Thread Cancellation
通常来说,多个线程并行执行直到它调用pthread_exit()或者从线程的start function中返回。
有时,我们想要向线程发出一个cancel信号来主动关闭线程。
32.1 Canceling a Thread
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
//Returns 0 on success, or a positive error number on error32.2 Calcellation State and Type
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_setcancelstate(int state, int *oldstate);
int pthread_setcanceltype(int type, int *oldtype);
//Both return 0 on success, or a positive error number on errorpthread_setcancelstate函数可用的state有:
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE线程不可取消。如果接收到一个取消请求,那么该请求会一直挂起直到取消状态变为enabledPTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE可取消状态。默认状态。
The thread’s previous cancelability state is returned in the location pointed to by oldstate.
If a thread is cancelable (PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE), then the treatment of a cancellation request is determined by the thread’s cancelability type, which is specified by the type argument in a call to pthread_setcanceltype(). This argument has one of the following values:
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS线程可以在任何时间被取消。很少用。PTHREAD_CANCEL_DEFERRED直到cacellation point才可以取消。
When a thread calls fork(), the child inherits the calling thread’s cancelability type and state. When a thread calls exec(), the cancelability type and state of the main thread of the new program are reset to PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE and PTHREAD_CANCEL_DEFERRED, respectively.
32.3 Cancellation Points
只有当被要求的线程正处于cancellation points时才可以被取消。SUSv3要求可以成为cancellation points的函数如下:
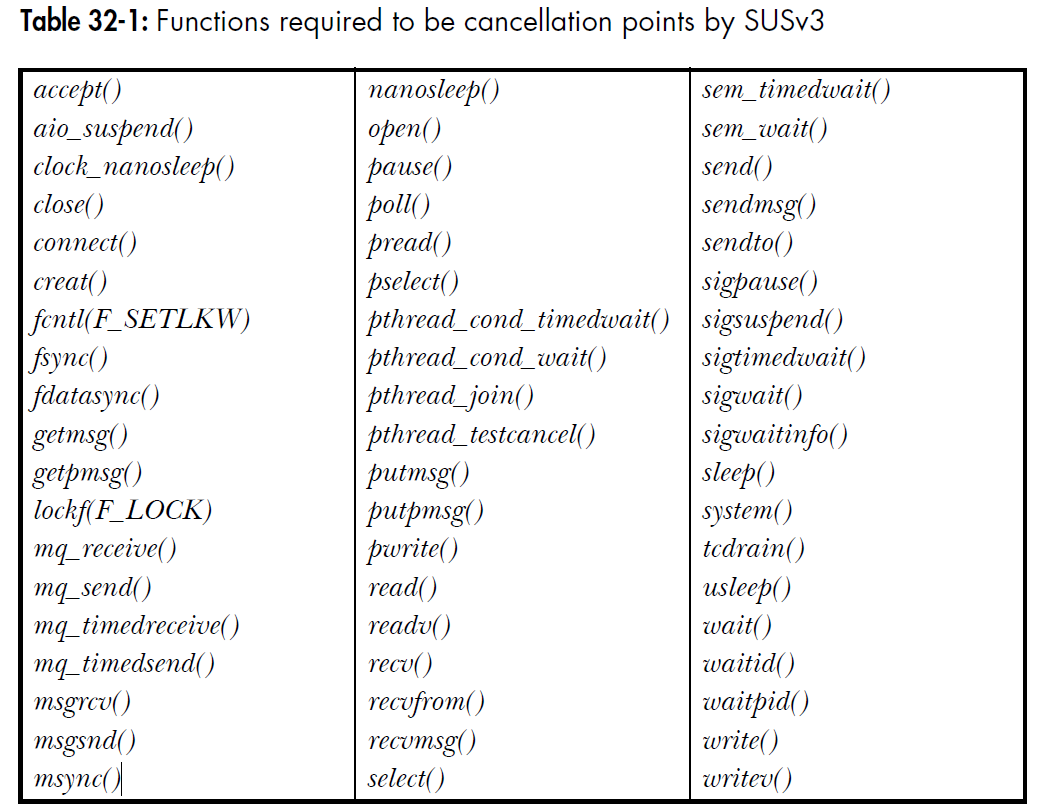
除此以外,SUSv3还规定了一大组函数。这组函数 may define as cancellation points. 其中包括有stdio函数,dlpoenAPI,syslogAPI,nftw(),popen(),semop(),unlink()等等。
Upon receiving a cancellation request, a thread whose cancelability is enabled and deferred terminates when it next reaches a cancellation point.
