1、回归模型预测波士顿房价
代码:
# 多元线性回归模型 from sklearn.datasets import load_boston from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 波士顿房价数据集 data = load_boston() # 划分数据集 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data.data,data.target,test_size=0.3) # 建立多元线性回归模型 mlr = LinearRegression() mlr.fit(x_train,y_train) print('系数',mlr.coef_,"\n截距",mlr.intercept_) # 检测模型好坏 from sklearn.metrics import regression y_predict = mlr.predict(x_test) # 计算模型的预测指标 print("预测的均方误差:", regression.mean_squared_error(y_test,y_predict)) print("预测的平均绝对误差:", regression.mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_predict)) # 打印模型的分数 print("模型的分数:",mlr.score(x_test, y_test)) # 多元多项式回归模型 # 多项式化 poly2 = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2) x_poly_train = poly2.fit_transform(x_train) x_poly_test = poly2.transform(x_test) # 建立模型 mlrp = LinearRegression() mlrp.fit(x_poly_train, y_train) # 预测 y_predict2 = mlrp.predict(x_poly_test) # 检测模型好坏 # 计算模型的预测指标 print("预测的均方误差:", regression.mean_squared_error(y_test,y_predict2)) print("预测的平均绝对误差:", regression.mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_predict2)) # 打印模型的分数 print("模型的分数:",mlrp.score(x_poly_test, y_test))
截图:
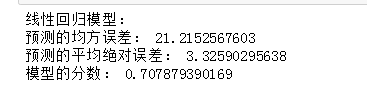
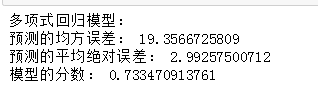
性能比较:
多项式回归做出来的模型显然会好一点。因为多项式模型不仅仅是一条直线,它是一条平滑的曲线,更贴合样本点的分布。并且多项式回归模型的误差也明显比线性的小。
2、新闻文本分类:
定义函数:读数据,清洗,分词。标签存入target_list,文本存入content_list
代码:
import os import numpy as np import sys from datetime import datetime import gc path = 'F:\\计算机\\python\\挖掘\\data' # 导入结巴库,并将需要用到的词库加进字典 import jieba # 导入停用词: with open(r'data\stopsCN.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f: stopwords = f.read().split('\n') def processing(tokens): # 去掉非字母汉字的字符 tokens = "".join([char for char in tokens if char.isalpha()]) # 结巴分词 tokens = [token for token in jieba.cut(tokens,cut_all=True) if len(token) >=2] # 去掉停用词 tokens = " ".join([token for token in tokens if token not in stopwords]) return tokens tokenList = [] targetList = [] # 用os.walk获取需要的变量,并拼接文件路径再打开每一个文件 for root,dirs,files in os.walk(path): for f in files: filePath = os.path.join(root,f) with open(filePath, encoding='utf-8') as f: content = f.read() # 获取新闻类别标签,并处理该新闻 target = filePath.split('\\')[-2] targetList.append(target) tokenList.append(processing(content))
截图:

将content_list列表向量化再建模,将模型用于预测并评估模型
代码:
# 划分训练集测试集并建立特征向量,为建立模型做准备 # 划分训练集测试集 from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB,MultinomialNB from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score from sklearn.metrics import classification_report x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(tokenList,targetList,test_size=0.2,stratify=targetList) # 转化为特征向量,这里选择TfidfVectorizer的方式建立特征向量。不同新闻的词语使用会有较大不同。 vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer() X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(x_train) X_test = vectorizer.transform(x_test) # 建立模型,这里用多项式朴素贝叶斯,因为样本特征的a分布大部分是多元离散值 mnb = MultinomialNB() module = mnb.fit(X_train, y_train) #进行预测 y_predict = module.predict(X_test) # 输出模型精确度 scores=cross_val_score(mnb,X_test,y_test,cv=5) print("Accuracy:%.3f"%scores.mean()) # 输出模型评估报告 print("classification_report:\n",classification_report(y_predict,y_test))
截图:
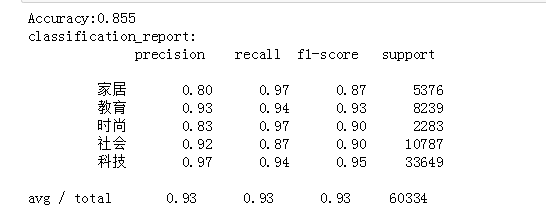
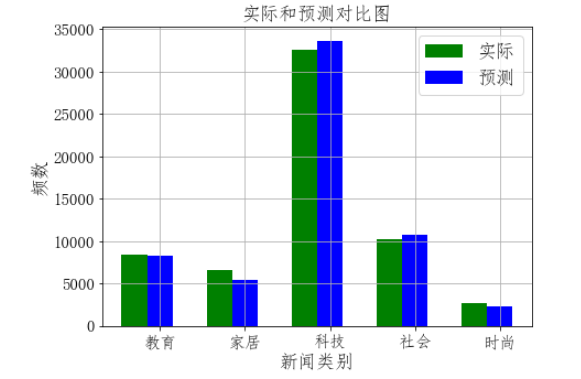
根据特征向量提取逆文本频率高的词汇,将预测结果和实际结果进行对比(用条形图)
# 将预测结果和实际结果进行对比 import collections import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from pylab import mpl mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FangSong'] # 指定默认字体 mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题 # 统计测试集和预测集的各类新闻个数 testCount = collections.Counter(y_test) predCount = collections.Counter(y_predict) print('实际:',testCount,'\n', '预测', predCount) # 建立标签列表,实际结果列表,预测结果列表, nameList = list(testCount.keys()) testList = list(testCount.values()) predictList = list(predCount.values()) x = list(range(len(nameList))) print("新闻类别:",nameList,'\n',"实际:",testList,'\n',"预测:",predictList) # 画图 plt.figure(figsize=(7,5)) total_width, n = 0.6, 2 width = total_width / n plt.bar(x, testList, width=width,label='实际',fc = 'g') for i in range(len(x)): x[i] = x[i] + width plt.bar(x, predictList,width=width,label='预测',tick_label = nameList,fc='b') plt.grid() plt.title('实际和预测对比图',fontsize=17) plt.xlabel('新闻类别',fontsize=17) plt.ylabel('频数',fontsize=17) plt.legend(fontsize =17) plt.tick_params(labelsize=15) plt.show()
截图:





















 646
646











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








