OpenGL ES渲染管线概述
渲染管线一般是由显示芯片GPU内部处理图形信号的并行处理单元组成,这些并行处理单元之间是独立的,从另一个角度看,渲染管线实际上也是一系列绘制过程,这一系列过程的输入是待绘制物体的相关描述信息,输出的是要显示的图像帧数据。
OpenGL ES管线主要包括:
读取顶点数据—>顶点着色器—>组装图元—>光栅化图元—>片元着色器—>写入帧缓冲区—>显示到屏幕上
- 读取顶点数据指的是将待绘制的图形的顶点数据传递给渲染管线中。
- 顶点着色器最终生成每个定点的最终位置,执行顶点的各种变换,它会针对每个顶点执行一次,确定了最终位置后,OpenGL就可以把这些顶点集合按照给定的参数类型组装成点,线或者三角形。
- 组装图元阶段包括两部分:图元的组装和图元处理,图元组装指的是顶点数据根据设置的绘制方式参数结合成完整的图元,例如点绘制方式中每个图元就只包含一个点,线段绘制方式中每个图源包含两个点;图元处理主要是剪裁以使得图元位于视景体内部的部分传递到下一个步骤,视景体外部的部分进行剪裁。视景体的概念与投影有关。
- 光栅化图元主要指的是将一个图元离散化成可显示的二维单元片段,这些小单元称为片元。一个片元对应了屏幕上的一个或多个像素,片元包括了位置,颜色,纹理坐标等信息,这些值是由图元的顶点信息进行插值计算得到的。
- 片元着色器为每个片元生成最终的颜色,针对每个片元都会执行一次。一旦每个片元的颜色确定了,OpenGL就会把它们写入到帧缓冲区中。
在OpenGL ES2.0中主要的两个部分就是上面的可编程顶点着色器和片段着色器。学习OpenGL ES主要是要了解渲染管线,了解CPU的渲染过程,主要编程工作在于顶点着色器和片元着色器的编写。
绘制一个六边形
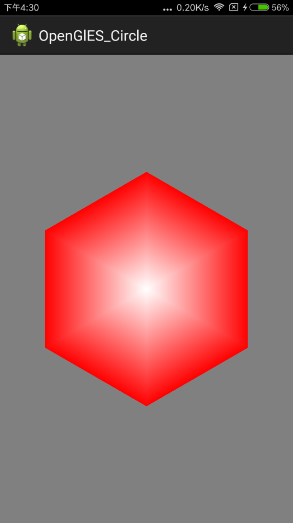
效果如图所示
六边形类
public class SixShape {
private FloatBuffer mVertexBuffer;
private FloatBuffer mColorBuffer;
private int mProgram;
private int mPositionHandle;
private int mColorHandle;
private int muMVPMatrixHandle;
public SixShape(float r) {
initVetexData(r);
}
public void initVetexData(float r) {
// 初始化顶点坐标
float[] vertexArray = new float[8*3];
// 初始化顶点颜色
float[] colorArray=new float[8*4];
int j = 0, k = 0;
vertexArray[j++] = 0;
vertexArray[j++] = 0;
vertexArray[j++] = 0;
colorArray[k++] = 1;
colorArray[k++] = 1;
colorArray[k++] = 1;
colorArray[k++] = 0;
for (int angle = 0; angle <= 360; angle += 60) {
vertexArray[j++] = (float) (r*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(angle)));
vertexArray[j++] = (float) (r*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(angle)));
vertexArray[j++] = 0;
colorArray[k++] = 1;
colorArray[k++] = 0;
colorArray[k++] = 0;
colorArray[k++] = 0;
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(vertexArray.length * 4);
buffer.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
mVertexBuffer = buffer.asFloatBuffer();
mVertexBuffer.put(vertexArray);
mVertexBuffer.position(0);
ByteBuffer cbb=ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(colorArray.length*4);
cbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
mColorBuffer=cbb.asFloatBuffer();
mColorBuffer.put(colorArray);
mColorBuffer.position(0);
int vertexShader = loaderShader(GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, vertexShaderCode);
int fragmentShader = loaderShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, fragmentShaderCode);
mProgram = GLES20.glCreateProgram();
GLES20.glAttachShader(mProgram, vertexShader);
GLES20.glAttachShader(mProgram, fragmentShader);
GLES20.glLinkProgram(mProgram);
mPositionHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgram, "aPosition");
mColorHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgram, "aColor");
muMVPMatrixHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(mProgram, "uMVPMatrix");
}
public void draw(float[] mvpMatrix) {
GLES20.glUseProgram(mProgram);
// 将顶点数据传递到管线,顶点着色器
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mPositionHandle, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 3 * 4, mVertexBuffer);