When a canceled thread is joined, the value returned in the second argument to pthread_join() is a special thread return value: PTHREAD_CANCELED.
32.4 Testing for Thread Cancellation
如果某个线程执行一个循环,该循环中不包括任何cancellation point。在这种情况下,线程将永远不会回应cancellation request.
#include <pthread.h>
void pthread_testcancel(void);此时,该函数可以将pthread_testcancel函数加入循环之中。该函数的作用就是作为一个cancellation points。
32.5 Cleanup Handlers
如果被要求取消的线程直接就终止,那么它所涉及到的共享变量以及Pthread objects可能会处于一种不一致的状态。
线程建立一个或者多个cleanup handlers,当线程被取消时,这些函数被自动执行。cleanup handler可以执行诸如修改全局变量的值,以及在线程终止之前unlock mutexes等工作。
Each thread can have a stack of cleanup handlers. When a thread is canceled, the cleanup handlers are executed working down from the top of the stack; that is, the most recently established handler is called first, then the next most recently established, and so on. When all of the cleanup handlers have been executed, the thread terminates.
#include <pthread.h>
void pthread_cleanup_push(void (*routine)(void*), void *arg);
void pthread_cleanup_pop(int execute);routine参数是一个指向具有如下形式的函数的指针:
void
routine(void *arg)
{
/* Code to perform cleanup */
}而通常来说,cleanup操作只需要在 线程处于某段特定代码中被取消 时才需要被执行。如果线程已经结束了这段代码,那么cleanup操作就不再需要进行。因此,每个对pthread_cleanup_push()的调用都伴随着一个对pthread_cleanup_pop()的调用。注意,如果execute参数非零,那么 handler 依然会被执行。This is convenient if we want to perform the cleanup action even if the thread was not canceled.
SUSv3中允许pthread_cleanup_push和pthread_cleanup_pop作为宏被实现,并且其中包含an opening ({) and closing (}) brace.
This means that each use of pthread_cleanup_push() must be paired with exactly one corresponding pthread_cleanup_pop() in the same lexical block.(这种实现的一个问题,所有在pthread_cleanup_push()和pthread_cleanup_pop之间定义的变量将会被限制在那个域中。)比如,下面的使用方式是不正确的:
pthread_cleanup_push(func, arg);
...
if (cond) {
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
}As a coding convenience, any cleanup handlers that have not been popped are also executed automatically if a thread terminates by calling pthread_exit() (but not if it does a simple return).
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
static pthread_mutex_t mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
static int glob = 0;
static void cleanupHandler(void* arg) {
int s;
printf("cleanup: freeing block at %p\n", arg);
free(arg);
printf("cleanup: unlocking mutex\n");
assert(pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx) == 0);
}
static void* threadFunc(void* arg) {
int s;
void* buf = NULL;
buf = malloc(0x10000);
printf("thread: allocated memory at %p\n", buf);
assert(pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx) == 0);
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanupHandler, buf);
while (glob == 0) {
assert(pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mtx) == 0);
}
printf("thread: condition wait loop completed\n");
pthread_cleanup_pop(1);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
pthread_t thr;
void* res;
int s;
assert(pthread_create(&thr, NULL, threadFunc, NULL) == 0);
sleep(2);
if (argc == 1) {
printf("main: about to cancle thread\n");
assert(pthread_cancel(thr) == 0);
} else {
printf("main: about to signal condition variable\n");
glob = 1;
assert(pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond) == 0);
}
assert(pthread_join(thr, &res) == 0);
if (res == PTHREAD_CANCELED)
printf("main: thread was canceled\n");
else {
printf("main: thread terminated naomally\n");
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}32.6 Asynchronous Cancelability
当线程处于 asynchronously cancelable 状态时,它可以在任何时刻被cancel。
问题:尽管cleanup handlers依然可以被调用,但是handlers无法知道线程处于何种状态。在上面的代码例子中,线程处于默认的deferred cancelability type, 线程只能在它执行对pthread_cond_wait的调用时被取消。





















 3391
3391











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








