“协程可以在遇到阻塞的时候中断主动让渡资源,调度程序选择其他的协程运行。从而实现非阻塞IO”
然而php是不支持原生协程的,遇到阻塞时如不交由异步进程来执行是没有任何意义的,代码还是同步执行的,如下所示:
functionfoo()
{$db=newDb();$result=(yield $db->query());
yield$result;
}
上面的数据库查询操作是阻塞的,当调度器调度该协程到这一步时发现执行了阻塞操作,此时调度器该怎么办?选择其余协程执行?那该协程的阻塞操作又该何时执行,交由谁执行呢?所以说在php协程中抛开异步调用谈非阻塞IO属于耍流氓。
而swoole的异步task提供了一个实现异步的解决方案,关于swoole_task可以参考官方文档
核心功能实现
将一次请求形成一个协程
首先创建一个swoole_server并设置回调
class HttpServer implementsServer
{private $swooleHttpServer;public function __construct(\swoole_http_server $swooleHttpServer)
{$this->swooleHttpServer = $swooleHttpServer;
}public functionstart()
{$this->swooleHttpServer->on('start', [$this, 'onStart']);$this->swooleHttpServer->on('shutdown', [$this, 'onShutdown']);$this->swooleHttpServer->on('workerStart', [$this, 'onWorkerStart']);$this->swooleHttpServer->on('workerStop', [$this, 'onWorkerStop']);$this->swooleHttpServer->on('workerError', [$this, 'onWorkerError']);$this->swooleHttpServer->on('task', [$this, 'onTask']);$this->swooleHttpServer->on('finish', [$this, 'onFinish']);$this->swooleHttpServer->on('request', [$this, 'onRequest']);$this->swooleHttpServer->start();
}
onRequest方法:public function onRequest(\swoole_http_request $request, \swoole_http_response $response)
{$requestHandler = new RequestHandler($request, $response);$requestHandler->handle();
}
在ReqeustHandler中执行handle方法,来解析请求的路由,并创建控制器,调用相应的方法,相public functionhandle()
{$this->context = new Context($this->request, $this->response, $this->getFd());$this->router = new Router($this->request);try{if (false === $this->router->parse()) {$this->response->output('');return;
}$coroutine = $this->doRun();$task = new Task($coroutine, $this->context);$task->run();
}catch (\Exception $e) {
PcsExceptionHandler::handle($e, $this->response);
}
}private functiondoRun()
{$ret = (yield $this->dispatch());
yield$this->response->send($ret);
}
上面代码中的ret是action()的调用结果,yield $this->response->send($ret);是向对客户端请求的应答。
$coroutine是这一次请求形成的一个协程(Genetator对象),包含了整个请求的流程,接下来就要对这个协程进行调度来获取真正的执行结果。
协程调度
namespace Pcs\Coroutine;usePcs\Network\Context\Context;classTask
{private $coroutine;private $context;private $status;private $scheduler;private $sendValue;public function __construct(\Generator $coroutine, Context $context)
{$this->coroutine = $coroutine;$this->context = $context;$this->scheduler = new Scheduler($this);
}public functionrun()
{while (true) {try{$this->status = $this->scheduler->schedule();switch ($this->status) {case TaskStatus::TASK_WAIT:
echo "task status: TASK_WAIT\n";return null;case TaskStatus::TASK_DONE:
echo "task status: TASK_DONE\n";return null;case TaskStatus::TASK_CONTINUE;echo "task status: TASK_CONTINUE\n";break;
}
}catch (\Exception $e) {$this->scheduler->throwException($e);
}
}
}public function setCoroutine($coroutine)
{$this->coroutine = $coroutine;
}public functiongetCoroutine()
{return $this->coroutine;
}public functionvalid()
{if ($this->coroutine->valid()) {return true;
}else{return false;
}
}public function send($value)
{$this->sendValue = $value;$ret = $this->coroutine->send($value);return $ret;