// 将顶点颜色传递到管线,顶点着色器
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mColorHandle, 4, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false,4*4, mColorBuffer);
// 将变换矩阵传递到管线
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(muMVPMatrixHandle, 1, false, mvpMatrix, 0);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mPositionHandle);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mColorHandle);
// 绘制图元
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLE_FAN, 0, 8);
}
private int loaderShader(int type, String shaderCode) {
int shader = GLES20.glCreateShader(type);
GLES20.glShaderSource(shader, shaderCode);
GLES20.glCompileShader(shader);
return shader;
}
private String vertexShaderCode = "uniform mat4 uMVPMatrix;"
+ "attribute vec3 aPosition;"
+ "attribute vec4 aColor;"
+ "varying vec4 aaColor;"
+ "void main(){"
+ "gl_Position = uMVPMatrix * vec4(aPosition,1);"
+ "aaColor = aColor;"
+ "}";
private String fragmentShaderCode = "precision mediump float;"
+ "varying vec4 aaColor;"
+ "void main(){"
+ "gl_FragColor = aaColor;"
+ "}";
}六边形View
public class SixView extends GLSurfaceView{
public SixView(Context context) {
super(context);
setEGLContextClientVersion(2);
setRenderer(new MyRender());
}
class MyRender implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer {
private SixShape circle;
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, EGLConfig config) {
GLES20.glClearColor(0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1);
circle = new SixShape(0.5f);
GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_DEPTH_TEST);
}
// 投影矩阵
private final float[] mProjectionMatrix = new float[16];
// 视图矩阵
private final float[] mViewMatrix = new float[16];
// 模型矩阵
private final float[] mMMatrix = new float[16];
private final float[] mViewProjectionMatrix = new float[16];
private final float[] mMVPMatrix = new float[16];
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) {
GLES20.glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
float ratio= (float) width / height;
// 设置正交投影
Matrix.orthoM(mProjectionMatrix, 0, -ratio, ratio, -1, 1, 0, 5);
// 设置视图矩阵
Matrix.setLookAtM(mViewMatrix, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0);
}
@Override
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) {
GLES20.glClear( GLES20.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
Matrix.multiplyMM(mViewProjectionMatrix, 0, mProjectionMatrix, 0, mViewMatrix, 0);
// 设置模型矩阵
Matrix.setIdentityM(mMMatrix, 0);
Matrix.translateM(mMMatrix,0,0,0,1);
Matrix.rotateM(mMMatrix, 0, 30, 0, 0, 1);
Matrix.multiplyMM(mMVPMatrix, 0, mViewProjectionMatrix, 0, mMMatrix, 0);
circle.draw(mMVPMatrix);
}
}
}接下来在Activity中就可以使用这个View了。上面的例子虽然简单,但是包括了使用OpenGL ES编程的主要流程,包括生成顶点数据,编写顶点着色器,片元着色器,传递数据给顶点/片元着色器,这里最主要的就是着色器语言。此外包括投影,平移,旋转等操作。在后面会详细学习每个细节以及上面例子没有涉及到的光照,纹理等OpenGL的知识。























 2718
2718

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








