文章转自 https://blog.csdn.net/delphiwcdj/article/details/6603910
(一) 有漏洞的程序
(二) 代码检查
(三) 取样法
(四) 使用gdb进行调试
(一) 有漏洞的程序
-
/* debug1.c */
-
typedef struct {
-
char *data;
-
int key;
-
}item;
-
-
item array[] = {
-
{ "bill", 3},
-
{ "neil", 4},
-
{ "john", 2},
-
{ "rick", 5},
-
{ "alex", 1},
-
};
-
-
void sort(item *a, int n)
-
{
-
int i = 0, j = 0;
-
int s = 1;
-
for(; i < n && s != 0; i++) {
-
s = 0;
-
for(j = 0; j < n; j++) {
-
if (a[j].key > a[j+ 1].key) {
-
item t = a[j];
-
a[j] = a[j+ 1];
-
a[j+ 1] = t;
-
s++;
-
}
-
}
-
n--;
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
-
main()
-
{
-
int i;
-
sort( array, 5);
-
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
-
printf( "array[%d] = {%s, %d}\n",
-
i, array[i].data, array[i].key);
-
}
-
}
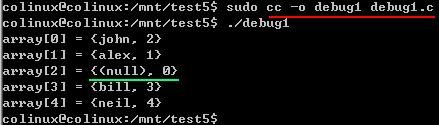
注意:输出的结果取决于所使用的Linux(或UNIX)版本及其具体设置情况。
(二) 代码检查
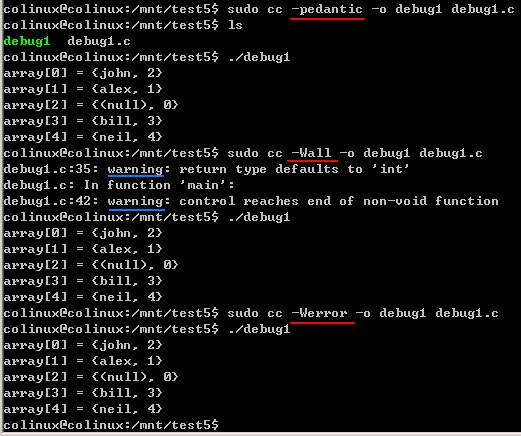
使用编译器的报警选项对代码进行检查。
(三) 取样法
取样法:是指在程序中添加一些代码以收集更多与程序运行时的行为相关的信息的方法。
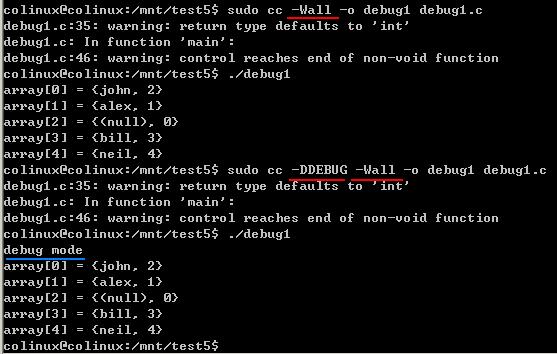
技巧1:用C语言的预处理器有选择地包括取样代码,这样只需重新编译程序就可以包含或去除调试代码。在编译程序时可以加上编译器标志 -DDEBUG。如果加上这个标志,就定义了DEBUG符号,从而可以在程序中包含额外的调试代码;如果未加上该标志,这些调试代码将被删除。
-
typedef struct {
-
char *data;
-
int key;
-
}item;
-
-
item array[] = {
-
{ "bill", 3},
-
{ "neil", 4},
-
{ "john", 2},
-
{ "rick", 5},
-
{ "alex", 1},
-
};
-
-
void sort(item *a, int n)
-
{
-
int i = 0, j = 0;
-
int s = 1;
-
for(; i < n && s != 0; i++) {
-
s = 0;
-
for(j = 0; j < n; j++) {
-
if (a[j].key > a[j+ 1].key) {
-
item t = a[j];
-
a[j] = a[j+ 1];
-
a[j+ 1] = t;
-
s++;
-
}
-
}
-
n--;
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
-
main()
-
{
-
-
printf( "debug mode\n");
-
-
-
int i;
-
sort( array, 5);
-
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
-
printf( "array[%d] = {%s, %d}\n",
-
i, array[i].data, array[i].key);
-
}
-
}
技巧2:还可以用数值调试宏来完成更复杂的调试应用。
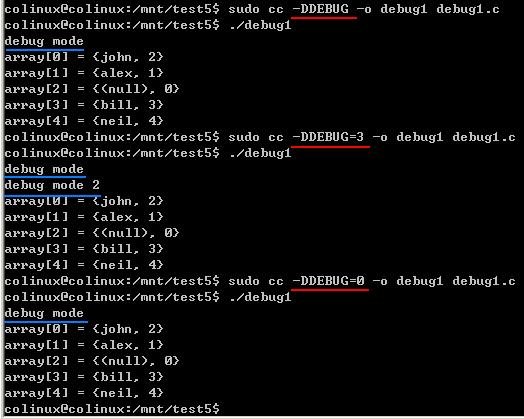
在这种情况下,我们必须总是定义DEBUG宏,但我们可以设置它为代表一组调试信息或代表一个调试级别。比如,编译器标志 -DDEBUG=5 将启用 BASIC_DEBUG 和 SUPER_DEBUG,但不包括 EXTRA_DEBUG。标志 -DDEBUG=0 将禁用所有的调试信息。
-
typedef struct {
-
char *data;
-
int key;
-
}item;
-
-
item array[] = {
-
{ "bill", 3},
-
