写在前面
本文主要是分析一个MappedStatement是如何生成最终的sql语句的,其中会涉及到动态SQL语句的解析,关于这部分的内容可以参考这篇文章。
想要系统学习的,可以参考这篇文章,重要!!!。
1:入口
当我们执行一次数据操作的是时候,使用的API是org.apach.ibatis.session.SqlSession,其内部调用org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor,然后执行器内部调用当前执行的statement的MappedStatement对象,MappeStatement对象内部会调用org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlSource的API来生成最终可执行的sql语句,最后通过JDBC的API执行,返回最终结果,如下是可能一个调用过程:

其中的org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlSource的API就是我们本文要分析的,也就是要分析的入口了,具体参考2:SqlSource获取SQL。
2:SqlSource获取SQL
接口org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlSource源码如下:
org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlSource.
// 代表来自XML或者是注解配置的MappedStatement对应的SQL语句信息,
// 通过传入用户参数获取最终可执行的sql语句对象
public interface SqlSource {
// 传入用户参数,获取可执行的sql语句对象
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
实现类:

不同的类对应了不同的MappedStatement的来源,如下:
1:存在动态SQL语句的statement(xml和注解):调用DynamicSqlSource,然后内部调用StaticSqlSource。
2:存在#{}形式参数的(xml和注解):调用RawSqlSource,然后内部调用StaticSqlSource。
3:sql provider:调用ProviderSqlSource,再调用StaticSqlSource。
关于存在动态SQL语句的statement的场景参考3:获取动态sql语句。关于存在#{}形式参数的场景参考5:获取Raw sql语句。sql provider形式参考6:sql provider生成sql语句。
3:获取动态sql语句
比如可能的如下配置:
<select id="queryListWithXmlDynamicSqlForeach" resultMap="myResultMap" parameterType="java.util.List">
SELECT * FROM test_dynamic_sql t
WHERE t.`id` IN
<foreach collection="list" index="" open="(" close=")" item="itemId" separator=",">
#{itemId}
</foreach>
</select>
源码如下:
org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.DynamicSqlSource#getBoundSql
// parameterObject:封装的是用户调用方法时传入的参数信息
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 使用全局配置文件对应的configuration对象和用户传入参数信息创建DynamicContext对象
// 该对象用于辅助解析动态sql节点生成sql语句
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
// rootSqlNode是MixSqlNode对象,封装了对应的动态sql节点的所有子节点信息
// apply方法调用后,在context中就生成了sql语句了
// <2021-08-19 13:43:10>
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
// 创建SqlSource构造器对象
// <2021-08-19 13:51:54>
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
// 执行getBoundSql获取sql,这里的类型一般是StaticSqlSource
// <2021-08-19 14:47:32>
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 获取动态生成的参数信息,并设置到BoundSql对象中
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) {
boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
// 返回BoundSql对象,用于后续的具体的sql执行工作
return boundSql;
}
<2021-08-19 13:43:10>处是应用动态sql语句的所有子节点,生成sql语句,具体参考这篇文章。<2021-08-19 13:51:54>处是创建SqlSourceBuilder对象,然后调用其parse方法,该对象用于替换sql语句中的#{}为?并获取占位符对应的ParameterMapping,具体参考4:SqlSourceBuilder。<2021-08-19 14:47:32>处是调用获取BoundSql对象,具体参考4.2:通过StaticBoundSql获取sql语句。
4:SqlSourceBuilder
构造函数如下:
org.apache.ibatis.builder.SqlSourceBuilder#SqlSourceBuilder
public SqlSourceBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
super(configuration);
}
public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
// 类型别名注册器
this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry();
// 类型处理器注册器
this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
}
parse方法源码如下:
org.apache.ibatis.builder.SqlSourceBuilder#parse
// originalSql:解析后生成的sql语句,如foreach场景中可能是:
// SELECT * FROM test_dynamic_sql t WHERE t.`id` IN ( #{__frch_itemId_0} , #{__frch_itemId_1} )
// parameterType:参数的类型
// additionalParameters:额外参数,即动态生成的参数,如bind,foreach动态生成参数
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
// 创建ParameterMappingTokenHandler对象
// <2021-08-19 14:09:55>
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
// 创建GenericTokenParser,并以"#{","}"进行解析
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
// 执行解析
// <2021-08-19 14:44:00>
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
// 创建StaticSqlSource并返回
// sql:替换#{xxx}为?后的sql语句,如INSERT INTO `test_dynamic_sql` (`myname`, `myage`) VALUES (?, ?)
