PLSA模型
PLSA和LDA很像,都属于主题模型,即它们都认为上帝在写文章时先以一定概率选择了一个主题,然后在这主题下以一定概率选择了一个词,重复这个过程就完成了一篇文章,即$p(d_i,w_j)=p(z_k|d_i)p(w_j|z_k)$,其中$d$表示文章,$w$表示词,$z$表示主题。
模型求解
模型求解即求出所有的$p(z_k|d_i)$和$p(w_j|z_k)$,这样就可以生成任意篇文章了。
这里有有必要补充个基础概念--条件概率和后验概率。所谓条件概率就是“由因得果”,在$p(z_k|d_i)$中$d_i$是因,$z_k$是果,所以$p(z_k|d_i)$就是个条件概率,同样$p(w_j|z_k)$也是条件概率。所谓后验概率就是“执果寻因”,即观察到了系统的输出和输出,去探寻系统内部的运作机理。对应到PLSA模型中就是观察到$d_i$中出现了一个词$w_j$(文档和词都是观察变量),去探寻连接$d_i$和$w_j$的是哪个主题(主题是隐含变量),如下图所示,其实就是求$p(z_k|d_i,w_j)$。
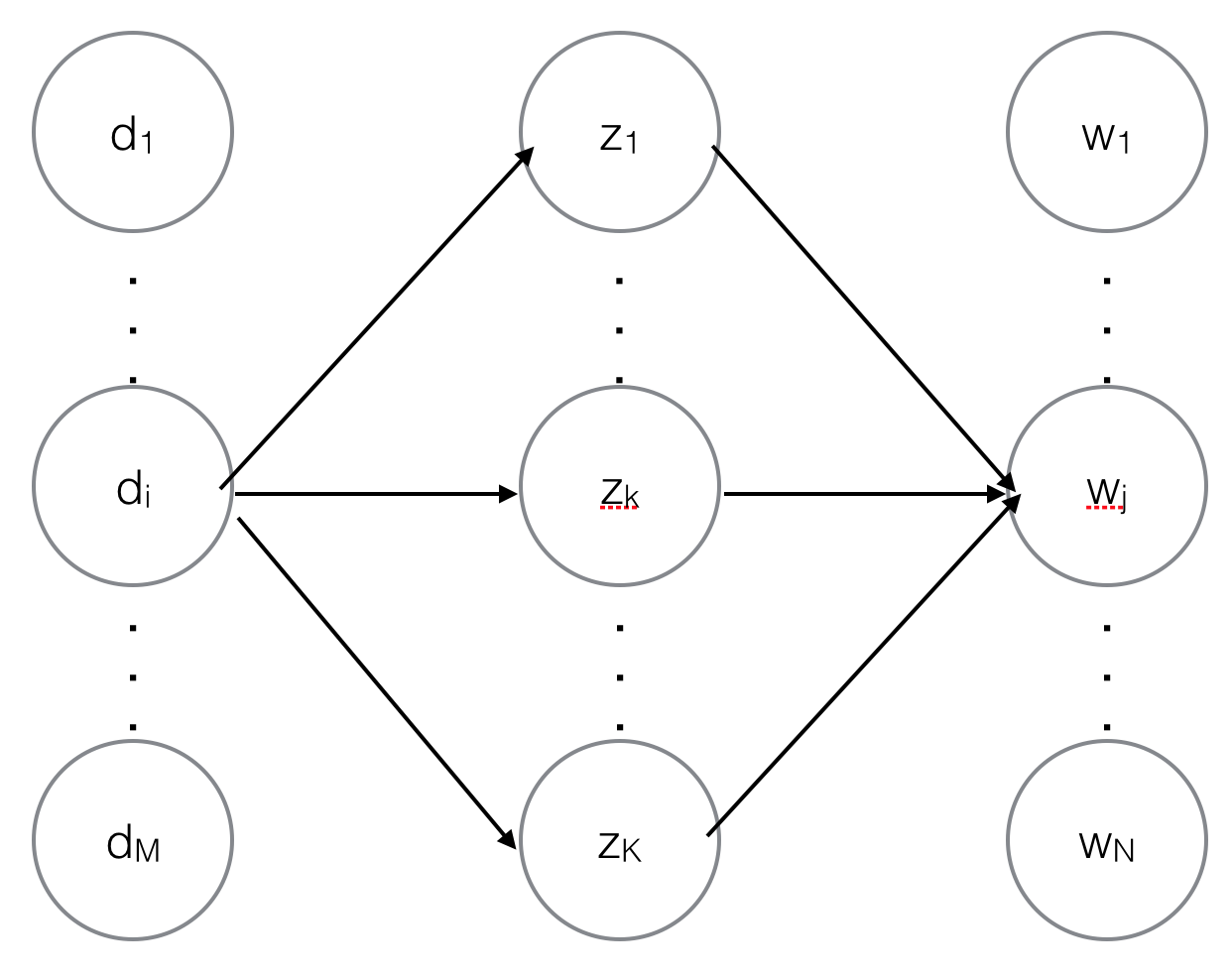
图1. PLSA的概率图模型
下面用EM算法求解模型参数$p(z_k|d_i)$和$p(w_j|z_k)$。
E-Step
E是Expection(期望)的意思,即根据上一轮得到的模型参数求隐含变量的期望,对应到PLSA模型中就是根据上轮得到的模型参数$p(z_k|d_i)$和$p(w_j|z_k)$计算每篇文档中每个词背后对应的主题的概率$p(z_k|d_i,w_j)$。回头看看图1,从$d_i$到$w_j$一共有$K$条路径,途经$z_k$的概率为
\begin{equation}p(z_k|d_i,w_j)=\frac{p(z_k|d_i)p(w_j|z_k)}{\sum_k{p(z_k|d_i)p(w_j|z_k)}}\label{post1}\end{equation}
这里的条件概率$p(z_k|d_i)$和$p(w_j|z_k)$是由上一轮的M-Step得到的,初始时$p(z_k|d_i)$和$p(w_j|z_k)$由随机赋值得到。
如果完全由贝叶斯公式推导是这样的
\begin{equation}p(z_k|d_i,w_j)=\frac{p(z_k)p(d_i,w_j|z_k)}{p(d_i,w_j)}=\frac{p(z_k)p(z_k|d_i)p(w_j|z_k)}{\sum_k{p(z_k|d_i)p(w_j|z_k)}}\label{post2}\end{equation}
跟公式\ref{post1}相比,公式\ref{post2}分子中多了个$p(z_k)$。于是计算$p(z_k|d_i,w_j)$就出现了两个不同的版本,两种版本的代码我都见过,但是PLSA原创作者使用的是公式\ref{post1}。
M-Step
M是极大似然估计(Maximum Likelihood Estimate,MLE)的意思,在已知后验概率的情况下通过MLE的方法求条件概率。
当我们已知所有的 $p(z_k|d_i,w_j)$时,统计一下在所有文章中由$z_k$到$w_j$的次数,再统计一下在所有文章中由$z_k$到任意$w$的次数,两个次数相除就得到了$p(w_j|z_k)$
\begin{equation}p(w_j|z_k)=\frac{\sum_i{p(z_k|d_i,w_j)}}{\sum_i{\sum_j{p(z_k|d_i,w_j)}}}\label{cond1}\end{equation}
同样,统计一下在文章$d_i$当中主题$z_k$出现的次数,再统计一下文章$d_i$中所有主题$z$的出现次数,两者相除就得到了$p(z_k|d_i)$
\begin{equation}p(z_k|d_i)=\frac{\sum_j{p(z_k|d_i,w_j)}}{\sum_j{\sum_k{p(z_k|d_i,w_j)}}}\label{cond2}\end{equation}
且慢,不是说M-Step是用MLE的方法求条件概率吗?这种简单地统计频数,让两个频数相除跟MLE有什么关系呢?其实频数相除就是由MLE推导出来的,我们举一个简单的例子来证明MLE和频数相除是等价的(直接拿PLSA的例子来证明会比较复杂,中间还牵涉到拉格朗日数乘法)。投了10次硬币,6次正面向上,4次反面向上,问这枚硬币正面向上的概率是多少。用频数相除的方法可以很容易地得到正面向上的概率是$\frac{6}{10}$。如果是用MLE求解,先设正面向上的概率为$p$,则似然函数为$p^6{(1-p)^4}$,对数似然函数为$ln{p^6}+ln{(1-p)^4}=6ln{p}+4ln{(1-p)}$,为求对数似然函数的极大值点我们令其导数为0,$\frac{6}{p}-\frac{4}{1-p}=0$,得$p=\frac{6}{10}$。所以两种方法等价。
