1、编写守护进程的步骤
python创建守护进程其实和c创建守护进程的方式大同小异了,其实就是那么几个步骤:
(1)创建子进程,父进程退出
(2)改变当前目录为根目录
(3)在子进程中创建新会话
(4)重设文件权限掩码
(5)子进中创建孙子进程,子进程退出,孙子进程成为真正的守护进程
(6)关闭文件描述符
2、定义一个Daemon类,有其他人写好的标准类,可以直接引用
daemon_python.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
import sys, os, time, atexit
from signal import SIGTERM
class Daemon:
"""
A generic daemon class.
Usage: subclass the Daemon class and override the run() method
"""
def __init__(self, pidfile, stdin='/dev/null', stdout='/dev/null', stderr='/dev/null'):
self.stdin = stdin
self.stdout = stdout
self.stderr = stderr
self.pidfile = pidfile
def daemonize(self):
"""
do the UNIX double-fork magic, see Stevens' "Advanced
Programming in the UNIX Environment" for details (ISBN 0201563177)
http://www.erlenstar.demon.co.uk/unix/faq_2.html#SEC16
"""
try:
pid = os.fork()
if pid > 0:
# exit first parent
sys.exit(0)
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write("fork #1 failed: %d (%s)\n" % (e.errno, e.strerror))
sys.exit(1)
# decouple from parent environment
os.chdir("/")
os.setsid()
os.umask(0)
# do second fork
try:
pid = os.fork()
if pid > 0:
# exit from second parent
sys.exit(0)
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write("fork #2 failed: %d (%s)\n" % (e.errno, e.strerror))
sys.exit(1)
# redirect standard file descriptors
sys.stdout.flush()
sys.stderr.flush()
si = file(self.stdin, 'r')
so = file(self.stdout, 'a+')
se = file(self.stderr, 'a+', 0)
os.dup2(si.fileno(), sys.stdin.fileno())
os.dup2(so.fileno(), sys.stdout.fileno())
os.dup2(se.fileno(), sys.stderr.fileno())
# write pidfile
atexit.register(self.delpid)
pid = str(os.getpid())
file(self.pidfile,'w+').write("%s\n" % pid)
def delpid(self):
os.remove(self.pidfile)
def start(self):
"""
Start the daemon
"""
# Check for a pidfile to see if the daemon already runs
try:
pf = file(self.pidfile, 'r')
pid = int(pf.read().strip())
pf.close()
except IOError:
pid = None
if pid:
message = "pidfile %s already exist. Daemon already running?\n"
sys.stderr.write(message % self.pidfile)
sys.exit(1)
# Start the daemon
self.daemonize()
self.run()
def stop(self):
"""
Stop the daemon
"""
# Get the pid from the pidfile
try:
pf = file(self.pidfile, 'r')
pid = int(pf.read().strip())
pf.close()
except IOError:
pid = None
if not pid:
message = "pidfile %s does not exist. Daemon not running?\n"
sys.stderr.write(message % self.pidfile)
return
try:
while 1:
os.kill(pid, SIGTERM)
time.sleep(0.1)
except OSError, err:
err = str(err)
if err.find("No such process") > 0:
if os.path.exists(self.pidfile):
os.remove(self.pidfile)
else:
print str(err)
sys.exit(1)
def restart(self):
"""
Restart the daemon
"""
self.stop()
self.start()
def run(self):
"""
You should override this method when you subclass Daemon. It will be called after the process has been
daemonized by start() or restart().
"""3、写一个测试的守护进程,每隔两秒向文件中写入数据
test.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
import sys, os, time, atexit
from signal import SIGTERM
from optparse import OptionParser
from daemon_python import Daemon
class my_daemon(Daemon):
def run(self):
"""
每两秒向文件写入信息
"""
while True:
pf = file('/tmp/python_example.txt', 'a+')
pf.write("this is test python daemon\n")
pf.close()
time.sleep(2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
newParser = OptionParser()
newParser.add_option("--action", dest="action", help=u'start|restart|stop daemon')
(args, option) = newParser.parse_args()
if not args.action:
print newParser.print_help()
exit(1)
daemon = my_daemon('/tmp/my_daemon.pid')
if args.action == 'start':
daemon.start()
elif args.action == 'restart':
daemon.restart()
elif args.action == 'stop':
daemon.stop()
else:
print 'unkowm command'运行结果:
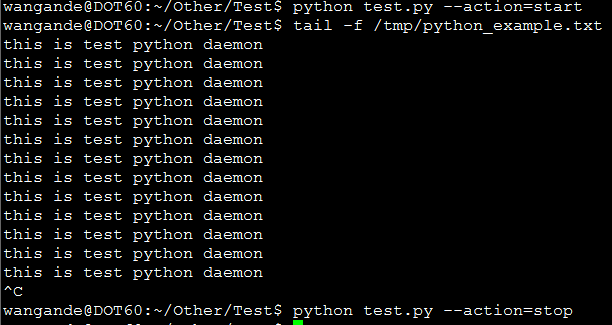
查看程序运行使用方法:
是不是很简单,你们自己也动手试一下吧。
这里用到的命令行解析函数OptionParser(),大家可以自己去查下,这个函数功能很强大






















 9782
9782

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