// handler.getParameterMappings():封装了sql语句中?对应的参数信息的ParameterMapping集合
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
<2021-08-19 14:09:55>处是创建ParameterMappingTokenHandler对象,关于该对象具体参考4.1:ParameterMappingTokenHandler,<2021-08-19 14:44:00>是解析#{xxx}配置的信息生成ParameterMapping对象,具体参考4.1:ParameterMappingTokenHandler。
4.1:ParameterMappingTokenHandler
该类负责将匹配的#{和}替换成?,并获取对应的ParemterMapping对象,构造函数如下:
handleToken方法用于解析参数对应的ParameterMapping对象,并添加到集合中,源码如下
org.apache.ibatis.builder.SqlSourceBuilder.ParameterMappingTokenHandler#handleToken
public String handleToken(String content) {
// 构建ParameterMapping并添加到paramterMapping集合中
// private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = new ArrayList<ParameterMapping>();
// <2021-08-19 14:24:42>
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
// 返回?号作为替换的值,即#{}变为?
return "?";
}
<2021-08-19 14:24:42>处源码如下:
org.apache.ibatis.builder.SqlSourceBuilder.ParameterMappingTokenHandler#buildParameterMapping
// content:#{xxx}中xxx的值
private ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) {
// 存储#{}内部所有信息的字典,如javaType,jdbcType,typeHandler等
Map<String, String> propertiesMap = parseParameterMapping(content);
// 获取#{}内的属性名称
String property = propertiesMap.get("property");
Class<?> propertyType;
// 获取当前属性的类型,即#{xxx}中配置的xxx的数据类型
if (metaParameters.hasGetter(property)) {
propertyType = metaParameters.getGetterType(property);
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterType)) {
propertyType = parameterType;
} else if (JdbcType.CURSOR.name().equals(propertiesMap.get("jdbcType"))) {
propertyType = java.sql.ResultSet.class;
} else if (property != null) {
MetaClass metaClass = MetaClass.forClass(parameterType);
if (metaClass.hasGetter(property)) {
propertyType = metaClass.getGetterType(property);
} else {
propertyType = Object.class;
}
} else {
propertyType = Object.class;
}
// 创建参数映射构造器对象
ParameterMapping.Builder builder = new ParameterMapping.Builder(configuration, property, propertyType);
Class<?> javaType = propertyType;
String typeHandlerAlias = null;
// 循环处理#{xxx}对应的字段的所有信息,处理所有可能配置的属性
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : propertiesMap.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
if ("javaType".equals(name)) {
javaType = resolveClass(value);
builder.javaType(javaType);
} else if ("jdbcType".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcType(resolveJdbcType(value));
} else if ("mode".equals(name)) {
builder.mode(resolveParameterMode(value));
} else if ("numericScale".equals(name)) {
builder.numericScale(Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if ("resultMap".equals(name)) {
builder.resultMapId(value);
} else if ("typeHandler".equals(name)) {
typeHandlerAlias = value;
} else if ("jdbcTypeName".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcTypeName(value);
} else if ("property".equals(name)) {
// Do Nothing
} else if ("expression".equals(name)) {
throw new BuilderException("Expression based parameters are not supported yet");
} else {
throw new BuilderException("An invalid property '" + name + "' was found in mapping #{" + content + "}. Valid properties are " + parameterProperties);
}
}
if (typeHandlerAlias != null) {
builder.typeHandler(resolveTypeHandler(javaType, typeHandlerAlias));
}
// 构造#{xxx}对应的ParameterMapping对象并返回
return builder.build();
}
如下是当配置为#{myname}时的结果:
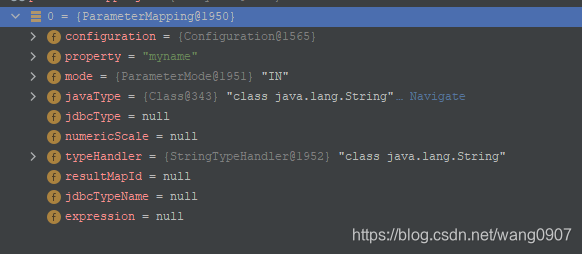
有参数名称信息,出参入参信息,java类型信息,数据库数据转换为当前属性值的类型处理器信息,等等,当查询结果后进行设置值时需要用到这里的信息。
4.2:通过StaticBoundSql获取sql语句
源码如下:
public class StaticSqlSource implements SqlSource {
// 待执行的sql语句,如select * from foo where id in (?, ?, ?)
