314. Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal
Given the root of a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from top to bottom, column by column).
If two nodes are in the same row and column, the order should be from left to right.
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,9,8,4,0,1,7] Output: [[4],[9],[3,0,1],[8],[7]]
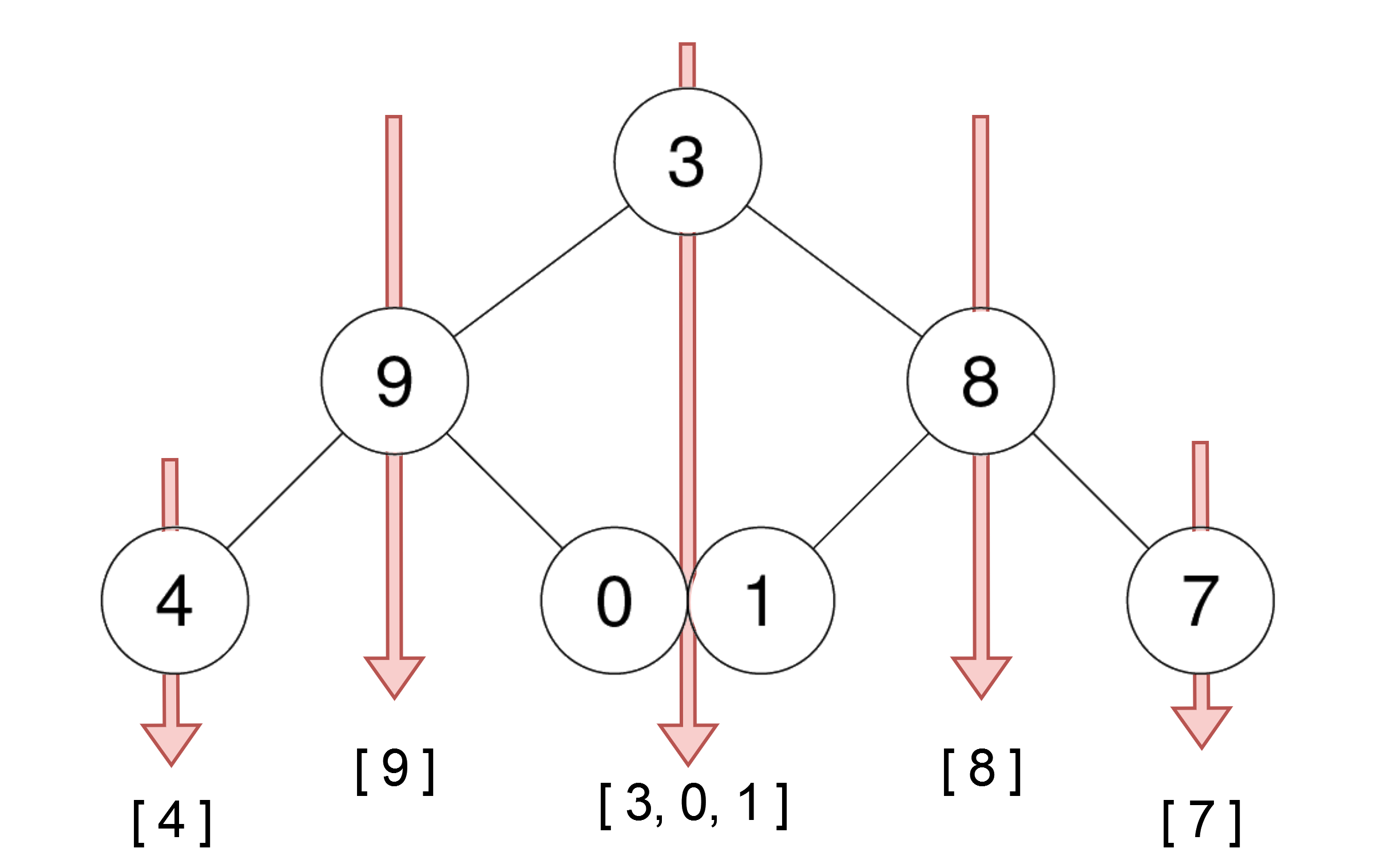
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,10,9,11,null,5,null,null,null,null,null,null,null,6] Output: [[4],[2,5],[1,10,9,6],[3],[11]]
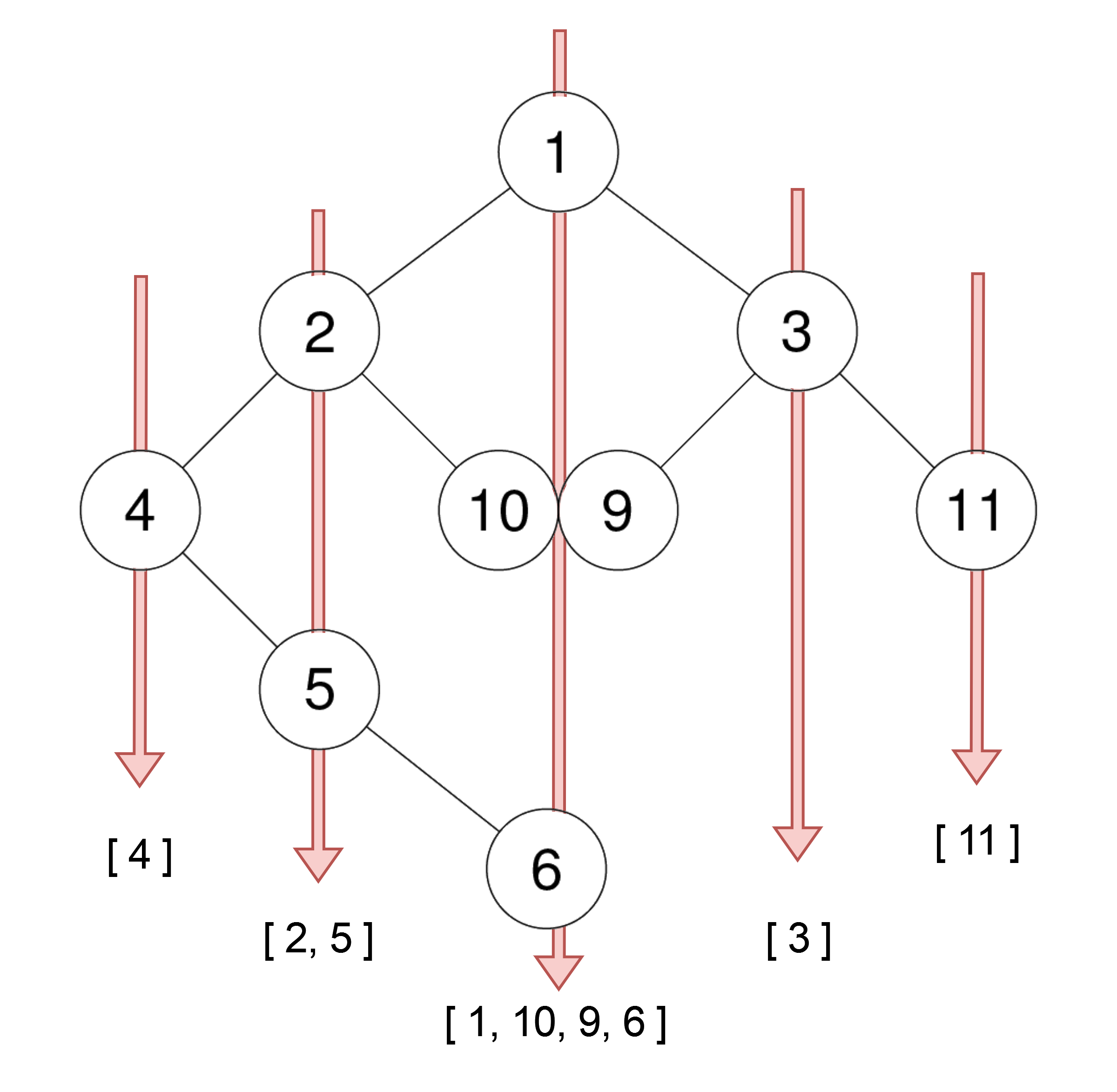
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def verticalOrder(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not root:
return []
queue=deque()
column2node=defaultdict(list)
queue.append((root,0))
while queue:
node,col=queue.popleft()
column2node[col].append(node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append((node.left,col-1))
if node.right:
queue.append((node.right,col+1))
ans=[]
for i in sorted(column2node.keys()):
ans.append(column2node[i])
return ans
每次处理当前node























 432
432

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








