Programming Exercise 3: Multi-class Classification and Neural Networks
带正则化的多分类Logistic回归
lrCostFunction
K(K>2)分类Logistic回归中,可以构造K个分类器,第K个分类器的假设函数\(h_\theta(X)=P(y=K|X;\theta)\),即,其输出的是样本分类为K的概率。
损失函数与Ex2中的一样,
\[J(\theta)=\frac 1 m \sum_{i=1}^m[-y^{(i)}log(h_\theta(X^{(i)}))-(1-y^{(i)})log(1-h_\theta(X^{(i)}))]+\frac \lambda {2m} \sum_{i=1}^n \theta_i^2\]
矩阵
\[X=\begin{pmatrix} X^{(1)}\\ \vdots\\ X^{(m)} \end{pmatrix}\]
\[y=\begin{pmatrix} y^{(1)}\\ \vdots\\ y^{(m)} \end{pmatrix}\]
\[\theta=\begin{pmatrix} \theta_{0}\\ \vdots\\ \theta_n \end{pmatrix}\]
则
\[h_\theta(X)=\begin{pmatrix} g(X^{(1)}\theta)\\ \vdots\\ g(X^{(m)}\theta) \end{pmatrix}=g(X\theta)\]
\[J(\theta)=\frac 1 m [-log(h_\theta(X))^Ty-log(1-h_\theta(X))^T(1-y)]+\frac \lambda {2m}\theta'^T\theta'\]
其中
\[\theta'=\begin{pmatrix} 0\\ \theta_{1}\\ \vdots\\ \theta_n \end{pmatrix}\]
梯度下降公式推导:
与Ex2相同,
\[\frac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta_0}=\frac 1 m \sum_{i=1}^m\ (g(X^{(i)}\theta)-y^{(i)})x_0^{(i)}=\frac 1 m (g(X\theta)-y)^T \begin{pmatrix} x_0^{(1)}\\ \vdots\\ x_0^{(m)} \end{pmatrix}\]
\[\frac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta_t}=\frac 1 m \sum_{i=1}^m\ (g(X^{(i)}\theta)-y^{(i)})x_t^{(i)}+\frac \lambda m \theta_t\]
\[=\frac 1 m (g(X\theta)-y)^T \begin{pmatrix} x_t^{(1)}\\ \vdots\\ x_t^{(m)} \end{pmatrix}+\frac \lambda m \theta_t ,\ \ \ \ t> 1\]
则
\[\begin{pmatrix} \frac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta_0} & \cdots & \frac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta_n} \end{pmatrix}= \frac 1 m (g(X\theta)-y)^TX+ \frac \lambda m \theta'^T \]
\[\begin{pmatrix} \frac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta_0} \\ \vdots \\ \frac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta_n} \end{pmatrix}= \frac 1 m X^T(g(X\theta)-y) +\frac \lambda m \theta' \]
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda)
%LRCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with
%regularization
% J = LRCOSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Hint: The computation of the cost function and gradients can be
% efficiently vectorized. For example, consider the computation
%
% sigmoid(X * theta)
%
% Each row of the resulting matrix will contain the value of the
% prediction for that example. You can make use of this to vectorize
% the cost function and gradient computations.
%
% Hint: When computing the gradient of the regularized cost function,
% there're many possible vectorized solutions, but one solution
% looks like:
% grad = (unregularized gradient for logistic regression)
% temp = theta;
% temp(1) = 0; % because we don't add anything for j = 0
% grad = grad + YOUR_CODE_HERE (using the temp variable)
%
tmp=-log(sigmoid(X*theta))'*y-log(1-sigmoid(X*theta))'*(1-y);
regterm=(lambda/(2*m))*(theta(2:length(theta))'*theta(2:length(theta)));
J=tmp/m+regterm;
theta2=theta;
theta2(1)=0;
grad=(X'*(sigmoid(X*theta)-y))/m+(lambda/m)*theta2;
% =============================================================
grad = grad(:);
end
oneVsAll
对应K分类问题,训练K个带正则化的二分类Logistic回归分类器,其中第i个分类器输出输入样本分类为i的概率
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
%ONEVSALL trains multiple logistic regression classifiers and returns all
%the classifiers in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta
%corresponds to the classifier for label i
% [all_theta] = ONEVSALL(X, y, num_labels, lambda) trains num_labels
% logisitc regression classifiers and returns each of these classifiers
% in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta corresponds
% to the classifier for label i
% Some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1);
% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the following code to train num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers with regularization
% parameter lambda.
