移动WEB开发之百分比布局及flex布局

flex
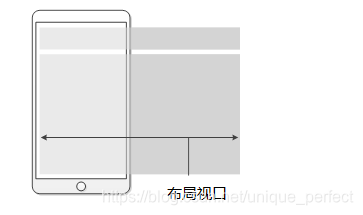
视口(viewport)就是浏览器显示页面内容的屏幕区域。 视
口可以分为布局视口、视觉视口和理想视口
布局视口 layout viewport,一般手机浏览器都默认设置了一
个布局
视口,用于解决早期的PC端页面在手机上显示的问题
iOS, Android基本都将这个视口分辨率设置为 980px,所以PC上的
网页大多都能在手机上呈现,只不过元素看上去很小,一般默认可
以通过手动缩放网页。
视觉视口 visual viewport用户正在看到的网站的区域
理想视口 ideal viewport理想视口,对设备来讲,是最理想的视口
尺寸

1.1 meta标签
meta视口标签的主要目的:布局视口的宽度应该与理想视口的宽度
一致,简单理解就是设备有多宽,我们布局的视口就多宽
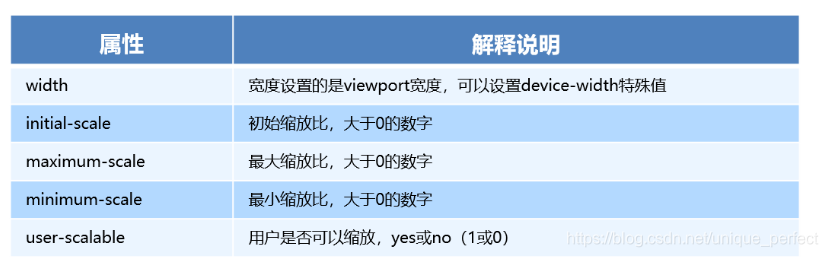
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no,
initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
meta视口标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
黑马程序员
</body>
</html>
1.2 二倍图
物理像素点指的是屏幕显示的最小颗粒,是物理真实存在的。
这是厂商在出厂时就设置好了,比如苹果6\7\8 是 750* 1334
我们开发时候的1px 不是一定等于1个物理像素的
PC端页面,1个px 等于1个物理像素的,但是移动端就不尽相同
一个px的能显示的物理像素点的个数,称为物理像素比或屏幕像素比
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* 我们需要一个50*50像素(css像素)的图片 直接放到我们的iphone8 里面会放大2倍 100* 100 就会模糊 */
/* 我们采取的是 放一个 100* 100 图片 然后手动的把这个图片 缩小为 50* 50 (css像素) */
/* 我们准备的图片 比我们实际需要的大小 大2倍,这就方式就是 2倍图 */
img:nth-child(2) {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 模糊的 -->
<img src="images/apple50.jpg" alt="">
<!-- 我们采取2倍图 -->
<img src="images/apple100.jpg" alt="">
</body>
</html>
1.3 物理像素比
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: pink;
}
/* 1. 物理像素 就是我们说的分辨率 iPhone8的物理像素是 750 */
/* 2. 在 iPhone8里面 1px 开发像素 = 2个物理像素 */
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
1.4 背景缩放background-size
background-size 属性规定背景图像的尺寸
单位: 长度|百分比|cover|contain;
cover把背景图像扩展至足够大,以使背景图像完全覆盖背景区域。
contain把图像图像扩展至最大尺寸,以使其宽度和高度完全适
应内容区域
背景缩放background-size
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 2px solid red;
background: url(images/dog.jpg) no-repeat;
/* background-size: 图片的宽度 图片的高度; */
/* background-size: 500px 200px; */
/* 1.只写一个参数 肯定是宽度 高度省略了 会等比例缩放 */
/* background-size: 500px; */
/* 2. 里面的单位可以跟% 相对于父盒子来说的 */
/* background-size: 50%; */
/* 3. cover 等比例拉伸 要完全覆盖div盒子 可能有部分背景图片显示不全 */
/* background-size: cover; */
/* 4. contain 高度和宽度等比例拉伸 当宽度 或者高度 铺满div盒子就不再进行拉伸了 可能有部分空白区域 */
background-size: contain;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>
背景图片2倍图
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* 1. 我们有一个 50 * 50的盒子需要一个背景图片,但是根据分析这个图片还是要准备2倍, 100*100 */
/* 2. 我们需要把这个图片缩放一半,也就是 50*50 background-size*/
div {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border: 1px solid red;
background: url(images/apple100.jpg) no-repeat;
background-size: 50px 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
1.5 移动端开发
移动端大量使用 CSS3盒子模型box-sizing
传统模式宽度计算:盒子的宽度 = CSS中设置的width + border + padding
CSS3盒子模型: 盒子的宽度= CSS中设置的宽度width 里面包含了 border 和 padding
也就是说,我们的CSS3中的盒子模型, padding 和 border 不会撑大盒子了
/*CSS3盒子模型*/
box-sizing: border-box;
/*传统盒子模型*/
box-sizing: content-box;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div:nth-child(1) {
/* 传统盒子模型= width + border + padding */
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
padding: 10px;
border: 10px solid red;
box-sizing: content-box;
}
div:nth-child(2) {
/* 有了这句话就让盒子变成CSS3盒子模型 */
/* padding 和 border 不会再撑大盒子了 */
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: purple;
padding: 10px;
border: 10px solid blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
1.6 移动端特殊样式
/*CSS3盒子模型*/
box-sizing: border-box;
-webkit-box-sizing: border-box;
/*点击高亮我们需要清除清除 设置为transparent 完成透明*/
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: transparent;
/*在移动端浏览器默认的外观在iOS上加上这个属性才能给按钮和输入框自定义样式*/
-webkit-appearance: none;
/*禁用长按页面时的弹出菜单*/
img,a { -webkit-touch-callout: none; }
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
a {
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: transparent;
}
input {
-webkit-appearance: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#">黑马</a>
<input type="button" value="按钮">
</body>
</html>
1.7 移动端常见布局
1.7.1 流式布局(百分比布局)
流式布局,就是百分比布局,也称非固定像素布局。
通过盒子的宽度设置成百分比来根据屏幕的宽度来进行伸缩,
不受固定像素的限制,内容向两侧填充。
流式布局方式是移动web开发使用的比较常见的布局方式。
max-width 最大宽度 (max-height 最大高度)
min-width 最小宽度 (min-height 最小高度)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
section {
width: 100%;
max-width: 980px;
min-width: 320px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
section div {
float: left;
width: 50%;
height: 400px;
}