}public functiongetSendVal()
{return $this->sendValue;
}
}
Task依赖于Generator对象$coroutine,在Task类中定义了一些get/set方法,以及一些Generator的方法,Task::run()方法用来执行对协程的调度,调度行为由Schedule来执行,每次调度都会返回当前这次调度的状态。多个协程共用一个调度器,而这里run方法会为每个协程创建一个调度器,原因是每个协程都是一个客户端的请求,使用一个单独的调度器能减少相互间的影响,而且多个协程之间的调度顺序是swoole来处理的,这里的调度器不用关心。下面给出调度的代码:
namespace Pcs\Coroutine;classScheduler
{private $task;private $stack;const SCHEDULE_CONTINUE = 10;public function __construct(Task $task)
{$this->task = $task;$this->stack = new\SplStack();
}public functionschedule()
{$coroutine = $this->task->getCoroutine();$value = $coroutine->current();$status = $this->handleSystemCall($value);if ($status !== self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE) return $status;$status = $this->handleStackPush($value);if ($status !== self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE) return $status;$status = $this->handleAsyncJob($value);if ($status !== self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE) return $status;$status = $this->handelYieldValue($value);if ($status !== self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE) return $status;$status = $this->handelStackPop();if ($status !== self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE) return $status;return TaskStatus::TASK_DONE;
}public functionisStackEmpty()
{return $this->stack->isEmpty();
}private function handleSystemCall($value)
{if (!$valueinstanceof SystemCall) {return self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE;
}
}private function handleStackPush($value)
{if (!$valueinstanceof \Generator) {return self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE;
}$coroutine = $this->task->getCoroutine();$this->stack->push($coroutine);$this->task->setCoroutine($value);return TaskStatus::TASK_CONTINUE;
}private function handleAsyncJob($value)
{if (!is_subclass_of($value, Async::class)) {return self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE;
}$value->execute([$this, 'asyncCallback']);return TaskStatus::TASK_WAIT;
}public function asyncCallback($response, $exception = null)
{if ($exception !== null
&& $exception instanceof \Exception) {$this->throwException($exception, true);
}else{$this->task->send($response);$this->task->run();
}
}private function handelYieldValue($value)
{if (!$this->task->valid()) {return self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE;
}$ret = $this->task->send($value);return TaskStatus::TASK_CONTINUE;
}private functionhandelStackPop()
{if ($this->isStackEmpty()) {return self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE;
}$coroutine = $this->stack->pop();$this->task->setCoroutine($coroutine);$value = $this->task->getSendVal();$this->task->send($value);return TaskStatus::TASK_CONTINUE;
}public function throwException($e, $isFirstCall = false)
{if ($this->isStackEmpty()) {$this->task->getCoroutine()->throw($e);return;
}try{if ($isFirstCall) {$coroutine = $this->task->getCoroutine();
}else{$coroutine = $this->stack->pop();