%
% Hint: theta(:) will return a column vector.
%
% Hint: You can use y == c to obtain a vector of 1's and 0's that tell use
% whether the ground truth is true/false for this class.
%
% Note: For this assignment, we recommend using fmincg to optimize the cost
% function. It is okay to use a for-loop (for c = 1:num_labels) to
% loop over the different classes.
%
% fmincg works similarly to fminunc, but is more efficient when we
% are dealing with large number of parameters.
%
% Example Code for fmincg:
%
% % Set Initial theta
% initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
%
% % Set options for fminunc
% options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
%
% % Run fmincg to obtain the optimal theta
% % This function will return theta and the cost
% [theta] = ...
% fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), ...
% initial_theta, options);
%
for poslabel=1:10
newy=(y==poslabel);
initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
% Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
[theta, cost] = ...
fmincg(@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, newy,lambda)), initial_theta, options);
all_theta(poslabel,:)=theta;
end
% =========================================================================
endpredictOneVsAll
用K分类的logistic回归对输入样本分类
只需输出预测概率最大的那个分类即可
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label for a trained one-vs-all classifier. The labels
%are in the range 1..K, where K = size(all_theta, 1).
% p = PREDICTONEVSALL(all_theta, X) will return a vector of predictions
% for each example in the matrix X. Note that X contains the examples in
% rows. all_theta is a matrix where the i-th row is a trained logistic
% regression theta vector for the i-th class. You should set p to a vector
% of values from 1..K (e.g., p = [1; 3; 1; 2] predicts classes 1, 3, 1, 2
% for 4 examples)
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(all_theta, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);
% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters (one-vs-all).
% You should set p to a vector of predictions (from 1 to
% num_labels).
%
% Hint: This code can be done all vectorized using the max function.
% In particular, the max function can also return the index of the
% max element, for more information see 'help max'. If your examples
% are in rows, then, you can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max
% for each row.
%
[~,p]=max(X*all_theta',[],2);
% =========================================================================
end神经网络正向传播
predict
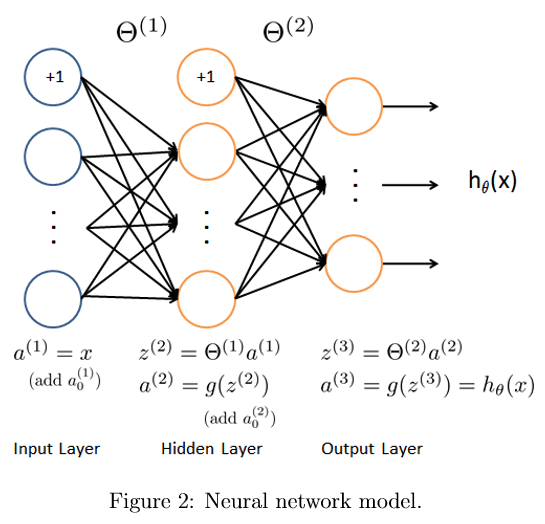
\(\theta_{i,j}^{(L)}\)表示第L层结点j到第L+1层结点i的参数,\(s_L\)表示第L层结点个数,\(a^{(L)}\)为第L层从L-1层接收数据,经激励函数Sigmoid处理后的输出值
\[\Theta^{(L)}=(\theta_{i,j}^{(L)})_{s_{L+1}\times s_{L}}\]
设输入数据为n维列向量\(x\),则令
\[a^{(1)}=\begin{pmatrix}1\\x\end{pmatrix}\]
\[a^{(2)}=\begin{pmatrix}1\\Sigmoid(\Theta^{(1)}a^{(1)})\end{pmatrix}\]
\[a^{(3)}=Sigmoid(\Theta^{(2)}a^{(2)})\]
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label of an input given a trained neural network
% p = PREDICT(Theta1, Theta2, X) outputs the predicted label of X given the
% trained weights of a neural network (Theta1, Theta2)
% Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned neural network. You should set p to a
% vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels.
