I recently started a new newsletter focus on AI education. TheSequence is a no-BS( meaning no hype, no news etc) AI-focused newsletter that takes 5 minutes to read. The goal is to keep you up to date with machine learning projects, research papers and concepts. Please give it a try by subscribing below:
我最近开始了一份有关AI教育的新时事通讯。 TheSequence是无BS(意味着没有炒作,没有新闻等),它是专注于AI的新闻通讯,需要5分钟的阅读时间。 目标是让您了解机器学习项目,研究论文和概念的最新动态。 请通过以下订阅尝试一下:
Querying relational data structures using natural languages has long been a dream of technologists in the space. With the recent advancements in deep learning and natural language understanding(NLU), we have seen attempts by mainstream software packages such as Tableau or Salesforce.com to incorporate natural language to interact with their datasets. However, those options remain extremely limited, constrained specific data structures and hardly resemble a natural language interaction. At the same time, we continue hitting milestones in question-answering models such as Google’s BERT or Microsoft’s Turing-NG. Could we leverage those advancements to interact with tabular data? Recently, Google Research unveiled TAPAS( Table parser), a model based on the BERT architecture that process questions and answers against tabular datasets.
使用自然语言查询关系数据结构一直是该领域技术人员的梦想。 随着深度学习和自然语言理解(NLU)的最新发展,我们已经看到Tableau或Salesforce.com等主流软件包尝试将自然语言与数据集进行交互的尝试。 但是,这些选项仍然极为有限,限制了特定的数据结构,几乎不像自然语言交互。 同时,我们继续在诸如Google的BERT或Microsoft的Turing-NG等问答模型中达到里程碑。 我们能否利用这些进步与表格数据进行交互? 最近,Google Research推出了TAPAS(表格解析器),这是一种基于BERT架构的模型,可针对表格数据集处理问题和答案。
Interacting with tabular data is natural language is one of those scenarios that looks conceptually trivial and results in a nightmare in the real world. Most attempts to solve this issue have been based on semantic parsing methods that process a natural language sentence and generate the corresponding SQL. That approach works in very constrained scenarios but is hardly scalable to real natural language interactions. Let’s take the following example the following datasets of American wrestling champions. The table to the right represents some possible questions that can be executed against that dataset.
与表格数据进行交互是自然语言,是在概念上看起来微不足道并导致现实世界中噩梦的那些场景之一。 解决此问题的大多数尝试都基于语义解析方法,该方法处理自然语言句子并生成相应SQL。 该方法在非常受限的情况下有效,但几乎无法扩展到真正的自然语言交互。 下面以美国摔跤冠军的以下数据集为例。 右边的表格代表可以针对该数据集执行的一些可能的问题。