公式\ref{cond1}和\ref{cond2}没有考虑到一个词出现在文章的不同位置其权重实际上是不一样的,比如一个词出现在正文里我们算作1次出现,如果出现在标题里就应该算作1.5次出现。于是改进后的条件概率计算公式为
\begin{equation}p(w_j|z_k)=\frac{\sum_i{weight_{ij}\cdot p(z_k|d_i,w_j)}}{\sum_i{\sum_j{weight_{ij}\cdot p(z_k|d_i,w_j)}}}\label{cond3}\end{equation}
\begin{equation}p(z_k|d_i)=\frac{\sum_j{weight_{ij}\cdot p(z_k|d_i,w_j)}}{\sum_j{\sum_k{weight_{ij}\cdot p(z_k|d_i,w_j)}}}\label{cond4}\end{equation}
$weight_{ij}$是$w_j$在$d_i$中的权重。
PLSA用于推荐
PLSA是一个词袋模型(BOW, Bag Of Word),它不考虑词在文档中出现的顺序,但可以把词在文档中的权重考虑进来。我们把这些概念平行推广到推荐系统中来,一个用户的购买记录看作是一个文档,购买的每一件商品看作是一个词,用户对商品的评分看作是词在文档中的权重。套用PLSA算法就可以得到用户在各个隐含主题上的向量表示$p(z_k|d_i)$,基于这个向量再去计算相似用户,接着套用协同过滤算法给用户推荐商品。
Java实现
PLSA.java
1 packageplsa;2
3 importjava.io.BufferedReader;4 importjava.io.BufferedWriter;5 importjava.io.File;6 importjava.io.FileReader;7 importjava.io.FileWriter;8 importjava.io.IOException;9 importjava.util.ArrayList;10 importjava.util.Collections;11 importjava.util.Comparator;12 importjava.util.HashMap;13 importjava.util.List;14 importjava.util.Map;15 importjava.util.Map.Entry;16
17 /**
18 * 最初的代码来自于https://code.google.com/archive/p/mltool4j/,源代码在计算p(z|d,w)时使用了p(z),但是在传统的PLSA算法中p(z)根本就没有出现过,所以我对源代码做了改动。19 *20 *@authororisun21 * @date 2016年7月13日22 */
23 public classPLSA {24 private Dataset dataset = null;25 private Posting[][] invertedIndex = null;26 private int M = -1; //文档数
27 private int V = -1; //词汇数
28 private int K = -1; //主题数
29
30 public boolean doPLSA(String datafilePath, int ntopics, intiters) {31 try{32 this.dataset = newDataset(datafilePath);33 } catch(IOException e) {34 e.printStackTrace();35 return false;36 }37 this.M = this.dataset.size();38 this.V = this.dataset.getFeatureNum();39 this.K =ntopics;40
41 //建立term-->doc的倒排索引,在计算p(w|z)时可以提高速度
42 this.buildInvertedIndex(this.dataset);43 this.runEM(iters);44 return true;45 }46
47 /**
48 * 建立term-->doc的倒排索引,在计算p(w|z)时可以提高速度49 *@paramds50 *@return
51 */
52 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")53 private booleanbuildInvertedIndex(Dataset ds) {54 ArrayList[] list = new ArrayList[this.V];55 for (int k = 0; k < this.V; ++k) {56 list[k] = new ArrayList();57 }58