%
% Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max
% function can also return the index of the max element, for more
% information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you
% can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row.
%
a1=[ones(m,1),X];
a2=[ones(1,m);sigmoid(Theta1*a1')];
a3=sigmoid(Theta2*a2);
[~,p]=max(a3,[],1);
p=p';
% =========================================================================
endProgramming Exercise 4: Neural Networks Learning
带正则化的两层MLP,损失函数为交叉熵
sigmoidGradient
直接写Sigmoid函数的导函数即可
\[Sigmoid'(x)=Sigmoid(x)(1-Sigmoid(x))\]
function g = sigmoidGradient(z)
%SIGMOIDGRADIENT returns the gradient of the sigmoid function
%evaluated at z
% g = SIGMOIDGRADIENT(z) computes the gradient of the sigmoid function
% evaluated at z. This should work regardless if z is a matrix or a
% vector. In particular, if z is a vector or matrix, you should return
% the gradient for each element.
g = zeros(size(z));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the gradient of the sigmoid function evaluated at
% each value of z (z can be a matrix, vector or scalar).
g=sigmoid(z).*(1-sigmoid(z));
% =============================================================
endnnCostFunction
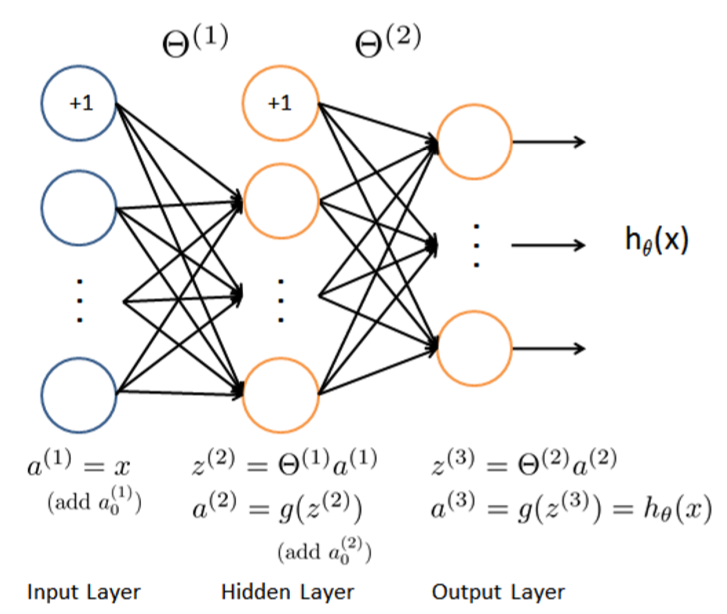
前向传播过程与Ex3一样,这里不再赘述
交叉熵损失函数
\[J(\theta)=\frac 1 m \sum_{i=1}^m\sum_{k=1}^K[-y_k^{(i)}log((h_\theta(x^{(i)}))_k)-(1-y_k^{(i)})log(1-(h_\theta(x^{(i)}))_k)]\]
\[\delta_k^{(3)}=a_k^{(3)}-y_k\]
若输入样本的真实分类为k,则\(y_k=1\),否则为0
\[\delta^{(2)}=(\Theta^{(2)})^T\delta^{(3)}.*g'(z^{(2)})\]
\[\Delta^{l}:=\Delta^{l}+\delta^{l+1}(a^{(l)})^T\]
\(\Delta^{l}_{i,j}\)表示第l层第j个结点到第l+1层第i个结点的参数,对应m个训练样本的梯度之和
则m个样本的平均梯度可以表示为
\[\frac \partial {\partial \Theta_{ij}^{(l)}}J(\Theta)=\frac 1 m \Delta_{ij}^{(l)}\]
再给损失函数加入正则化:
\[J(\theta)=\frac 1 m \sum_{i=1}^m\sum_{k=1}^K[-y_k^{(i)}log((h_\theta(x^{(i)}))_k)-(1-y_k^{(i)})log(1-(h_\theta(x^{(i)}))_k)]+ \frac \lambda {2m}[\sum_{j=1}^{s_2}\sum_{k=1}^{s_1}(\Theta_{j,k}^{(1)})^2+\sum_{j=1}^{s_3}\sum_{k=1}^{s_2}(\Theta_{j,k}^{(2)})^2]\]
\[\frac \partial {\partial \Theta_{ij}^{(l)}}J(\Theta)=\frac 1 m \Delta_{ij}^{(l)}+\frac \lambda m \Theta_{ij}^{(l)}\]
function [J grad] = nnCostFunction(nn_params, ...
input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, ...
