一、boston房价预测
1. 读取数据集
2. 训练集与测试集划分
3. 线性回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。
4. 多项式回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。
#1. 读取数据集
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
data = load_boston()
#2. 训练集与测试集划分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test= train_test_split(data.data,data.target,test_size=0.3)
#3. 线性回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
mlr = LinearRegression()
mlr.fit(x_train,y_train)
print('系数',mlr.coef_,"\n","截距",mlr.intercept_)
from sklearn.metrics import regression
y_pred = mlr.predict(x_test)
print("预测的均方误差:", regression.mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred))
print("预测的平均绝对误差:", regression.mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_pred))
print("模型的分数:",mlr.score(x_test, y_test))
#4. 多项式回归模型:建立13个变量与房价之间的预测模型,并检测模型好坏。
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
a = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
x_poly_train = a.fit_transform(x_train)
x_poly_test = a.transform(x_test)
mlrp = LinearRegression()
mlrp.fit(x_poly_train, y_train)
y_pred2 = mlrp.predict(x_poly_test)
print("预测的均方误差:", regression.mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred2))
print("预测的平均绝对误差:", regression.mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_pred2))
print("模型的分数:",mlrp.score(x_poly_test, y_test))
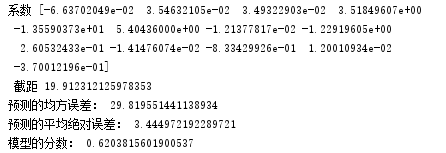