section div:nth-child(1) {
background-color: pink;
}
section div:nth-child(2) {
background-color: purple;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<section>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</section>
</body>
</html>
normalize.css # 去除默认样式
/*! normalize.css v5.0.0 | MIT License | github.com/necolas/normalize.css */
/**
* 1. Change the default font family in all browsers (opinionated).
* 2. Correct the line height in all browsers.
* 3. Prevent adjustments of font size after orientation changes in
* IE on Windows Phone and in iOS.
*/
/* Document
========================================================================== */
html {
font-family: sans-serif; /* 1 */
line-height: 1.15; /* 2 */
-ms-text-size-adjust: 100%; /* 3 */
-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; /* 3 */
}
/* Sections
========================================================================== */
/**
* Remove the margin in all browsers (opinionated).
*/
body {
margin: 0;
}
/**
* Add the correct display in IE 9-.
*/
article,
aside,
footer,
header,
nav,
section {
display: block;
}
/**
* Correct the font size and margin on `h1` elements within `section` and
* `article` contexts in Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
*/
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
margin: 0.67em 0;
}
/* Grouping content
========================================================================== */
/**
* Add the correct display in IE 9-.
* 1. Add the correct display in IE.
*/
figcaption,
figure,
main { /* 1 */
display: block;
}
/**
* Add the correct margin in IE 8.
*/
figure {
margin: 1em 40px;
}
/**
* 1. Add the correct box sizing in Firefox.
* 2. Show the overflow in Edge and IE.
*/
hr {
box-sizing: content-box; /* 1 */
height: 0; /* 1 */
overflow: visible; /* 2 */
}
/**
* 1. Correct the inheritance and scaling of font size in all browsers.
* 2. Correct the odd `em` font sizing in all browsers.
*/
pre {
font-family: monospace, monospace; /* 1 */
font-size: 1em; /* 2 */
}
/* Text-level semantics
========================================================================== */
/**
* 1. Remove the gray background on active links in IE 10.
* 2. Remove gaps in links underline in iOS 8+ and Safari 8+.
*/
a {
background-color: transparent; /* 1 */
-webkit-text-decoration-skip: objects; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Remove the outline on focused links when they are also active or hovered
* in all browsers (opinionated).
*/
a:active,
a:hover {
outline-width: 0;
}
/**
* 1. Remove the bottom border in Firefox 39-.
* 2. Add the correct text decoration in Chrome, Edge, IE, Opera, and Safari.
*/
abbr[title] {
border-bottom: none; /* 1 */
text-decoration: underline; /* 2 */
text-decoration: underline dotted; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Prevent the duplicate application of `bolder` by the next rule in Safari 6.
*/
b,
strong {
font-weight: inherit;
}
/**
* Add the correct font weight in Chrome, Edge, and Safari.
*/
b,
strong {
font-weight: bolder;
}
/**
* 1. Correct the inheritance and scaling of font size in all browsers.
* 2. Correct the odd `em` font sizing in all browsers.
*/
code,
kbd,
samp {
font-family: monospace, monospace; /* 1 */
font-size: 1em; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Add the correct font style in Android 4.3-.
*/
dfn {
font-style: italic;
}
/**
* Add the correct background and color in IE 9-.
*/
mark {
background-color: #ff0;
color: #000;
}
/**
* Add the correct font size in all browsers.
*/
small {
font-size: 80%;
}
/**
* Prevent `sub` and `sup` elements from affecting the line height in
* all browsers.
*/
sub,
sup {
font-size: 75%;
line-height: 0;
position: relative;
vertical-align: baseline;
}
sub {
bottom: -0.25em;
}
sup {
top: -0.5em;
}
/* Embedded content
========================================================================== */
/**
* Add the correct display in IE 9-.
*/
audio,
video {
display: inline-block;
}
/**
* Add the correct display in iOS 4-7.
*/
audio:not([controls]) {
display: none;
height: 0;
}
/**
* Remove the border on images inside links in IE 10-.
*/
img {
border-style: none;
}
/**
* Hide the overflow in IE.
*/
svg:not(:root) {
overflow: hidden;
