String
字符串一旦创建就不可改变
带有双引号的字符串在字符串常量池中存储
字符串比较时需要使用 equals 方法,String 类重写了 equals 和 toString 方法
创建字符串
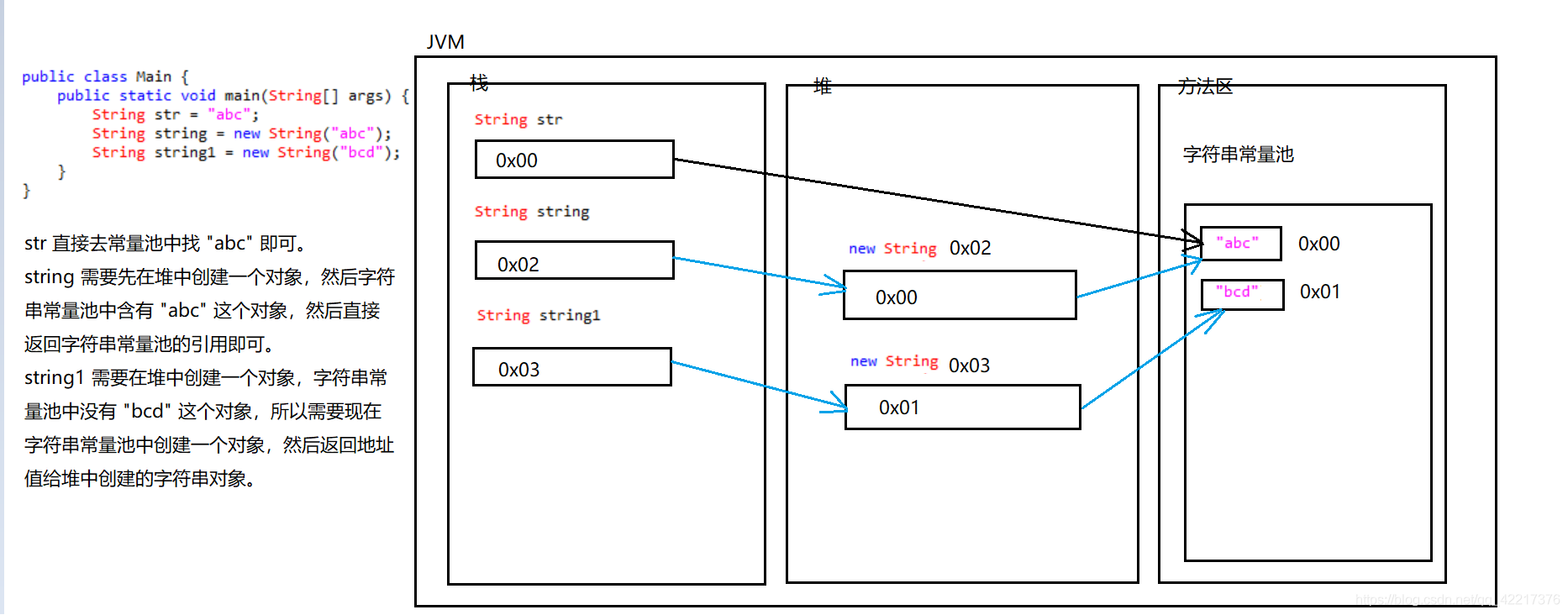
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abc";
String string = new String("abc");
String string1 = new String("bcd");
}
}
内存图分析
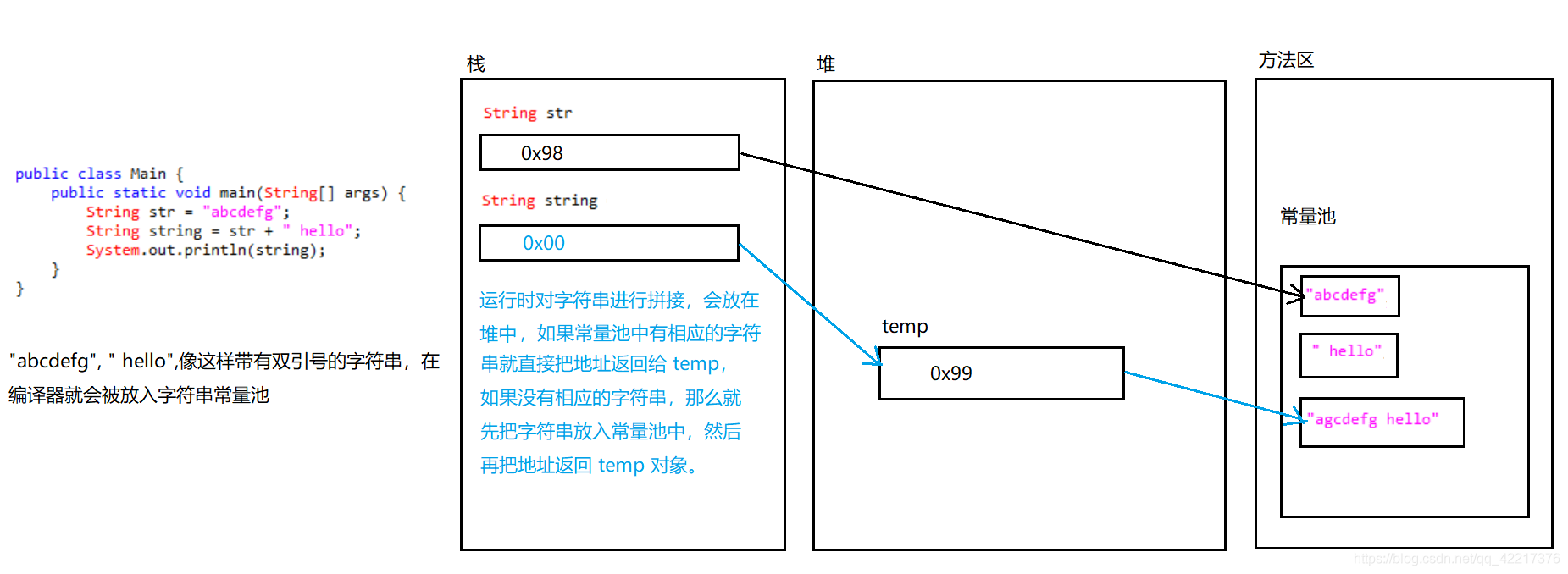
拼接
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdefg";
String string = "abcdefg" + " hello";
System.out.println(string);//abcdefg hello
}
}
如果想要修改字符串的某一个字符,是不支持对某一个位置的字符修改的,这也是字符串的不可变性,如果需要进行修改就必须截取一部分字符,然后通过 + 进行拼接,这样相当于新生成了一个字符串,字符串的不可变性是指你不能修改str中的单个字符,但是你可以让str指向另外一个引用,不可变字符串优点:可以让字符串共享。
内存图分析
常用方法
子串
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdefg";
String string = str.substring(0, 3);
System.out.println(string);
}
}
endsWith:判断字符串是否以指定的后缀结束
startsWith:判断字符串是否以指定的前缀开始
charAt:返回指定位置的字符
compareTo:按照字典序比较两个字符串
contains:判断字符串是否包含某一个字符串
equals:判断两个字符串是否相等,不忽略大小写。JDK 8 底层转换为 char 进行比较,未使用 comparTo 方法。
equalsIgnoreCase:判断两个字符串是否相等,忽略大小写
indexOf:返回指定字符串第一次出现的位置
String str = "aabcabc";
System.out.println(str.indexOf("abc"));//1
lastIndexOf:返回指定字符串最后一次出现的位置
empty:判断字符串是否为空
length:返回字符串的长度
replace:字符串替换
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "aabcabc";
str = str.replace("a", "-");
System.out.println(str);//--bc-bc
}
}
trim:去除字符串的首位空格
toLowerCase:字符串变小写
toUpperCase:字符串变大写
split:字符串分割
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "aa.bc.abc";
String[] strings = str.split("\\.");
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.print(string + " ");//aa bc abc
}
}
}
valueOf:静态方法,将其他类型转换为字符串
空串和null
null 是指某一个对象没有执行任何一个地址,空引用,使用这个对象将发生空指针异常(引用类型默认值为 null)
空串是指这个对象指向了一个地址,是一个有效的地址,只不过这个地址上存储的字符串长度为 0
StringBuffer
StringBuffer 底层是可变的 char 数组,所以字符串可以变化,但是 String 底层的 char 数组被 final 修饰,一旦指向了某一个引用,那么这个数组将不能在进行修改。
StringBuffer 默认初始化容量为 16
public StringBuffer() {
super(16);
}
我们在使用 String 拼接字符串的时候,中间会产生大量的空间浪费,字符串常量池中会产生很多字符串对象(参考上述内存分析图),但是如果我们使用 StringBuffer 就可以避免这种空间浪费。