private String sql;
// 待执行sql语句对应的参数值集合
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
// 全局配置文件对应的Configuration对象
private Configuration configuration;
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql) {
this(configuration, sql, null);
}
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 创建BoundSql对象并返回
// <2021-08-19 14:52:12>
return new BoundSql(configuration, sql, parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
}
<2021-08-19 14:52:12>处是创建BoundSql并返回,其中BoundSql是一个用于封装sql和参数等信息的对象,源码如下:
// 封装处理了动态sql内容后的sql语句信息,可能包含?,以及对应顺序的ParameterMapping参数信息
// 在ParamterMapping中包含了至少参数名称的信息,以便获取参数信息,当然也可能有通过动态sql
// 生成的参数信息,比如通过bind
public class BoundSql {
// 要执行的sql
private String sql;
// 参数信息
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
// 原始参数对象
private Object parameterObject;
// 动态生成的参数信息,如通过bind,或者是foreach动态生成的
private Map<String, Object> additionalParameters;
private MetaObject metaParameters;
public BoundSql(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings, Object parameterObject) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.parameterObject = parameterObject;
this.additionalParameters = new HashMap<String, Object>();
this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters);
}
// 获取sql语句
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
// 获取要使用的参数
public List<ParameterMapping> getParameterMappings() {
return parameterMappings;
}
public Object getParameterObject() {
return parameterObject;
}
public boolean hasAdditionalParameter(String name) {
return metaParameters.hasGetter(name);
}
public void setAdditionalParameter(String name, Object value) {
metaParameters.setValue(name, value);
}
public Object getAdditionalParameter(String name) {
return metaParameters.getValue(name);
}
}
5:获取Raw sql语句
比如可能的如下配置:
org.apache.ibatis.scripting.defaults.RawSqlSource#getBoundSql
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// sqlSource为StaticSqlSource
// <2021-08-19 15:04:54>
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
<2021-08-19 15:04:54>处具体参考4.2:通过StaticBoundSql获取sql语句。
6:sql provider生成sql语句
可能如下配置:
@InsertProvider(type = MySelectSqlProvider.class, method = "provideInsertSql")
/*
@SelectKey(
statement = { "SELECT UNIX_TIMESTAMP(NOW())" },
keyProperty = "id",
before = true,
resultType = java.lang.Void.class,
statementType = org.apache.ibatis.mapping.StatementType.PREPARED)
*/
void insertWithSelectSqlProvider(TestMybatisAnnotationDto testMybatisAnnotationDto);
源码如下:
org.apache.ibatis.builder.annotation.ProviderSqlSource#getBoundSql
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 创建SqlSource,这里结果为StaticSqlSource
// <2021-08-19 15:13:16>
SqlSource sqlSource = createSqlSource(parameterObject);
// 生成BoundSql
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
<2021-08-19 15:13:16>处源码如下:
org.apache.ibatis.builder.annotation.ProviderSqlSource#createSqlSource
private SqlSource createSqlSource(Object parameterObject) {
try {
String sql;
// 反射调用sql provider类的方法获取sql语句
if (providerTakesParameterObject) {
sql = (String) providerMethod.invoke(providerType.newInstance(), parameterObject);
} else {
sql = (String) providerMethod.invoke(providerType.newInstance());
}
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
// 解析生成SqlSource对象
// <2021-08-19 15:17:03>
return sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, parameterType, new HashMap<String, Object>());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error invoking SqlProvider method ("
+ providerType.getName() + "." + providerMethod.getName()
+ "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
<2021-08-19 15:17:03>处具体参考4:SqlSourceBuilder。
写在后面
到这里,终于生成了可以执行的sql语句了,那么接下来的问题就是sql到底是如何执行的了,关于这部分内容可以参考这篇文章。
























 265
265

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