}
/* Forms
========================================================================== */
/**
* 1. Change the font styles in all browsers (opinionated).
* 2. Remove the margin in Firefox and Safari.
*/
button,
input,
optgroup,
select,
textarea {
font-family: sans-serif; /* 1 */
font-size: 100%; /* 1 */
line-height: 1.15; /* 1 */
margin: 0; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Show the overflow in IE.
* 1. Show the overflow in Edge.
*/
button,
input { /* 1 */
overflow: visible;
}
/**
* Remove the inheritance of text transform in Edge, Firefox, and IE.
* 1. Remove the inheritance of text transform in Firefox.
*/
button,
select { /* 1 */
text-transform: none;
}
/**
* 1. Prevent a WebKit bug where (2) destroys native `audio` and `video`
* controls in Android 4.
* 2. Correct the inability to style clickable types in iOS and Safari.
*/
button,
html [type="button"], /* 1 */
[type="reset"],
[type="submit"] {
-webkit-appearance: button; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Remove the inner border and padding in Firefox.
*/
button::-moz-focus-inner,
[type="button"]::-moz-focus-inner,
[type="reset"]::-moz-focus-inner,
[type="submit"]::-moz-focus-inner {
border-style: none;
padding: 0;
}
/**
* Restore the focus styles unset by the previous rule.
*/
button:-moz-focusring,
[type="button"]:-moz-focusring,
[type="reset"]:-moz-focusring,
[type="submit"]:-moz-focusring {
outline: 1px dotted ButtonText;
}
/**
* Change the border, margin, and padding in all browsers (opinionated).
*/
fieldset {
border: 1px solid #c0c0c0;
margin: 0 2px;
padding: 0.35em 0.625em 0.75em;
}
/**
* 1. Correct the text wrapping in Edge and IE.
* 2. Correct the color inheritance from `fieldset` elements in IE.
* 3. Remove the padding so developers are not caught out when they zero out
* `fieldset` elements in all browsers.
*/
legend {
box-sizing: border-box; /* 1 */
color: inherit; /* 2 */
display: table; /* 1 */
max-width: 100%; /* 1 */
padding: 0; /* 3 */
white-space: normal; /* 1 */
}
/**
* 1. Add the correct display in IE 9-.
* 2. Add the correct vertical alignment in Chrome, Firefox, and Opera.
*/
progress {
display: inline-block; /* 1 */
vertical-align: baseline; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Remove the default vertical scrollbar in IE.
*/
textarea {
overflow: auto;
}
/**
* 1. Add the correct box sizing in IE 10-.
* 2. Remove the padding in IE 10-.
*/
[type="checkbox"],
[type="radio"] {
box-sizing: border-box; /* 1 */
padding: 0; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Correct the cursor style of increment and decrement buttons in Chrome.
*/
[type="number"]::-webkit-inner-spin-button,
[type="number"]::-webkit-outer-spin-button {
height: auto;
}
/**
* 1. Correct the odd appearance in Chrome and Safari.
* 2. Correct the outline style in Safari.
*/
[type="search"] {
-webkit-appearance: textfield; /* 1 */
outline-offset: -2px; /* 2 */
}
/**
* Remove the inner padding and cancel buttons in Chrome and Safari on macOS.
*/
[type="search"]::-webkit-search-cancel-button,
[type="search"]::-webkit-search-decoration {
-webkit-appearance: none;
}
/**
* 1. Correct the inability to style clickable types in iOS and Safari.
* 2. Change font properties to `inherit` in Safari.
*/
::-webkit-file-upload-button {
-webkit-appearance: button; /* 1 */
font: inherit; /* 2 */
}
/* Interactive
========================================================================== */
/*
* Add the correct display in IE 9-.
* 1. Add the correct display in Edge, IE, and Firefox.
*/
details, /* 1 */
menu {
display: block;
}
/*
* Add the correct display in all browsers.
*/
summary {
display: list-item;
}
/* Scripting
========================================================================== */
/**
* Add the correct display in IE 9-.
*/
canvas {
display: inline-block;
}
/**
* Add the correct display in IE.
*/
template {
display: none;
}
/* Hidden
========================================================================== */
/**
* Add the correct display in IE 10-.
*/
[hidden] {
display: none;
}
1.7.2 移动WEB开发之flex布局
1.7.2.1 flex原理
就是通过给父盒子添加flex属性,来控制子盒子的位置和排列方式
注意:
我们为父盒子设为 flex 布局以后,子元素的 float、clear 和 vertical-align 属性将失效。
伸缩布局 = 弹性布局 = 伸缩盒布局 = 弹性盒布局 =flex布局