}$this->task->setCoroutine($coroutine);$coroutine->throw($e);$this->task->run();
}catch (\Exception $e) {$this->throwException($e);
}
}
}
Scheduler中的schedule方法会获取当前Task的协程,并通过current()方法获取当前中断点的返回值,接着依次调用5个方法来对返回值进行处理。
1:handleSystemCall
如果返回的值是SystemCall类型的对象,则执行系统调用,如killTask之类的操作,systemCall是第一优先级。
2:handleStackPush
在A函数中调用B函数,则B函数称为A函数的子例程(子函数),然而在协程中却不能像普通函数那样调用。
functionfuncA()
{returnfuncB();
}functiongenA()
{
yield genB();
}
在funcA中funcB();会返回funcB的执行结果,但是在genA中,yield genB();会返回一个Generator对象,而不是genB的最终执行结果。想得到genB的执行结果需要对genB进行调度,而genB中又可能有genC()genD()的协程嵌套,所以为了让协程像函数一眼正常调用,这里使用协程栈来实现。
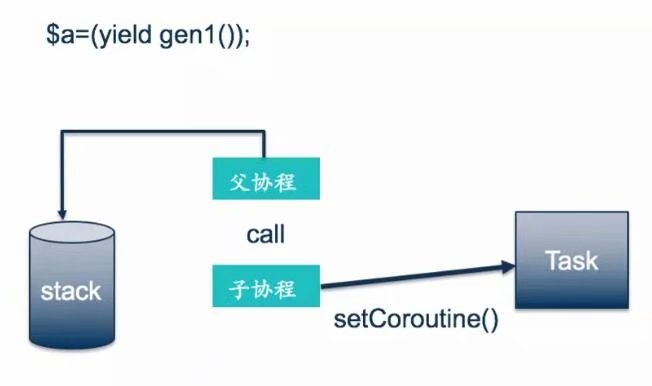
如上图,当调度器获取到GenA(父协程)的返回值is instance of Generator时,调度器会把父协程push到stack中,然后把子协程分配给Task,继续调度子协程。如此反复直到最后一个子协程返回,然后开始pop,将stack中的协程依次取出
3:handleAsyncJob
handleAsyncJob是整个协程调度的核心
private function handleAsyncJob($value)
{if (!is_subclass_of($value, Async::class)) {return self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE;
}$value->execute([$this, 'asyncCallback']);return TaskStatus::TASK_WAIT;
}public function asyncCallback($response, $exception = null)
{if ($exception !== null
&& $exception instanceof \Exception) {$this->throwException($exception, true);
}else{$this->task->send($response);$this->task->run();
}
}
当协程调度的返回值是继承了Async的子类或者是实现了Asycn接口的实例的时候,会执行Async的execute方法。这里用mysqli数据库查询类举例。public function execute(callable $callback)
{$this->callback = $callback;$serv = ServerHolder::getServer();$serv->task($this->sql, -1, [$this, 'queryReady']);
}public function queryReady(\swoole_http_server $serv, $task_id, $data)
{$queryResult = unserialize($data);$exception = null;if ($queryResult->errno != 0) {$exception = new \Exception($queryResult->error);
}call_user_func_array($this->callback, [$queryResult, $exception]);
}
execute方法接收一个函数作为该异步操作完成之后的回调函数,在Mysqli类中的execute方法中,启动了一个异步swoole_task,将sql操作交给swoole_task异步执行,在执行结束后会执行queryReady方法,该方法在解析异步返回数据之后执行$this->callback()也就是之前在调度器中传入的 asyncCallback方法,该方法在检测异常之后会执行send()方法将异步执行的结果发送到中断处,继续执行。
handleAsyncJob不会等待异步操作的返回结果,而是直接返回TASK_WAIT信号,回到上面的Task->run()方法可以看到TASK_WAIT信号会导致run()方法返回null,释放当前worker,调度流程图如下图所示,
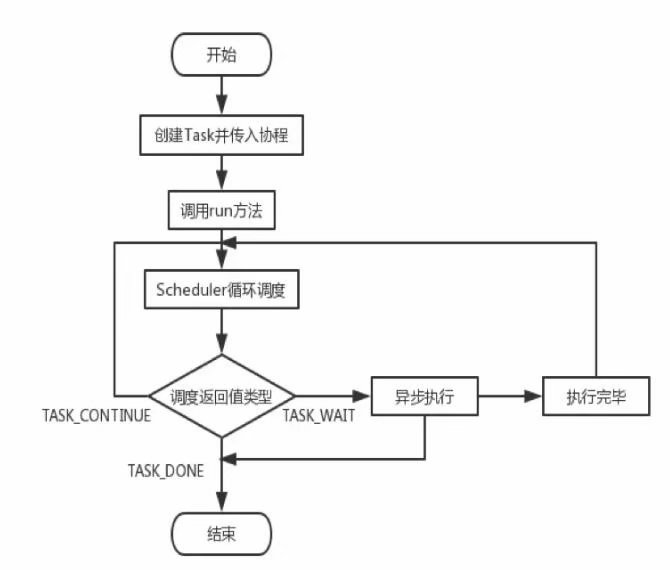
4:handleYieldValue
private function handelYieldValue($value)
{if (!$this->task->valid()) {return self::SCHEDULE_CONTINUE;
}$ret = $this->task->send($value);return TaskStatus::TASK_CONTINUE;
}
如果某次yield的返回值既不是异步调用也不是Generator,那么判断当前的generator是否是valid(是否执行完)如果执行完毕,继续调度,执行下面的handleStackPush方法,否则的话返回Task_Continue继续调度,也就是说在一个generator中多次yield,最后只会取最后一次yield的返回值。
5:handleStackPush
当上一步中判断!$this->task->valid()也就是当前生成器执行完毕的时候,会执行本方法来控制之前的协程stack进行pop操作,首先检查Stac是否是非空,非空的话pop出一个父协程,并将当前协程的返回值send()到父协程中断出继续执行。
协程优势在哪里
当一次请求遇到IO的时候,同步操作会导致当前请求阻塞在IO处等待IO返回,体现在swoole上就是一个请求一直占用一个worker。
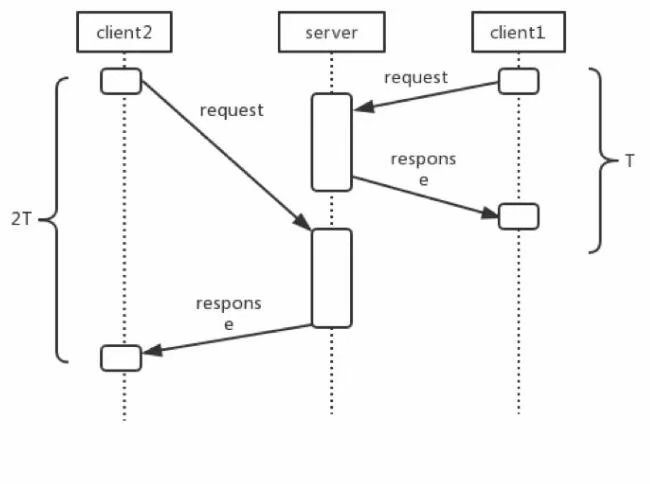
但是当使用了协程调度之后,用户可以在阻塞的地方通过yield手动中断,交由swoole_task去异步操作,同时释放worker占用来处理其他请求。
当异步处理执行结束后再继续调度。
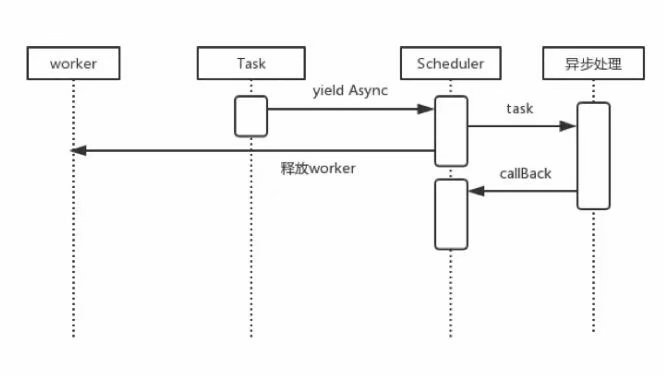
注意 php的协程只负责中断,异步操作是Swoole_task做的




















 262
262











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