Some questions such as #1: “Which wrestler had the most number of reigns?” directly maps to a SQL sentence “SELECT TOP Name ORDER BY No. Of Reigns DESC”. Those queries are easy to process by a semantic parser. However, queries such as #5: “Which of the following wrestlers were ranked in the bottom 3? Out of these, who had more than one reign?” are conversational natural and more difficult to process. Additionally, if you factor in common conversational elements such as ambiguity, long-form sentences or synonymous, just to list a few, you start getting a picture of the complexity of using natural language to interact with tabular data.
诸如#1这样的问题:“ 哪个摔跤手的统治次数最多?” 直接映射到SQL语句“ SELECT TOP Name ORDER BY No. Of Reigns DESC” 。 这些查询很容易由语义解析器处理。 但是,诸如#5这样的查询:“ 以下哪个摔角运动员排名前3位? 在这些人中,谁拥有一个以上的统治权?” 很自然,而且很难处理。 此外,如果您将常见的对话元素(例如歧义,长句或同义词)考虑在内,仅举几例,您就会开始了解使用自然语言与表格数据进行交互的复杂性。
TAPAS方法 (The TAPAS Approach)
Instead of creating a model that is constrained to a specific table structure, Google decided to follow a more holistic approach building a neural network that can be adapted to any form of a tabular dataset. To accomplish that, Google decided to based TAPAS in its famous BERT encoder architecture that set new records for natural language models a couple of years ago. TAPAS extends the BERT model in four fundamental areas:
Google决定不采用局限于特定表结构的模型,而是采用更全面的方法来构建可适应任何形式的表格数据集的神经网络。 为此,Google决定将TAPAS基于其著名的BERT编码器架构,该架构在几年前为自然语言模型创造了新记录。 TAPAS在四个基本领域扩展了BERT模型:
1) Additional Embeddings
1)其他嵌入
2) Cell Selection
2)单元格选择
3) Aggregation-Operation-Prediction
3)聚合-操作-预测
4) Inference
4)推论
附加嵌入 (Additional Embeddings)
The most notable addition to the base BERT model is the use of extra embeddings for encoding the textual input. Tapas leverages learned embeddings for the row and column indexes as well as for one special rank index that represents the order of elements in numerical columns. More specifically, TAPAS adds the following types of positional embeddings:
基本BERT模型最引人注目的新增功能是使用了额外的嵌入来对文本输入进行编码。 Tapas对行和列索引以及一个表示数字列中元素顺序的特殊排名索引利用了学习的嵌入。 更具体地说,TAPAS添加了以下类型的位置嵌入:
· Position ID: Just like BERT, this embedding represents the index of the token in the flattened sequence.
·位置ID:与BERT一样,此嵌入表示扁平化序列中令牌的索引。
· Segment ID: Encodes a table header as 0 and a table cell as 1.
·段ID:将表头编码为0,将表单元格编码为1。
· Column/Row ID: The index of the column or row containing the token.
·列/行ID:包含令牌的列或行的索引。
· Rank ID: This embedding is designed to process superlative questions from numeric values. If the cell values are numbers, this embedding sorts them and assign them a value based on their numeric rank.
· 等级ID:此嵌入旨在处理来自数值的最高级问题。 如果单元格值是数字,则此嵌入将对它们进行排序,并根据其数字排名为其分配值。
· Previous Answer: This embedding is designed for scenarios such as question #5 that combines multiple questions. Specifically, this embedding indicates whether a cell token was the answer to a previous question.
·先前的答案:此嵌入是针对诸如问题5的场景的,该问题结合了多个问题。 具体而言,此嵌入指示单元令牌是否是先前问题的答案。
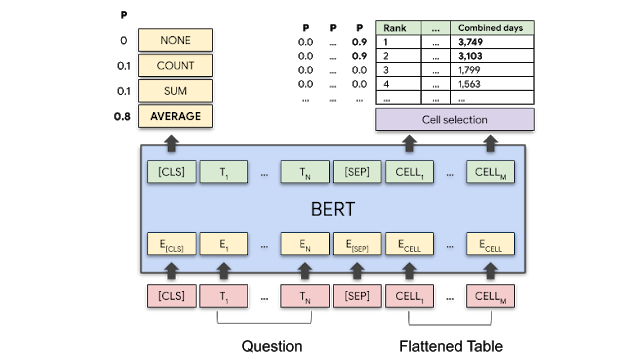
In TAPAS, every language input is encoded as the sum of the different embeddings that represent word, position and segment as illustrated in the following figure:
在TAPAS中,每种语言输入都编码为代表单词,位置和句段的不同嵌入的总和,如下图所示:

单元格选择 (Cell Selection)
TAPAS also extends BERT with a classification layer that can select the subset of the table cells and scores the probability that those cells will be in the final answer or they can be used to compute the final answer. This step is important to optimize query processing time.
TAPAS还使用分类层扩展了BERT,该分类层可以选择表单元格的子集,并对这些单元格将在最终答案中或它们可用于计算最终答案的可能性进行评分。 此步骤对于优化查询处理时间很重要。
聚合操作预测 (Aggregation Operation Prediction)
TAPAS includes an aggregation operator as part of the output to indicate which mathematical operations such as SUM, COUNT, AVERAGE or others need to be applied to the target cells.
TAPAS包含一个聚合运算符作为输出的一部分,以指示哪些数学运算(例如SUM,COUNT,AVERAGE或其他运算)需要应用于目标单元格。
推理 (Inference)
In the TAPAS model, the data selection is not exact but based on probabilities. TAPAS also extends BERT with an inference layer to predict the most likely outcome of the operators and cells that need to be selected.
在TAPAS模型中,数据选择不是精确的,而是基于概率的。 TAPAS还通过推理层扩展了BERT,以预测需要选择的运营商和小区的最可能结果。
You should think about these enhancements about adapting BERT’s state of the art question-answering capabilities to tabular datasets. Let’s go back to our sample wrestling dataset and try to answer the question “Average time as a champion for top 2 wrestlers?” TAPAS uses the base BERT model to encode both the questions and the table. Subsequently, the aggregation-operation prediction layer determines that the AVG operation has a high probability of being used in the answer. Similarly, the cell selection layer detects that cells with the numbers 3,749 and 3,103 also have a high probability to form part of the answer.
您应该考虑这些改进,以使BERT的最新问答功能适应表格数据集。 让我们回到示例摔跤数据集中,尝试回答以下问题:“作为前两名摔跤冠军的平均时间?” TAPAS使用基本的BERT模型对问题和表格进行编码。 随后,聚合操作预测层确定AVG操作具有在答案中使用的高可能性。 同样,单元选择层会检测到编号为3749和3103的单元也很有可能形成答案的一部分。
预训练 (Pretraining)
To follow BERT’s steps, Google pre-trained TAPAS using a dataset of 6.2 million table-text pairs from the English Wikipedia dataset. The maximum number of cells per table was about 500. Additionally, TAPAS was trained using weak and strong supervision models to learn how to answer questions from a table.
为了遵循BERT的步骤,Google使用了来自英语维基百科数据集的620万个表文本对的数据集对TAPAS进行了预培训。 每张桌子的最大单元数约为500。此外,还使用弱和强监督模型对TAPAS进行了培训,以学习如何从桌子中回答问题。
TAPAS实战 (TAPAS in Action)
Google evaluated TAPAS using three fundamental datasets: SQA, WikiTableQuestions (WTQ) and WikiSQL and a series of state-of-the-art models trained using them. In all benchmarks, TAPAS showed levels of performance vastly superior to alternatives as shown in the following charts:
Google使用以下三个基本数据集对TAPAS进行了评估: SQA ,WikiTableQuestions( WTQ )和WikiSQL以及使用它们进行训练的一系列最新模型。 在所有基准测试中,TAPAS的性能水平都大大优于替代产品,如下表所示:

TAPAS is a very interesting approach to leverage natural language to interact with tabular datasets. The results are still highly theoretical and there are questions as to whether this approach will scale to really large datasets. However, the ideas seem to be directionally correct. Leveraging some of the advancements in transformer-based models like BERT to interact with tabular datasets can open new possibilities in the space.
TAPAS是一种非常有趣的方法,可以利用自然语言与表格数据集进行交互。 结果仍然是高度理论化的,并且对于这种方法是否可以扩展到真正的大型数据集存在疑问。 但是,这些想法似乎在方向上是正确的。 利用基于BERT的基于变压器的模型中的某些进步与表格数据集进行交互,可以为空间开辟新的可能性。







 Google的TAPAS模型基于BERT架构,旨在使用自然语言处理表格数据。它通过单元格选择、聚合操作预测、推理等方法实现与表格的交互,以解决复杂的查询问题。TAPAS在SQA、WTQ和WikiSQL等数据集上的表现优越,展示了自然语言处理在表格数据交互中的潜力。
Google的TAPAS模型基于BERT架构,旨在使用自然语言处理表格数据。它通过单元格选择、聚合操作预测、推理等方法实现与表格的交互,以解决复杂的查询问题。TAPAS在SQA、WTQ和WikiSQL等数据集上的表现优越,展示了自然语言处理在表格数据交互中的潜力。














 691
691

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