1.7.2.2 理解布局原理

容器默认存在两根轴:水平的主轴(main axis)和垂直的交叉轴(cross axis).
主轴的开始位置(与边框的交叉点)叫做main start,结束位置叫做main end;
交叉轴的开始位置叫做cross start,结束位置叫做cross end.
项目默认沿主轴排列.单个项目占据的主轴空间叫做main size,占据的交叉
轴空间叫做cross size.
1.7.2.3 flex布局父项常见属性

1.7.2.3.1 flex-direction
flex-direction:决定主轴的方向.
它的四个取值:
row(默认值):主轴为水平方向,起点在左端.
row-reverse:主轴为水平方向,起点在右端.
column:主轴为垂直方向,起点在上沿.
column-reverse:主轴为垂直方向,起点在下沿.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: orange;
}
.item {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.item1{
background-color: firebrick;
}
.item2{
background-color: fuchsia;
}
.item3 {
background-color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="item item1">item1</div>
<div class="item item2">item2</div>
<div class="item item3">item3</div>
<div></div>
</div>
<strong>strong元素</strong>
</body>
</html>
row:
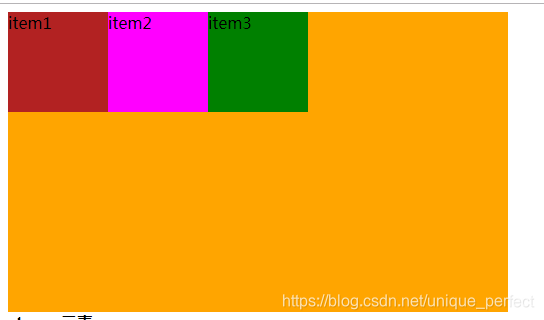
row-reverse:

column:

column-reverse
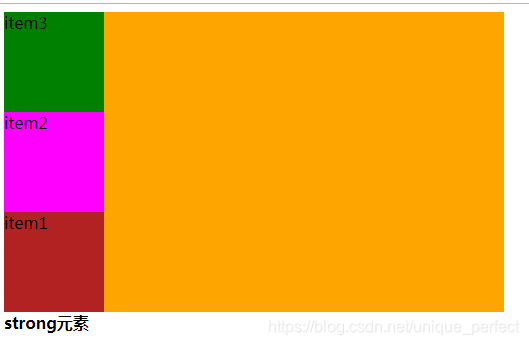
1.7.2.3.2 justify-content
决定了flex items在main axis的对齐方式
它的五个取值:
flex-start(默认值):左对齐
flex-end:右对齐
center:居中
space-evenly:
space-between:两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等。
space-around:每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的
间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍。
flex-start;

flex-end

center

space-evenly
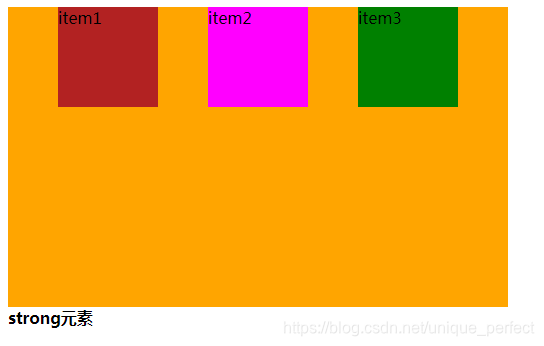
space-around

space-between

1.7.2.3.3 flex-wrap
决定flex-container是单行还是多行
nowrap(默认):不换行
wrap:换行
wrap-reverse:多行
wrap

wrap-reverse
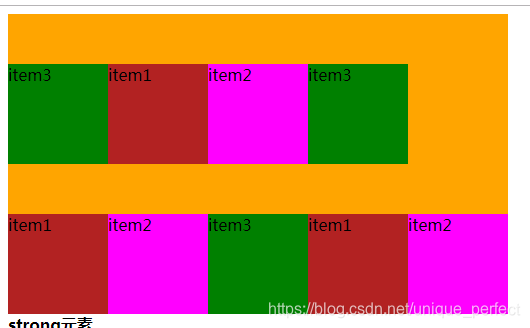
nowrap

1.7.2.3.4 align-items
设置侧轴上的子元素排列方式(单行 )
stretch(默认值):如果项目未设置高度或设为auto,将自动
拉伸填充flex containter.
flex-start:交叉轴的起点对齐.
flex-end:交叉轴的终点对齐.
center:交叉轴的中点对齐.
stretch

flex-start

flex-end
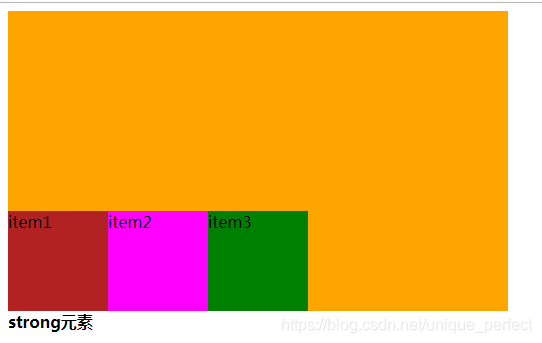
center

1.7.2.3.5 align-content
设置侧轴上的子元素的排列方式(多行)
stretch(默认值):与align-items的stretch类似
flex-start:默认值在侧轴的头部开始排列
flex-end:在侧轴的尾部开始排列
center:在侧轴中间显示
space-between:子项在侧轴先分布在两头,再平分剩余空间
space-around:子项在侧轴平分剩余空间
stretch