5. 比较线性模型与非线性模型的性能,并说明原因。
非线性模型,即多项式回归模型性能较好,因为它是有很多点连接而成的曲线,对样本的拟合程度较高,预测效果误差较小
二、中文文本分类
按学号未位下载相应数据集。
147:财经、彩票、房产、股票、
258:家居、教育、科技、社会、时尚、
0369:时政、体育、星座、游戏、娱乐
分别建立中文文本分类模型,实现对文本的分类。基本步骤如下:
1.各种获取文件,写文件
2.除去噪声,如:格式转换,去掉符号,整体规范化
3.遍历每个个文件夹下的每个文本文件。
4.使用jieba分词将中文文本切割。
中文分词就是将一句话拆分为各个词语,因为中文分词在不同的语境中歧义较大,所以分词极其重要。
可以用jieba.add_word('word')增加词,用jieba.load_userdict('wordDict.txt')导入词库。
维护自定义词库
5.去掉停用词。
维护停用词表
6.对处理之后的文本开始用TF-IDF算法进行单词权值的计算
7.贝叶斯预测种类
8.模型评价
9.新文本类别预测
处理过程中注意:
- 实验过程中文件遍历从少量到多量,调试无误后再处理全部文件
- 判断文件大小决定读取方法
- 注意保存中间结果,以免每次从头读取文件重复处理
- 内存不足时进行分批处理
- 利用数组的保存np.save('x1.npy',x1)与数组的读取np.load('x1.npy')和数组的拼接np.concatenate((x1,x2),axis=0)
- 及时用 del(x1) 释放大块内存,用gc.collect()回收内存。
- 边处理边保存数据,不要处理完了一次性保存。万一中间发生的异常情况,就全部白做了。
- 进行Python 异常处理,把出错的文件单独记录,程序可以继续执行。回头再单独处理出错的文件。
- 在准备长时间无监督运行程序之前,请关闭windows自动更新、自动屏保关机等......
import os
import numpy as np
import sys
from datetime import datetime
import gc
path = 'G:\\258'
# 导入结巴库,并将需要用到的词库加进字典
import jieba
jieba.load_userdict('jiaju.txt')
# 导入停用词:
with open(r'stopsCN.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:
stopwords = f.read().split('\n')
def processing(tokens):
# 去掉非字母汉字的字符
tokens = "".join([char for char in tokens if char.isalpha()])
# 结巴分词
tokens = [token for token in jieba.cut(tokens,cut_all=True) if len(token) >=2]
# 去掉停用词
tokens = " ".join([token for token in tokens if token not in stopwords])
return tokens
# 用os.walk获取需要的变量,并拼接文件路径再打开每一个文件
tokenList = []
targetList = []
for root,dirs,files in os.walk(path):
for f in files:
filePath = os.path.join(root,f)#地址拼接
with open(filePath, encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
# 获取类别标签,并处理该新闻
target = filePath.split('\\')[-2]
targetList.append(target)
tokenList.append(processing(content))
# 划分训练集测试集并建立特征向量,为建立模型做准备
# 划分训练集测试集
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB,MultinomialNB
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(tokenList,targetList,test_size=0.2,stratify=targetList)
# 转化为特征向量,这里选择TfidfVectorizer的方式建立特征向量。不同新闻的词语使用会有较大不同。
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()
X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(x_train)
X_test = vectorizer.transform(x_test)
# 建立模型,这里用多项式朴素贝叶斯,因为样本特征的a分布大部分是多元离散值
mnb = MultinomialNB()
module = mnb.fit(X_train, y_train)
#进行预测
y_predict = module.predict(X_test)
# 输出模型精确度
scores=cross_val_score(mnb,X_test,y_test,cv=5)
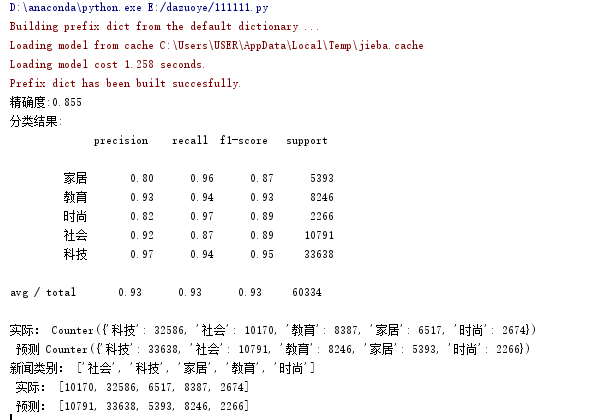
print("精确度:%.3f"%scores.mean())
# 输出模型评估报告
print("分类结果:\n",classification_report(y_predict,y_test))
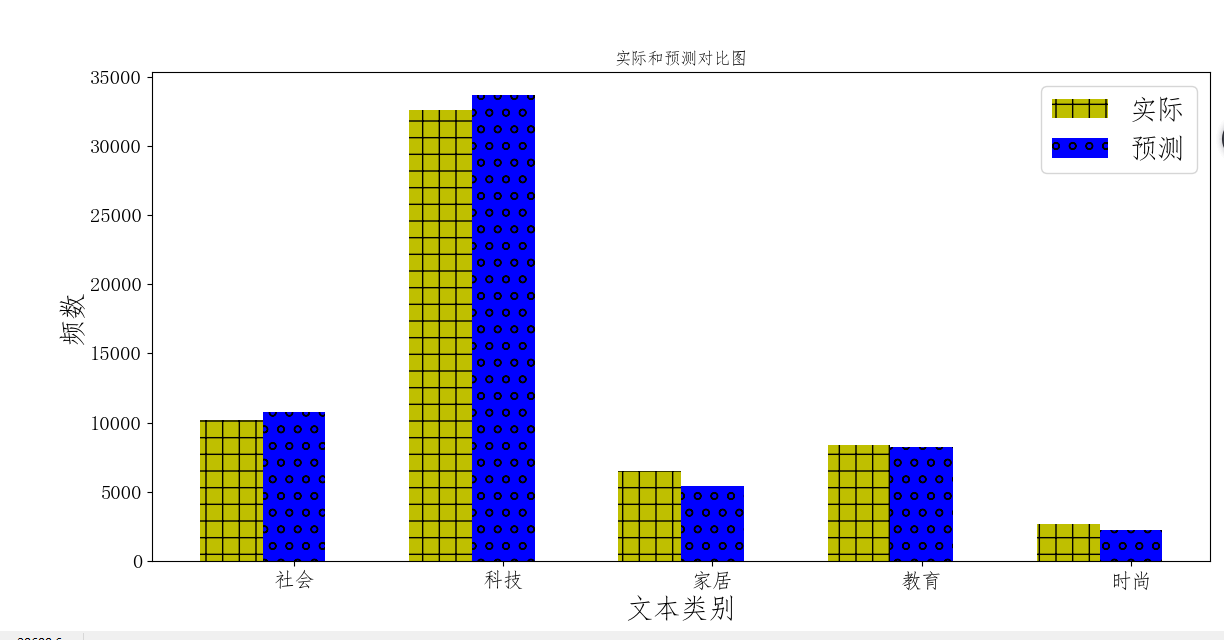
# 将预测结果和实际结果进行对比
# 统计测试集和预测集的各类新闻个数
import collections
testCount = collections.Counter(y_test)
predCount = collections.Counter(y_predict)
print('实际:',testCount,'\n', '预测', predCount)
# 建立标签列表,实际结果列表,预测结果列表,
nameList = list(testCount.keys())
testList = list(testCount.values())
predictList = list(predCount.values())
x = list(range(len(nameList)))
print("文本类别:",nameList,'\n',"实际:",testList,'\n',"预测:",predictList)
# 画图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pylab import mpl
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FangSong'] # 指定默认字体
plt.figure(figsize=(7,5))
total_width, n = 0.6, 2
width = total_width / n
plt.bar(x, testList, width=width,label='实际',facecolor = 'y',hatch = '+')
for i in range(len(x)):
x[i] = x[i] + width
plt.bar(x, predictList,width=width,label='预测',tick_label = nameList,facecolor='b',hatch = 'o')
plt.title('实际和预测对比图',fontsize=20)
plt.xlabel('文本类别',fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel('频数',fontsize=20)
plt.legend(fontsize =20)
plt.tick_params(labelsize=15)
plt.show()





















 873
873











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








