MyBatis 3.5.4源码之旅五之获取sqlSession对象
对照的流程图

如何获取sqlSession对象
就是下面简单一句,我们来看看:
sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
DefaultSqlSessionFactory的openSessionFromDataSource
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//获取环境
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//获取JDBC事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
先获取我们配置的环境:

然后获得事务工厂transactionFactory,再创建事务tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);里面是创建了JdbcTransaction:
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit);
}
Configuration的newExecutor
再获得执行器configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);我们会获得SimpleExecutor的默认执行器,:
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
看看执行器的父类构造方法,可以看到localCache这个就是所说的一级缓存:
protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
this.transaction = transaction;
this.deferredLoads = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache");
this.localOutputParameterCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalOutputParameterCache");
this.closed = false;
this.configuration = configuration;
this.wrapper = this;
}
然后我们判断是否需要二级缓存cacheEnabled,默认是开启的,所以执行器又被包装成了CachingExecutor,里面的做事的还是SimpleExecutor。
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);
}
然后如果有拦截链就放进拦截链里:
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
最后生成默认DefaultSqlSession,默认没有自动提交autoCommit=false:
new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
如何获取接口映射接口对象
看看接口实现类是怎么来的:
userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
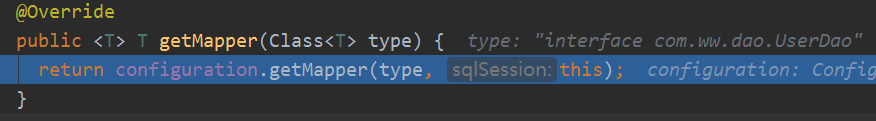
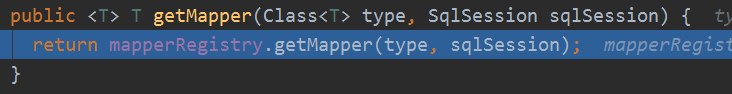
MapperRegistry的getMapper
重点来了:
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
首先先去我们初始化时候解析的knownMappers里获取相应的MapperProxyFactory,然后实例化接口:
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
会创建一个MapperProxy对象,这个类其实是实现了InvocationHandler接口,大家应该能猜到后面应该是JDK的动态代理了吧,实现了我们传进去的接口mapperInterface ,目标对象就是mapperProxy:
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}

至此我们的初始化对象基本都获得了,后面就可以运行增删改查了。
附上我整理的大致流程的脑图:

好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。






















 502
502











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








