前言
最近看了一个讲如何面试的视频,里面说到不要只写自己阅读过某某源码,要把它体现在项目中,就算自己做的项目中没有,也可以说自己看到别人的项目中利用了某个框架的某些特性,于是我就准备自己动手试试,学习一下优秀框架的精髓,我手动整合了spring和mybatis,视图体会mybatis的优秀之处。
开始
要开始整合spring和mybatis,自然是要先搭建一个maven的项目,我在整合spring和mybatis的同时还整合了log4j方便查看日志,整合了阿里的druid作为mysql的数据库连接池,由于我只是要整合spring和mybatis并找到mybatis基于spring的扩展点及整合的原理,没有必要使用web项目,所以我只引入了spring-context包。项目pom文件如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ww</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.3.25.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.25.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis-spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>由于我不喜欢使用xml,所以本次搭建我是用了纯注解的形式,在项目的resource目录下,我建立了application.properties文件
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testmybatis
spring.datasource.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver编写配置类,获取application.properties中配置的数据库信息
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class PropertiesConfig {
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
public String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
public String username;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
public String password;
@Value("${spring.datasource.driver}")
public String driver;
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public String getDriver() {
return driver;
}
}mapper文件如下
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select id,name,height,weight from user where id=#{id}")
public User selectUser(Integer id);
}实体类
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String height;
private String weight;
}相对应的,在mysql中我建了一个数据库,表名为user

service类
@Service
public class UserService{
@Autowired
UserMapper mapper;
public User getUser(int id) {
//一开始log4j并没有输出日志,在官网上查了之后说加上这句话就可以打印日志了
org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory.useLog4JLogging();
return mapper.selectUser(id);
}
}让spring来启动的主配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.ww")
@MapperScan("com.ww.mapper")
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class MybatisConfig {
//这些都是mybatis-spring官网上的例子,照着改改就行
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(PropertiesConfig config) {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(config.getDriver());
dataSource.setUrl(config.getUrl());
dataSource.setPassword(config.getPassword());
dataSource.setUsername(config.getUsername());
return dataSource;
}
//这些都是mybatis-spring官网上的例子,照着改改就行
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return factoryBean.getObject();
}
}到这里项目算搭建完成了,接下来我们运行项目,来观察mybatis整合spring之后的运行过程,以及mybatis整合spring和不整合spring究竟有什么不同
首先我们看到主配置类上有一行@MapperScan的注解,表示扫描mapper到spring容器中,把mapper交给spring管理,那么我想知道mapper是什么时候被spring扫描并注入的呢,我们点进这个注解,看到这个注解是一个组合注解,其中有这么一行注解引起了我的注意
@Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)这个注解是什么意思呢,Import注解的意思是导入资源,那么我们看看它导入的是个什么资源,看类的名字,我猜想这可能是一个mapper扫描器的注册器,于是我就点进去看看
public class MapperScannerRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, ResourceLoaderAware {
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AnnotationAttributes annoAttrs = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(MapperScan.class.getName()));
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
// this check is needed in Spring 3.1
if (resourceLoader != null) {
scanner.setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass = annoAttrs.getClass("annotationClass");
if (!Annotation.class.equals(annotationClass)) {
scanner.setAnnotationClass(annotationClass);
}
Class<?> markerInterface = annoAttrs.getClass("markerInterface");
if (!Class.class.equals(markerInterface)) {
scanner.setMarkerInterface(markerInterface);
}
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> generatorClass = annoAttrs.getClass("nameGenerator");
if (!BeanNameGenerator.class.equals(generatorClass)) {
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(generatorClass));
}
Class<? extends MapperFactoryBean> mapperFactoryBeanClass = annoAttrs.getClass("factoryBean");
if (!MapperFactoryBean.class.equals(mapperFactoryBeanClass)) {
scanner.setMapperFactoryBean(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(mapperFactoryBeanClass));
}
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(annoAttrs.getString("sqlSessionTemplateRef"));
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(annoAttrs.getString("sqlSessionFactoryRef"));
List<String> basePackages = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String pkg : annoAttrs.getStringArray("value")) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(pkg)) {
basePackages.add(pkg);
}
}
for (String pkg : annoAttrs.getStringArray("basePackages")) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(pkg)) {
basePackages.add(pkg);
}
}
for (Class<?> clazz : annoAttrs.getClassArray("basePackageClasses")) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
}
scanner.registerFilters();
//调用ClassPathMapperScanner中的doScan方法,来扫描mapper并组装成beanDefinition
scanner.doScan(StringUtils.toStringArray(basePackages));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
}可以看到这个类实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar这个接口,这就引出了spring的第一个扩展点,ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口可以用来动态注册bean,它可以支持我们自己写的代码封装成BeanDefinition对象。在这里,mybatis作为一个第三方框架因为没有办法像第一方组件那样使用@Component或者@Service来表示这是一个需要注入的bean,所以只能扩展这个接口来动态的注入bean。
我们再来看registerBeanDefinitions这个方法,这个方法的含义就是注册bd(为了方便起见,以下beanDefinition都简称bd),我们看到方法最后调用了ClassPathMapperScanner的doScan()方法,我们看看ClassPathMapperScanner这个类
public class ClassPathMapperScanner extends ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner {
...