flex-start
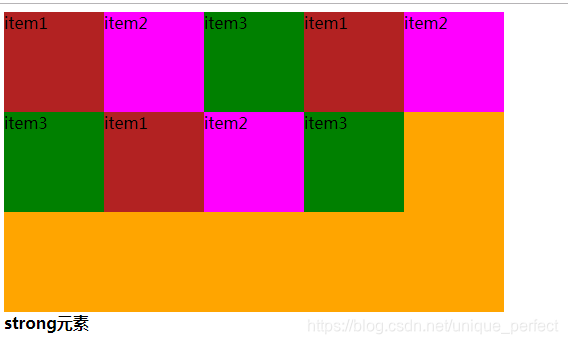
flex-end

center:

space-between
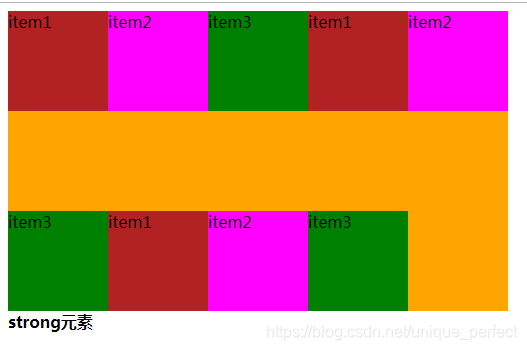
space-around

1.7.2.3.6 align-content 和 align-items 区别
align-items 适用于单行情况下, 只有上对齐、下对齐、
居中和 拉伸
align-content 适应于换行(多行)的情况下(单行情况下无效),
可以设置 上对齐、 下对齐、居中、拉伸以及平均分配剩余空
间等属性值。
总结就是单行找 align-items 多行找 align-content
1.7.2.3.7 flex-flow
flex-flow 属性是 flex-direction 和 flex-wrap 属性的复
合属性
flex-flow:row wrap;
1.7.2.3.8 flex布局父项常见属性总结
flex-direction:设置主轴的方向
justify-content:设置主轴上的子元素排列方式
flex-wrap:设置子元素是否换行
align-content:设置侧轴上的子元素的排列方式(多行)
align-items:设置侧轴上的子元素排列方式(单行)
flex-flow:复合属性,相当于同时设置了 flex-direction
和 flex-wrap
1.7.2.3.9 flex布局子项常见属性
order
align-self
flex-grow
flex-shrink
flex-basis
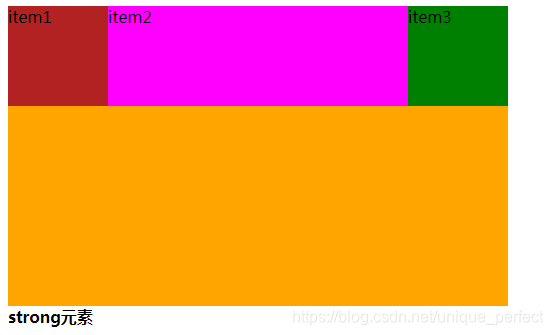
flex 定义子项目分配剩余空间,用flex来表示占多少份数。
1.7.2.3.9.1 flex
flex 属性定义子项目分配剩余空间,用flex来表示占多少份数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: orange;
display: flex;
}
.item {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.item1 {
background-color: firebrick;
}
.item2 {
background-color: fuchsia;
flex: 1;
}
.item3 {
background-color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="item item1">item1</div>
<div class="item item2">item2</div>
<div class="item item3">item3</div>
</div>
<strong>strong元素</strong>
</body>
</html>
1.7.2.3.9.2 align-self
若想给其中一个元素搞特殊,可以使用align-self属性,覆盖align-items的
属性.效果跟align-items一致
1.7.2.3.9.3 order
order属性定义项目的排列顺序。数值越小,排列越靠前,默认为0.
.item1{
background-color: firebrick;
order: 3;
}
.item2{
background-color: fuchsia;
order: 2;
}
.item3 {
background-color: green;
order: 1;
}

想要获取该该课程markdown笔记(脑图+笔记)。可以扫描以下
微信公众号二维码。或者搜索微信公众号-Java大世界。回复
flex即可获取笔记获取方式。























 4287
4287











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










