【审计日志】,简单的说就是系统需要记录谁,在什么时间,对什么数据,做了什么样的更改!任何一个 IT 系统,如果要过审,这项任务基本上也是必审项!
实现【审计日志】这个需求,我们有一个很好的技术解决方案,就是使用 Spring 的切面编程。
- 先创建审计日志表

然后编写一个注解类
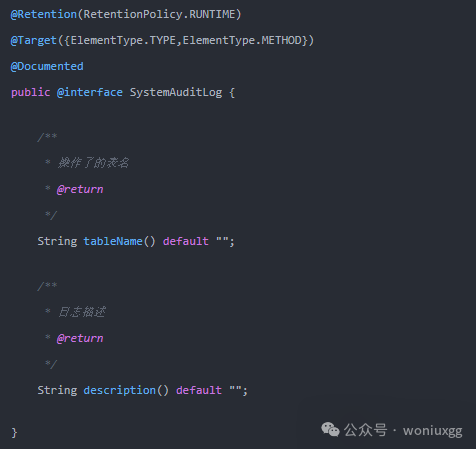
接着编写一个代理类
@Component
@Aspect
public class SystemAuditLogAspect {
@Autowired
private SystemAuditLogService systemAuditLogService;
/**
* 定义切入点,切入所有标注此注解的类和方法
*/
@Pointcut("@within(com.example.demo.core.annotation.SystemAuditLog)|| @annotation(com.example.demo.core.annotation.SystemAuditLog)")
public void methodAspect() {
}
/**
* 方法调用前拦截
*/
@Before("methodAspect()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("SystemAuditLog代理 -> 调用方法执行之前......");
}
/**
* 方法调用后拦截
*/
@After("methodAspect()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("SystemAuditLog代理 -> 调用方法执行之后......");
}
/**
* 调用方法结束拦截
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "methodAspect()")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Exception {
System.out.println("SystemAuditLog代理 -> 调用方法结束拦截......");
//封装数据
AuditLog entity = warpAuditLog(joinPoint);
entity.setResult(0);
//插入到数据库
systemAuditLogService.add(entity);
}
/**
* 抛出异常拦截
*/
@AfterThrowing(value="methodAspect()", throwing="ex")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("SystemAuditLog代理 -> 抛出异常拦截......");
//封装数据
AuditLog entity = warpAuditLog(joinPoint);
entity.setResult(1);
//封装错误信息
entity.setExMsg(ex.getMessage());
//插入到数据库
systemAuditLogService.add(entity);
}
/**
* 封装插入实体
* @param joinPoint
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private AuditLog warpAuditLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Exception {
//获取请求上下文
HttpServletRequest request = getHttpServletRequest();
//获取注解上的参数值
SystemAuditLog systemAuditLog = getServiceMethodDescription(joinPoint);
//获取请求参数
Object requestObj = getServiceMethodParams(joinPoint);
//封装数据
AuditLog auditLog = new AuditLog();
auditLog.setId(SnowflakeIdWorker.getInstance().nextId());
//从请求上下文对象获取相应的数据
if(Objects.nonNull(request)){
auditLog.setUserAgent(request.getHeader("User-Agent"));
//获取登录时的ip地址
auditLog.setIpAddress(IpAddressUtil.getIpAddress(request));
//调用外部接口,获取IP所在地
auditLog.setIpAddressName(IpAddressUtil.getLoginAddress(auditLog.getIpAddress()));
}
//封装操作的表和描述
if(Objects.nonNull(systemAuditLog)){
auditLog.setTableName(systemAuditLog.tableName());
auditLog.setOperateDesc(systemAuditLog.description());
}
//封装请求参数
auditLog.setRequestParam(JSON.toJSONString(requestObj));
//封装请求人
if(Objects.nonNull(requestObj) && requestObj instanceof BaseRequest){
auditLog.setOperateUserId(((BaseRequest) requestObj).getLoginUserId());
auditLog.setOperateUserName(((BaseRequest) requestObj).getLoginUserName());
}
auditLog.setOperateTime(new Date());
return auditLog;
}
/**
* 获取当前的request
* 这里如果报空指针异常是因为单独使用spring获取request
* 需要在配置文件里添加监听
*
* 如果是spring项目,通过下面方式注入
* <listener>
* <listener-class>
* org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextListener
* </listener-class>
* </listener>
*
* 如果是springboot项目,在配置类里面,通过下面方式注入
* @Bean
* public RequestContextListener requestContextListener(){
* return new RequestContextListener();
* }
* @return
*/
private HttpServletRequest getHttpServletRequest(){
RequestAttributes ra = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes sra = (ServletRequestAttributes)ra;
HttpServletRequest request = sra.getRequest();
return request;
}
/**
* 获取请求对象
* @param joinPoint
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private Object getServiceMethodParams(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object[] arguments = joinPoint.getArgs();
if(Objects.nonNull(arguments) && arguments.length > 0){
return arguments[0];
}
return null;
}
/**
* 获取自定义注解里的参数
* @param joinPoint
* @return 返回注解里面的日志描述
* @throws Exception
*/
private SystemAuditLog getServiceMethodDescription(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Exception {
//类名
String targetName = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
//方法名
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
//参数
Object[] arguments = joinPoint.getArgs();
//通过反射获取示例对象
Class targetClass = Class.forName(targetName);
//通过实例对象方法数组
Method[] methods = targetClass.getMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
//判断方法名是不是一样
if(method.getName().equals(methodName)) {
//对比参数数组的长度
Class[] clazzs = method.getParameterTypes();
if(clazzs.length == arguments.length) {
//获取注解里的日志信息
return method.getAnnotation(SystemAuditLog.class);
}
}
}
return null;
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
- 150.
- 151.
- 152.
- 153.
- 154.
- 155.
- 156.
- 157.
- 158.
- 159.
- 160.
- 161.
- 162.
- 163.
- 164.
- 165.
- 166.
- 167.
- 168.
- 169.
- 170.
- 171.
- 172.
- 173.
- 174.
- 175.
- 最后,只需要在对应的接口或者方法上添加审计日志注解即可