}这个类属于spring-mybatis包下,继承了spring的ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner类
@Override
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
//调用spring的doScan方法来扫描bd
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
//扫描完成后执行bd处理
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}由于spring先执行componentScan,我把断点打在ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的doScan方法中的时候,首先扫描我自己的bean的时候也会进入这个断点,本次由于不分析componentScan,这一部分略过。跳过这个断点,此时控制台上输出
Registering bean definition for @Bean method com.ww.config.MybatisConfig.dataSource()
Registering bean definition for @Bean method com.ww.config.MybatisConfig.sqlSessionFactory()表示我自己的bean已经注册完成了,接下来就应该进入mapper扫描了,我把断点打在MapperScannerRegistrar类中registerBeanDefinitions()方法的第一行,果然断点跳了进来,一路执行下去,当执行完ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的doScan的方法之后,控制台输出一句:
Identified candidate component class: file [E:\mycode\gitclone\mybatis-spring\target\classes\com\ww\mapper\UserMapper.class]确认了候选的组件类,也就是说明spring已经扫描到mapper了,同时spring已经注册了bd,接下来再执行,则会进入processBeanDefinitions()方法
//处理注册好的bd
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {
GenericBeanDefinition definition;
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName()
+ "' and '" + definition.getBeanClassName() + "' mapperInterface");
}
// the mapper interface is the original class of the bean
// but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean
definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(definition.getBeanClassName()); // issue #59
//bd中加入mapperFactoryBean类,由此可见一个mapper对应的beanClass就是mapperFactoryBean,这是mybatis核心类之一,会详细说
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBean.getClass());
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (!explicitFactoryUsed) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.");
}
//自动注入类型为byType
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
}
}
}等这个方法处理完成之后,整个bd算是建立完了,接下来mybatis就开始初始化的过程了,首先我们来看之前被添加进bd中的MapperFactoryBean类
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
private Class<T> mapperInterface;
private boolean addToConfig = true;
public MapperFactoryBean() {
//intentionally empty
}
public MapperFactoryBean(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", e);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public Class<T> getObjectType() {
return this.mapperInterface;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
//------------- mutators --------------
/**
* Sets the mapper interface of the MyBatis mapper
*
* @param mapperInterface class of the interface
*/
public void setMapperInterface(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
/**
* Return the mapper interface of the MyBatis mapper
*
* @return class of the interface
*/
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
/**
* If addToConfig is false the mapper will not be added to MyBatis. This means
* it must have been included in mybatis-config.xml.
* <p/>
* If it is true, the mapper will be added to MyBatis in the case it is not already
* registered.
* <p/>
* By default addToCofig is true.
*
* @param addToConfig
*/
public void setAddToConfig(boolean addToConfig) {
this.addToConfig = addToConfig;
}
/**
* Return the flag for addition into MyBatis config.
*
* @return true if the mapper will be added to MyBatis in the case it is not already
* registered.
*/
public boolean isAddToConfig() {
return addToConfig;
}
}
MapperFactoryBean扩展了Spring的FactoryBean接口,FactoryBean作为Spring的扩展点,FactoryBean的功能是可以让我们自定义Bean的创建过程
//返回的对象实例
T getObject() throws Exception;
//Bean的类型
Class<?> getObjectType();
//true是单例,false是非单例 在Spring5.0中此方法利用了JDK1.8的新特性变成了default方法,返回true
boolean isSingleton();同时MapperFactory还继承了SqlSessionDaoSupport类,SqlSessionDaoSupport类又继承了Spring的DaoSupport类,利用了Spring中InitializingBean这个扩展点,在属性设置之后对bean进行操作,我们来看SqlSessionDaoSupport类和DaoSupport类都是做什么的
public abstract class SqlSessionDaoSupport extends DaoSupport {
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private boolean externalSqlSession;
//设置sqlSessionFactory,由于mapperScan最后执行了definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE),所以这个set方法会自动注入进spring容器中
public void setSqlSessionFactory(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
if (!this.externalSqlSession) {
this.sqlSession = new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
//设置sqlSessionTemplate,spring-mybatis的核心类之一,替代了普通mybatis中的DefaultSqlSession类,这个类控制sqlSession,包含一个内部类用来执行动态代理,同时sqlSessionTemplate类线程安全,可以在spring中作为单例bean使用
public void setSqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSessionTemplate;
this.externalSqlSession = true;
}
/**
* Users should use this method to get a SqlSession to call its statement methods
* This is SqlSession is managed by spring. Users should not commit/rollback/close it
* because it will be automatically done.
