一、为什么要有Hash算法
Java中的集合有两类,一类是List,一类是Set。List内的元素是有序的,元素可以重复。Set元素无序,但元素不可重复。要想保证元素不重复,两个元素是否重复应该依据什么来判断呢?用Object.equals方法。但若每增加一个元素就检查一次,那么当元素很多时,后添加到集合中的元素比较的次数就非常多了。也就是说若集合中已有1000个元素,那么第1001个元素加入集合时,它就要调用1000次equals方法。这显然会大大降低效率。于是Java采用了哈希表的原理。哈希(Hash)是个人名,由于他提出哈希算法的概念就以他的名字命名了。
二、Hash算法原理
当Set接收一个元素时根据该对象的内存地址算出hashCode,看它属于哪一个区间,在这个区间里调用equeals方法。
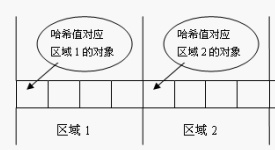
确实提高了效率。但一个面临问题:若两个对象equals相等,但不在一个区间,根本没有机会进行比较,会被认为是不同的对象。所以Java对于eqauls方法和hashCode方法是这样规定的:
1 如果两个对象相同,那么它们的hashCode值一定要相同。也告诉我们重写equals方法,一定要重写hashCode方法。
2 如果两个对象的hashCode相同,它们并不一定相同,这里的对象相同指的是用eqauls方法比较。
三、例子
1 没有重写hashCode和equals的方法
package cn.xy.test;
public class Point1
{
private int x;
private int y;
public Point1(int x, int y)
{
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX()
{
return x;
}
public void setX(int x)
{
this.x = x;
}
public int getY()
{
return y;
}
public void setY(int y)
{
this.y = y;
}
}
public class HashSetAndHashCode
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSet hs1 = new HashSet();
Point1 p11 = new Point1(3, 3);
Point1 p12 = new Point1(3, 3);
Point1 p13 = new Point1(3, 5);
hs1.add(p11);
hs1.add(p11);
hs1.add(p12);
hs1.add(p13);
System.out.println(hs1.size());
}
}
答案是3
2 重写hashCode和equals的方法
package cn.xy.test;
public class Point2
{
private int x;
private int y;
public Point2(int x, int y)
{
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + x;
result = prime * result + y;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if (this == obj) return true;
if (obj == null) return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;
Point2 other = (Point2) obj;
if (x != other.x) return false;
if (y != other.y) return false;
return true;
}
public int getX()
{
return x;
}
public void setX(int x)
{
this.x = x;
}
public int getY()
{
return y;
}
public void setY(int y)
{
this.y = y;
}
}
public class HashSetAndHashCode
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSet hs2 = new HashSet();
Point2 p21 = new Point2(3, 3);
Point2 p22 = new Point2(3, 3);
Point2 p23 = new Point2(3, 5);
hs2.add(p21);
hs2.add(p22);
hs2.add(p23);
System.out.println(hs2.size());
}
}
答案是2。p21和p22被认为是同一个对象。
3 没有重写hashCode的方法,但重写equals的方法
package cn.xy.test;
public class Point3
{
private int x;
private int y;
public Point3(int x, int y)
{
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if (this == obj) return true;
if (obj == null) return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;
Point3 other = (Point3) obj;
if (x != other.x) return false;
if (y != other.y) return false;
return true;
}
public int getX()
{
return x;
}
public void setX(int x)
{
this.x = x;
}
public int getY()
{
return y;
}
public void setY(int y)
{
this.y = y;
}
}
public class HashSetAndHashCode
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSet hs3 = new HashSet();
Point3 p31 = new Point3(3, 3);
Point3 p32 = new Point3(3, 3);
Point3 p33 = new Point3(3, 5);
hs3.add(p31);
hs3.add(p32);
hs3.add(p33);
System.out.println(hs3.size());
}
}
可能是2,可能是3。因为根据内存地址算出的hashcode不知道是否在一个区域。
关于hash碰撞问题:
作为存储Map集合,一共可以插入的数据量:2的32次方,当超出这个范围就会发生因hashCode 相同的hash碰撞。




















 355
355











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