59 for (int m = 0; m < this.M; m++) {60 Data d =ds.getDataAt(m);61 for (int position = 0; position < d.size(); position++) {62 int w =d.getFeatureAt(position).dim;63 list[w].add(newPosting(m, position));64 }65 }66 this.invertedIndex = new Posting[this.V][];67 for (int w = 0; w < this.V; w++) {68 this.invertedIndex[w] = list[w].toArray(new Posting[0]);69 }70 return true;71 }72
73 private boolean runEM(intiters) {74 //p(z|d), size: M x K
75 double[][] Pz_d = new double[this.M][this.K];76
77 //p(w|z), size: K x V
78 double[][] Pw_z = new double[this.K][this.V];79
80 //p(z|d,w), size: M x K x doc.size()
81 double[][][] Pz_dw = new double[this.M][this.K][];82
83 //L: log-likelihood value
84 double L = -1;85
86 //初始时,随机初始化参数
87 this.init(Pz_d, Pw_z, Pz_dw);88 for (int it = 0; it < iters; it++) {89 System.out.println("iteration " +it);90 //E-step
91 if (!this.Estep(Pz_d, Pw_z, Pz_dw)) {92 System.out.println("EM, in E-step");93 }94
95 //M-step
96 if (!this.Mstep(Pz_dw, Pw_z, Pz_d)) {97 System.out.println("EM, in M-step");98 }99
100 File modelPath = new File("model");101 if(modelPath.exists()) {102 if(modelPath.isFile()) {103 modelPath.delete();104 modelPath.mkdirs();105 }106 } else{107 modelPath.mkdirs();108 }109 //进入最后几轮迭代时,保存参数
110 if (it > iters - 10) {111 L =calcLoglikelihood(Pz_d, Pw_z);112 System.out.println("[" + it + "]" + "\tlikelihood: " +L);113 outputPzd(Pz_d, "model/doc_topic." + it);//即文档向量
114 outputPwz(Pw_z, "model/topic_word." +it);115 }116 }117
118 return false;119 }120
121 /**
122 * 拿计算好的文档向量,去计算所有文档跟第1篇文档的相似度。以此来验证PLSA得到的文档向量是合理的。123 */
124 public voidtest(String docVecFile) {125 BufferedReader br = null;126 try{127 br = new BufferedReader(newFileReader(docVecFile));128 String line =br.readLine();129 if (line == null) {130 return;131 }132 String[] arr = line.split("\\s+");133 if (arr.length < 1 + this.K) {134 System.err.println("1st doc vector's length is less than " + this.K);135 return;136 }137 double[] vec1 = new double[this.K];138 double norm1 = 0.0;//向量模长