*
* @return Spring managed thread safe SqlSession
*/
public SqlSession getSqlSession() {
return this.sqlSession;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
notNull(this.sqlSession, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' or 'sqlSessionTemplate' are required");
}
}
//实现InitializingBean接口,会执行afterPropertiesSet()方法,在mybatis整合了spring后会执行MapperFactoryBean类中的checkDaoConfig()方法
public abstract class DaoSupport implements InitializingBean {
/** Logger available to subclasses */
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@Override
public final void afterPropertiesSet() throws IllegalArgumentException, BeanInitializationException {
// Let abstract subclasses check their configuration.
checkDaoConfig();
// Let concrete implementations initialize themselves.
try {
initDao();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Initialization of DAO failed", ex);
}
}
/**
* Abstract subclasses must override this to check their configuration.
* <p>Implementors should be marked as {@code final} if concrete subclasses
* are not supposed to override this template method themselves.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case of illegal configuration
*/
protected abstract void checkDaoConfig() throws IllegalArgumentException;
/**
* Concrete subclasses can override this for custom initialization behavior.
* Gets called after population of this instance's bean properties.
* @throws Exception if DAO initialization fails
* (will be rethrown as a BeanInitializationException)
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException
*/
protected void initDao() throws Exception {
}
}把断点打在MapperFactoryBean类中的checkDaoConfig()方法上,继续执行,我们看到执行了configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface),点进去,我们看到跳入了org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration类中的addMapper方法
//mapper注册器,添加和获取mapper的实际类
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}于是乎再进入一层
//mapper被加入到MapperProxyFactory类中
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
//加入到map中后立即解析mapper中的注解,目的是拿到mapper中的注解sql语句
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
//动态代理回调方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
//mapper代理类的实例化方法
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
继续往下执行,同时注意控制台的输出情况,看到控制台输出一句Finished creating instance of bean 'userMapper',此时mapper实例化完成,既然实例化完成了,那么就要返回实例化好的mapper,由于bd中放的beanClass是mapperFactoryBean,所以mapper实例要从mapperFactoryBean的getObject方法中来获得,来看代码
//org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean#getObject
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
//org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate#getMapper
//sqlSessionTemplate作为sqlSession
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this);
}
//org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#getMapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
//org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry#getMapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
//之前说过,这里返回的是个代理的对象,也就是经过动态代理的mapper
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
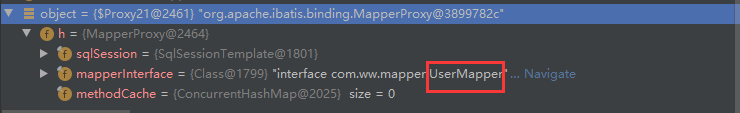
}我们观察变量的变化,发现最终返回的object被MapperProxy所代理,到此为止,mapper已经被spring所管理,spring将通过动态代理技术使用代理类来执行mapper中的各种操作。
总结
经过自己动手用纯注解的方式整合spring和mybatis,我们看到了mybatis基于spring做的许多扩展,同时也看到了spring的很多扩展点,比如ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar、InitializingBean、FactoryBean,下面总结一下mybatis整合spring过程中所用到的几个关键的类和这些类的基本功能
- ClassPathMapperScanner:继承Spring的ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,作用是在classPath中扫描mapper以及扫描之后处理beanDefinition,mapperFactoryBean在这个类中的processBeanDefinitions方法中被加入beanDefinition
- MapperFactoryBean:继承mybatis-spring的SqlSessionDaoSupport,实现了Spring的FactoryBean接口,作用是自定义bean,同时负责在mybatis的初始化结束之后添加mapper以及获取mapper的代理对象
- MapperRegistry:mapper注册器,添加和获取mapper的实际类
- MapperProxy:mapper代理类,调用invoke方法来执行代理方法代理实际mapper中的操作及缓存mapper中的method
- MapperMethod:mapper方法类,包含目标方法对象和sql命令对象,主要作用是执行目标方法的sql语句
- SqlSessionTemplate:mybatis整合spring的核心类,这个类控制sqlSession,包含一个内部类用来执行动态代理
























 387
387











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








