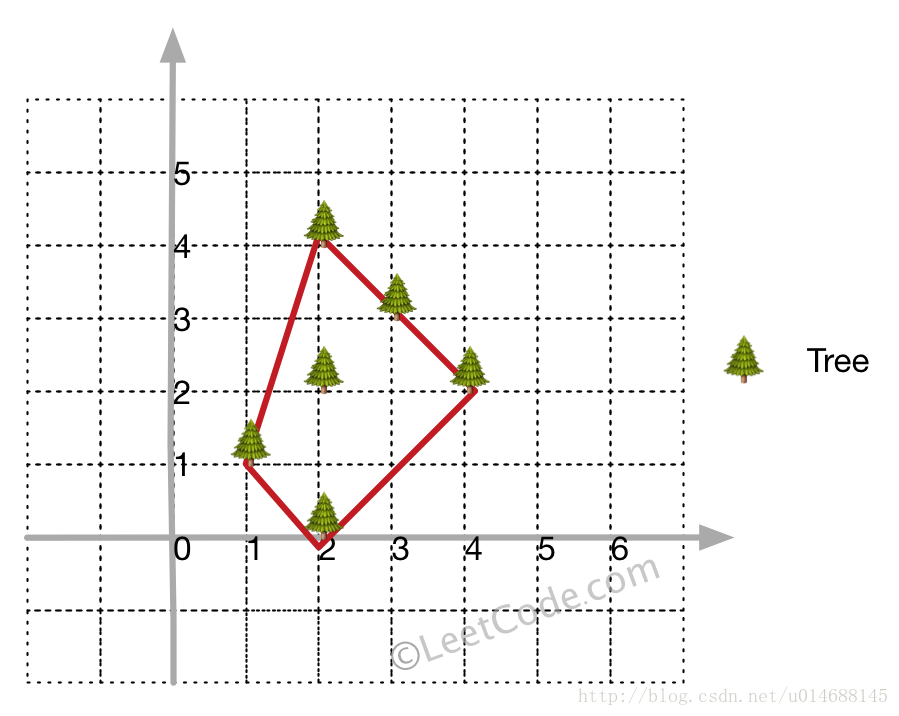
Input: [[1,1],[2,2],[2,0],[2,4],[3,3],[4,2]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,0],[4,2],[3,3],[2,4]]
Explanation:
Example 2:
Input: [[1,2],[2,2],[4,2]]
Output: [[1,2],[2,2],[4,2]]
Explanation:
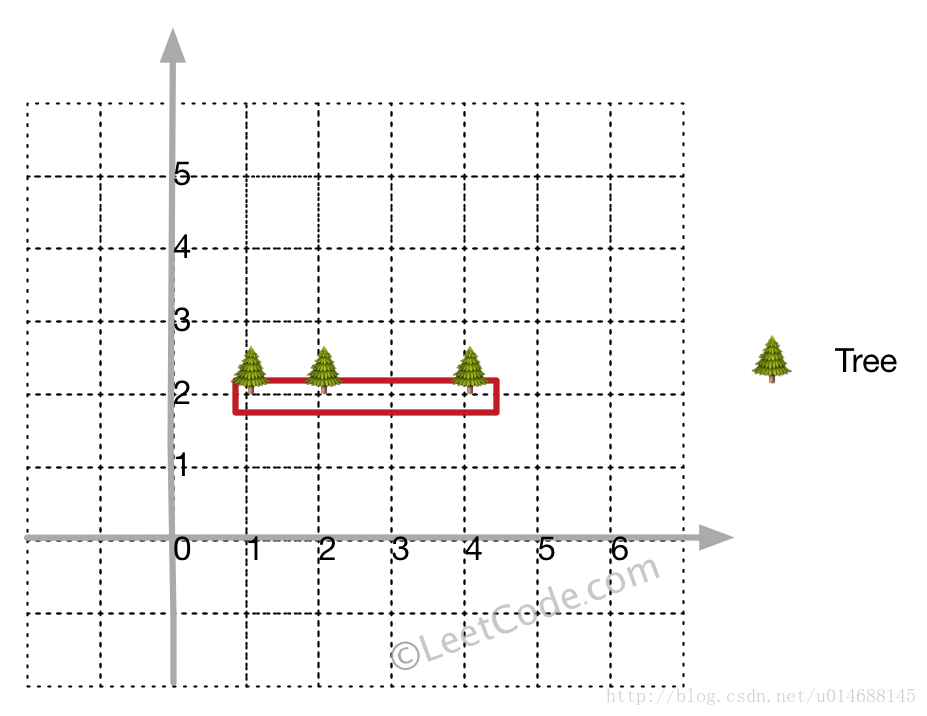
Even you only have trees in a line, you need to use rope to enclose them.
Note:
- All trees should be enclosed together. You cannot cut the rope to enclose trees that will separate them in more than one group.
- All input integers will range from 0 to 100.
- The garden has at least one tree.
- All coordinates are distinct.
- Input points have NO order. No order required for output.
寻找凸包问题,暂且还没学习,先把代码贴上,重新开篇文章专门研究下凸包。
代码如下:
public List<Point> outerTrees(Point[] points) {
Point first = points[0];
int firstIndex = 0;
// Find the leftmost point
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
Point point = points[i];
if (point.x < first.x) {
first = point;
firstIndex = i;
}
}
Set<Point> answer = new HashSet<>();
Point cur = first;
int curIndex = firstIndex;
answer.add(first);
do {
Point next = points[0];
int nextIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
if (i == curIndex)
continue;
Point p = points[i];
int cross = crossProductLength(p, cur, next);
if (nextIndex == curIndex || cross > 0 ||
// Handle multi points in a line
(cross == 0 && distance(p, cur) > distance(next, cur))) {
next = p;
nextIndex = i;
}
}
// Handle multi points in a line
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
Point p = points[i];
int cross = crossProductLength(p, cur, next);
if (i != curIndex && cross == 0) {
answer.add(p);
}
}
cur = next;
curIndex = nextIndex;
} while (curIndex != firstIndex);
return new ArrayList<>(answer);
}
private int crossProductLength(Point A, Point B, Point C) {
// Get the vectors' coordinates.
int BAx = A.x - B.x;
int BAy = A.y - B.y;
int BCx = C.x - B.x;
int BCy = C.y - B.y;
// Calculate the Z coordinate of the cross product.
return (BAx * BCy - BAy * BCx);
}
private int distance(Point p1, Point p2) {
return (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y);
}补充:(2017-05-16)
上述代码用到了jarvisMarch方法,是凸包计算中的一个
O(nh)
的算法。关于凸包的更多算法可参考博文【算法细节系列(18):凸包的三种计算】。























 1294
1294











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