139 for (int i = 1; i < 1 + this.K; i++) {140 vec1[i - 1] =Double.parseDouble(arr[i]);141 norm1 += vec1[i - 1] * vec1[i - 1];142 }143 norm1 =Math.sqrt(norm1);144 Map simMap = new HashMap();145 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {146 arr = line.split("\\s+");147 if (arr.length == 1 + this.K) {148 String docName = arr[0];149 double[] vec2 = new double[this.K];150 double norm2 = 0.0;//向量模长
151 double prod = 0.0;//向量内积
152 for (int i = 1; i < 1 + this.K; i++) {153 vec2[i - 1] =Double.parseDouble(arr[i]);154 norm2 += vec2[i - 1] * vec2[i - 1];155 prod += vec1[i - 1] * vec2[i - 1];156 }157 norm2 =Math.sqrt(norm2);158 double sim = prod / (norm1 *norm2);159 simMap.put(docName, sim);160 }161 }162
163 //按相似度从大到小排序
164 List> simList = new ArrayList>(165 simMap.entrySet());166 Collections.sort(simList, new Comparator>() {167 @Override168 public int compare(Entry o1, Entryo2) {169 if (o1.getValue() >o2.getValue()) {170 return -1;171 } else if (o1.getValue()
179 for (int i = 0; i < 100 && i < simList.size(); i++) {180 System.out.println(simList.get(i).getKey() + "\t" +simList.get(i).getValue());181 }182 } catch(IOException e) {183 e.printStackTrace();184 } finally{185 try{186 br.close();187 } catch(IOException e) {188 }189 }190
191 }192
193 private boolean init(double[][] Pz_d, double[][] Pw_z, double[][][] Pz_dw) {194 //p(z|d), size: M x K
195 for (int m = 0; m < this.M; m++) {196 double norm = 0.0;197 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {198 Pz_d[m][z] =Math.random();199 norm +=Pz_d[m][z];200 }201
202 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {203 Pz_d[m][z] /=norm;204 }205 }206
207 //p(w|z), size: K x V
208 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {209 double norm = 0.0;210 for (int w = 0; w < this.V; w++) {211 Pw_z[z][w] =Math.random();212 norm +=Pw_z[z][w];213 }214
215 for (int w = 0; w < this.V; w++) {216 Pw_z[z][w] /=norm;217 }218 }219
220 //p(z|d,w), size: M x K x doc.size()
221 for (int m = 0; m < this.M; m++) {222 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {223 Pz_dw[m][z] = new double[this.dataset.getDataAt(m).size()];224 }225 }226 return false;227 }228