X, y, lambda)
%NNCOSTFUNCTION Implements the neural network cost function for a two layer
%neural network which performs classification
% [J grad] = NNCOSTFUNCTON(nn_params, hidden_layer_size, num_labels, ...
% X, y, lambda) computes the cost and gradient of the neural network. The
% parameters for the neural network are "unrolled" into the vector
% nn_params and need to be converted back into the weight matrices.
%
% The returned parameter grad should be a "unrolled" vector of the
% partial derivatives of the neural network.
%
% Reshape nn_params back into the parameters Theta1 and Theta2, the weight matrices
% for our 2 layer neural network
Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(1:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1)), ...
hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + 1));
Theta2 = reshape(nn_params((1 + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1))):end), ...
num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + 1));
% Setup some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
Theta1_grad = zeros(size(Theta1));
Theta2_grad = zeros(size(Theta2));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the code by working through the
% following parts.
%
% Part 1: Feedforward the neural network and return the cost in the
% variable J. After implementing Part 1, you can verify that your
% cost function computation is correct by verifying the cost
% computed in ex4.m
%
% Part 2: Implement the backpropagation algorithm to compute the gradients
% Theta1_grad and Theta2_grad. You should return the partial derivatives of
% the cost function with respect to Theta1 and Theta2 in Theta1_grad and
% Theta2_grad, respectively. After implementing Part 2, you can check
% that your implementation is correct by running checkNNGradients
%
% Note: The vector y passed into the function is a vector of labels
% containing values from 1..K. You need to map this vector into a
% binary vector of 1's and 0's to be used with the neural network
% cost function.
%
% Hint: We recommend implementing backpropagation using a for-loop
% over the training examples if you are implementing it for the
% first time.
%
% Part 3: Implement regularization with the cost function and gradients.
%
% Hint: You can implement this around the code for
% backpropagation. That is, you can compute the gradients for
% the regularization separately and then add them to Theta1_grad
% and Theta2_grad from Part 2.
%
a1=[ones(1,m);X'];
z2=Theta1*a1;
a2=[ones(1,m);sigmoid(z2)];
z3=Theta2*a2;
a3=sigmoid(z3);
for i=1:m
for k=1:size(a3,1)
if(y(i)==k)
J=J-log(a3(k,i));
else
J=J-log(1-a3(k,i));
end
end
end
J=J/m;
J=J+lambda*(sum(sum(Theta1.*Theta1))+sum(sum(Theta2.*Theta2)))/(2*m);
ay=a3;
for i=1:m
for num=1:size(a3,1)
if(y(i)==num)
ay(num,i)=1;
else
ay(num,i)=0;
end
end
end
for i=1:m
delta3=(a3(:,i)-ay(:,i));
delta2=(Theta2'*delta3).*sigmoidGradient([1;z2(:,i)]);
Theta2_grad=Theta2_grad+delta3*a2(:,i)';
Theta1_grad=Theta1_grad+delta2(2:end)*a1(:,i)';
end
Theta1_grad=Theta1_grad/m;
Theta2_grad=Theta2_grad/m;
%Regularization terms
Theta1_grad(:,2:end)=Theta1_grad(:,2:end)+(lambda/m)*Theta1(:,2:end);
Theta2_grad(:,2:end)=Theta2_grad(:,2:end)+(lambda/m)*Theta2(:,2:end);
% -------------------------------------------------------------
% =========================================================================
% Unroll gradients
grad = [Theta1_grad(:) ; Theta2_grad(:)];
end




















 1001
1001











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








