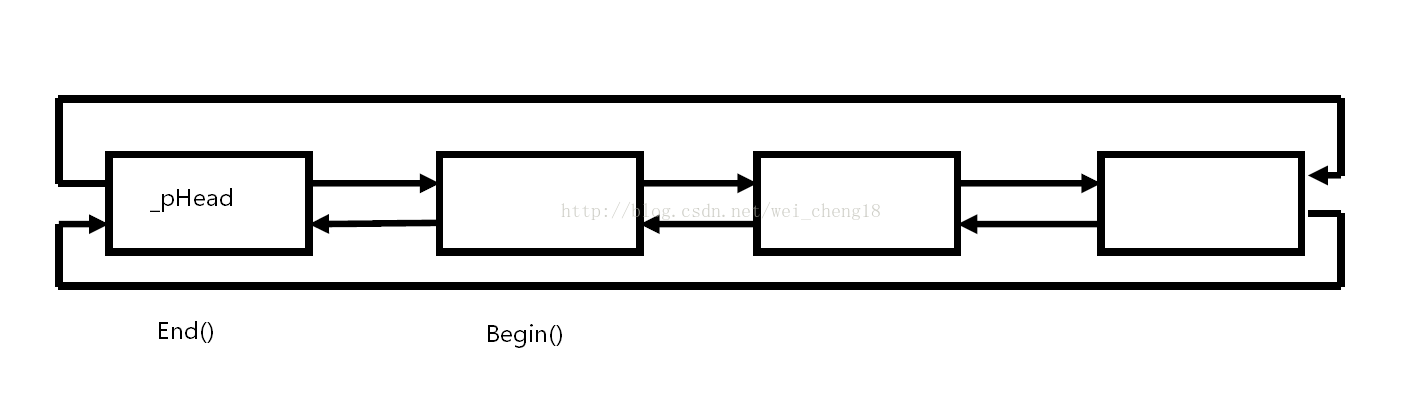
STL中的list是带头结点的双向循环链表,之前我们写过不带头结点的双向循环链表,在此基础上,增加了头结点和迭代器。
结点的结构
template <typename T>
struct Node
{
Node(const T& data = T())
: _data(data)
, _next(NULL)
, _pre(NULL)
{}
T _data;
struct Node* _next;
struct Node* _pre;
};
template<typename T,typename Ref,typename Ptr>//T,T&,T*
struct ListIterator
{
public:
typedef Node<T> Node;
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
ListIterator()
: _pCur(NULL)
{}
ListIterator(Node* pCur)
: _pCur(pCur)
{}
ListIterator(const Self& s)
: _pCur(s._pCur)
{}
Self& operator=(const Self& s)
{
if (*this != s)
_pCur = s._pCur;
return *this;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _pCur->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_pCur->_data);
}
Self& operator++()//前置++
{
_pCur = _pCur->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置++
{
Self tmp(*this);
_pCur = _pCur->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()//前置--
{
_pCur = _pCur->_pre;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--
{
Self tmp(*this);
_pCur = _pCur->_pre;
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _pCur == s._pCur;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _pCur != s._pCur;
}
Node* _pCur;
};template <typename T>
class List
{
public:
typedef Node<T> Node;
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
List()//构造函数
: _pHead(new Node)
{
_pHead->_next = _pHead;
_pHead->_pre = _pHead;
}
List(const T* arr, size_t size)//构造函数
: _pHead(new Node)
{
_pHead->_next = _pHead;
_pHead->_pre = _pHead;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
PushBack(arr[i]);
}
List(const List<T>& list)//拷贝构造
: _pHead(new Node(list._pHead->_data))
{
_pHead->_next = _pHead;
_pHead->_pre = _pHead;
Node* cur = list._pHead->_next;
while (cur != list._pHead)
{
PushBack(cur->_data);
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
bool operator==(const List<T>& list)
{
return _pHead == list._pHead;
}
bool operator!=(const List<T>& list)
{
return _pHead != list._pHead;
}
List<T>& operator=(const List<T>& list)//赋值运算符重载
{
if (*this != list)
{
_pHead = new Node(list._pHead->_data);
_pHead->_next = _pHead;
_pHead->_pre = _pHead;
Node* cur = list._pHead->_next;
while (cur != list._pHead)
{
PushBack(cur->_data);
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return *this;
}
~List()//析构函数
{
Clear();
delete _pHead;
_pHead = NULL;
}
//Iterator///
Iterator Begin() //迭代器
{
return Iterator(_pHead->_next);
}
Iterator End()
{
return Iterator(_pHead);
}
Capacity
bool Empty()//判断是否为空
{
return _pHead->_next == _pHead;
}
size_t Size()const//结点个数
{
size_t size = 0;
Node* pcur = _pHead->_next;
while (pcur != _pHead)
{
size++;
pcur = pcur->_next;
}
return size;
}
///Element access//
T& Front()//首元素
{
return _pHead->_next->_data;
}
const T& Front()const
{
return _pHead->_next->_data;
}
T& Back()//尾元素
{
return _pHead->_pre->_data;