- 相关的实体类
@Data
public class AuditLog {
/**
* 审计日志,主键ID
*/
private Long id;
/**
* 操作的表名,多个用逗号隔开
*/
private String tableName;
/**
* 操作描述
*/
private String operateDesc;
/**
* 请求参数
*/
private String requestParam;
/**
* 执行结果,0:成功,1:失败
*/
private Integer result;
/**
* 异常信息
*/
private String exMsg;
/**
* 请求代理信息
*/
private String userAgent;
/**
* 操作时设备IP
*/
private String ipAddress;
/**
* 操作时设备IP所在地址
*/
private String ipAddressName;
/**
* 操作时间
*/
private Date operateTime;
/**
* 操作人ID
*/
private String operateUserId;
/**
* 操作人
*/
private String operateUserName;
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
public class BaseRequest implements Serializable {
/**
* 请求token
*/
private String token;
/**
* 登录人ID
*/
private String loginUserId;
/**
* 登录人姓名
*/
private String loginUserName;
public String getToken() {
return token;
}
public void setToken(String token) {
this.token = token;
}
public String getLoginUserId() {
return loginUserId;
}
public void setLoginUserId(String loginUserId) {
this.loginUserId = loginUserId;
}
public String getLoginUserName() {
return loginUserName;
}
public void setLoginUserName(String loginUserName) {
this.loginUserName = loginUserName;
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
整个程序的实现过程,主要使用了 Spring AOP 特性,对特定方法进行前、后拦截,从而实现业务方的需求。
最后说一句(求关注!别白嫖!)
如果这篇文章对您有所帮助,或者有所启发的话,求一键三连:点赞、转发、在看。
关注公众号:woniuxgg,在公众号中回复:笔记 就可以获得蜗牛为你精心准备的java实战语雀笔记,回复面试、开发手册、有超赞的粉丝福利!




















 237
237

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








