Channel
通道和io的流类似,主要差别为:通道是双向的,可读可写,io流是单向的。仅仅能读或写,并且操作通道不会直接从通道中写入或读取数据。都是由通道将数据放入缓冲区(buffer)中。
最经常使用的通道:
Filechannel 读取/写入 文件数据
Socketchannel TCP协议的socket 读写数据
Datagramchannel UDP协议读写数据
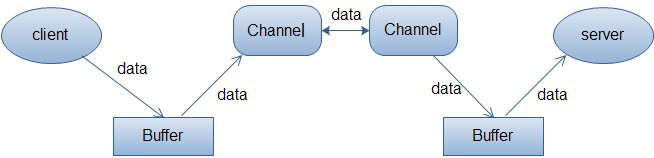
以下是客服端发送读或写的请求过程。
用Filechannel往文件里读取和写入数据的简单样例
读取文件内容:
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fin = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream("c:\\nio.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 获取通道
FileChannel fc = fin.getChannel();
// 创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 读取数据到缓冲区
try {
fc.read(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.remaining() > 0) {
byte b = buffer.get();
System.out.print(((char) b));
}
try {
fin.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
写入文件内容:
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("c:\\nio.txt");
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
FileChannel channel = outputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer bufferWrite = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String string = "hello nio...";
bufferWrite.put(string.getBytes());
//这里必须调用flip(),先读取数据到Buffer。再从Buffer中读取数据。
bufferWrite.flip();
try {
channel.write(bufferWrite);
channel.close();
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
Select
Select 能检測到注冊的全部通道上是否有读写请求,当有请求的时候才会进行读写,一个线程管理了多个通道。避免了多线程切换导致的开销。也不用去维护多个线程,操作原理例如以下图

这里介绍了javaio和nio的差别,以及nio的主要概念。还有简单的nio读写文件数据的样例,对nio就不做深入了。
有兴趣的同学能够看Jakob Jenkov的系列文章。http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-nio/index.html
接下来会分享nio框架netty的一些学习心得,以及netty在实际项目架构中的使用





















 6099
6099

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