{ "neil", 4},
-
{ "john", 2},
-
{ "rick", 5},
-
{ "alex", 1},
-
};
-
-
void sort(item *a, int n)
-
{
-
int i = 0, j = 0;
-
int s = 1;
-
for(; i < n && s != 0; i++) {
-
s = 0;
-
for(j = 0; j < n; j++) {
-
if (a[j].key > a[j+ 1].key) {
-
item t = a[j];
-
a[j] = a[j+ 1];
-
a[j+ 1] = t;
-
s++;
-
}
-
}
-
n--;
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
main()
-
{
-
-
printf( "debug mode\n");
-
-
-
printf( "debug mode 2\n");
-
-
-
int i;
-
sort( array, 5);
-
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
-
printf( "array[%d] = {%s, %d}\n",
-
i, array[i].data, array[i].key);
-
}
-
}
技巧3:C语言预处理器定义的一些宏可以帮助我们进行调试。这些宏在扩展后会提供当前编译操作的相关信息。
__LINE__ 代表当前行号的十进制常数
__FILE__ 代表当前文件名的字符串
__DATE__ mmm dd yyyy格式的字符串,代表当前日期
__TIME__ hh:mm:ss格式的字符串,代表当前时间
注意:
(1) 这些符号的前后各有两个下划线,这是标准的预处理器符号通常的做法,你应该注意避免选择可能会与它们冲突的符号。
(2) “当前”指的是预处理操作正在执行的那一时刻,即正在运行编译器对文件进行处理时的时间和日期。
-
typedef struct {
-
char *data;
-
int key;
-
}item;
-
-
item array[] = {
-
{ "bill", 3},
-
{ "neil", 4},
-
{ "john", 2},
-
{ "rick", 5},
-
{ "alex", 1},
-
};
-
-
void sort(item *a, int n)
-
{
-
int i = 0, j = 0;
-
int s = 1;
-
for(; i < n && s != 0; i++) {
-
s = 0;
-
for(j = 0; j < n; j++) {
-
if (a[j].key > a[j+ 1].key) {
-
item t = a[j];
-
a[j] = a[j+ 1];
-
a[j+ 1] = t;
-
s++;
-
}
-
}
-
n--;
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
main()
-
{
-
-
printf( "debug mode\n");
-
printf( "Compiled: "__DATE__ " at "__TIME__ "\n");
-
printf( "This is line %d of file %s\n", __LINE__, __FILE__);
-
-
-
printf( "debug mode 2\n");
-
-
-
int i;
-
sort( array, 5);
-
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
-
printf( "array[%d] = {%s, %d}\n",
-
i, array[i].data, array[i].key);
-
}
-
exit( 0);
-
}
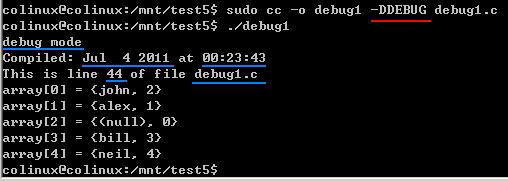
注意:ANSI C 标准定义相邻的字符串可以被看作为一个字符串。
(四) 使用gdb进行调试

注意:可以使用命令 strip <file> 将可执行文件中的调试信息删除而不需要重新编译程序。
gdb本身是一个基于文本的应用程序,但它为一些重复性的任务准备了一些快捷键。
(1) gdb的许多版本都具备带历史记录的命令行编辑功能,用户可以(尝试用方向键)回卷并再次执行以前输入过的命令。
(2) gdb的所有版本都支持“空命令”,即直接按下回车键再次执行最近执行过的那条命令。在用step或next命令单步执行程序时,空命令非常有用。






















 4477
4477

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