public AbstractStringBufferappend(String str) {
if (str == null)
return appendNull();
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
//扩容
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0) {
value = Arrays.copyOf(value,
newCapacity(minimumCapacity));
}
}
//在进行扩容的时候,将原来的char数组拷贝到一个新的char数组中
//原来的char数组将会被垃圾回收器回收这样就实现了扩容
//相比于String的拼接省了很多空间
public static char[] copyOf(char[] original, int newLength) {
char[] copy = new char[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
如果在创建字符串的时候就指定了容量,这个就提高了程序的执行效率,因为底层可以不用进行扩容,省去了扩容所浪费的时间。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer(100);
str.append("a");
str.append("b");
}
}
insert
在使用的时候需要注意数组越界的问题
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer(100);
str.append("a");
str.append("b");
str.insert(0, "---");
System.out.println(str);//---ab
}
}
delete
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer(100);
str.append("abcd");
str.append("b");
System.out.println(str);//abcdb
str.delete(0, 1);
System.out.println(str);//bcdb
str.deleteCharAt(3);
System.out.println(str);//bcd
}
}
replace
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer(100);
str.append("abcd");
str.append("b");
System.out.println(str);//abcdb
str.replace(0, 3, "-");//-db
System.out.println(str);
}
}
toString
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer(100);
str.append("abcd");
str.append("b");
System.out.println(str);//abcdb
String string = str.toString();
System.out.println(string);//abcdb
}
}
reverse
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer(100);
str.append("abcd");
str.append("b");
System.out.println(str);//abcdb
str.reverse();
System.out.println(str);//bdcba
}
}
StringBuilder
StringBuffer 是 StringBuilder 的前身,StringBuffer 中的方法都有 synchronized 关键字来修饰,StringBuffer 是线程安全的,但是他的效率比较低,允许采用多线程的方式添加或者删除字符串。StringBuilder 是非线程安全的,如果所有的程序都在单个线程的环境下执行,那么我们就可以使用 StringBuilder。




















 7371
7371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