}
const T& Back()const
{
return _pHead->_pre->_data;
}
//Modifiers///
void PushBack(const T& data)//尾插
{
/*Node* newNode = new Node(data);
if (Empty())
{
_pHead->_next = newNode;
newNode->_next = _pHead;
newNode->_pre = _pHead;
_pHead->_pre = newNode;
}
else
{
Node* pTail = _pHead->_pre;
pTail->_next = newNode;
newNode->_pre = pTail;
newNode->_next = _pHead;
_pHead->_pre = newNode;
}*/
Insert(End(), data);
}
void PopBack()//尾删
{
//if (Empty())
// return;
//Node* pTail = _pHead->_pre;
//pTail->_pre->_next = _pHead;
//_pHead->_pre = pTail->_pre;
//delete pTail;
//pTail = NULL;
Erase(--End());//先--,后使用,不能删头结点end(),所以需要--
}
void PushFront(const T& data)//头插
{
//Node* newNode = new Node(data);
//newNode->_next = _pHead->_next;//只有头结点时,_pHead->_next=_pHead;
//newNode->_pre = _pHead;
//_pHead->_next->_pre = newNode;
//_pHead->_next = newNode;
Insert(Begin(), data);
}
void PopFront()//头删
{
//if (Empty())
// return;
//Node* pDel = _pHead->_next;
//_pHead->_next = pDel->_next;
//pDel->_next->_pre = _pHead;
//delete pDel;
//pDel = NULL;
Erase(Begin());//头删
}
Iterator Insert(Iterator pos, const T& data)//任意位置插入
{
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
Node* cur = pos._pCur->_pre;
newNode->_next = pos._pCur;
newNode->_pre = cur;
cur->_next = newNode;
pos._pCur->_pre = newNode;
return Iterator(newNode);
}
Iterator Erase(Iterator pos)//任意位置删除
{
assert(pos._pCur != _pHead);//pos不能是头结点
Node* cur = pos._pCur->_pre;
cur->_next = pos._pCur->_next;
pos._pCur->_next->_pre = cur;
delete pos._pCur;
pos._pCur = NULL;
return Iterator(cur->_next);//返回pos的下一个节点
}
void Clear()//清空有效结点,即只剩下头结点
{
Iterator it = Begin();
while (it != End())
it = Erase(it);
_pHead->_next = _pHead;
_pHead->_pre = _pHead;
}
private:
Node* _pHead;
};测试函数如下:
int main()
{
int arr[3] = { 1, 2, 3 };
List<int> list;
List<int> list1(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
List<int> list2(list1);
List<int> list3;
list3 = list1;
list.PushBack(1);
list.PushBack(2);
list.PushBack(3);
list.PopBack();
list.PopBack();
list.PopBack();
list.PushFront(1);
list.PushFront(2);
list.PushFront(3);
list.PopFront();
list.PopFront();
list.PopFront();
List<int>::Iterator it = list.Begin();
while (it != list.End())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << list.Size() << endl;
cout << list.Back() << endl;
cout << list.Front() << endl;
list.Insert(list.Begin(), 100);
list.Insert(list.Begin(), 200);
list.Insert(list.Begin(), 300);
list.Insert(list.Begin(), 400);
list.Erase(list.Begin());
list.Erase(--list.End());//使用erase不能删除头结点,即end();
list.Clear();
List<int>::Iterator it = list.Begin();
while (it != list.End())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << list.Size() << endl;
cout << list.Back() << endl;
cout << list.Front() << endl;
return 0;
}





















 870
870

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