229 private boolean Estep(double[][] Pz_d, double[][] Pw_z, double[][][] Pz_dw) {230 for (int m = 0; m < this.M; m++) {231 Data data = this.dataset.getDataAt(m);232 for (int position = 0; position < data.size(); position++) {233 //get word(dimension) at current position of document m
234 int w =data.getFeatureAt(position).dim;235 double norm = 0.0;236 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {237 double val = Pz_d[m][z] *Pw_z[z][w];238 Pz_dw[m][z][position] =val;239 norm +=val;240 }241 //当前文档中的当前词,在各个主题上的概率分布进行归一化
242 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {243 Pz_dw[m][z][position] /=norm;244 }245 }246 }247 return true;248 }249
250 private boolean Mstep(double[][][] Pz_dw, double[][] Pw_z, double[][] Pz_d) {251 //p(z|d)
252 for (int m = 0; m < this.M; m++) {253 double norm = 0.0;254 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {255 double sum = 0.0;256 Data d = this.dataset.getDataAt(m);257 for (int position = 0; position < d.size(); position++) {258 double n =d.getFeatureAt(position).weight;259 sum += n *Pz_dw[m][z][position];260 }261 Pz_d[m][z] =sum;262 norm +=sum;263 }264
265 //normalization
266 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {267 Pz_d[m][z] /=norm;268 }269 }270
271 //p(w|z)
272 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {273 double norm = 0.0;274 for (int w = 0; w < this.V; w++) {275 double sum = 0.0;276 Posting[] postings = this.invertedIndex[w];277 for(Posting posting : postings) {278 int m =posting.docID;279 int position =posting.pos;280 double n = this.dataset.getDataAt(m).getFeatureAt(position).weight;281 sum += n *Pz_dw[m][z][position];282 }283 Pw_z[z][w] =sum;284 norm +=sum;285 }286 //normalization
287 for (int w = 0; w < this.V; w++) {288 Pw_z[z][w] /=norm;289 }290 }291
292 return true;293 }294
295 private double calcLoglikelihood(double[][] Pz_d, double[][] Pw_z) {296 double L = 0.0;297 for (int m = 0; m < this.M; m++) {298 Data d = this.dataset.getDataAt(m);299 for (int position = 0; position < d.size(); position++) {300 Feature f =d.getFeatureAt(position);301 int w =f.dim;302 double n =f.weight;303
304 double sum = 0.0;305 for (int z = 0; z < this.K; z++) {306 sum += Pz_d[m][z] *Pw_z[z][w];307 }308 L += n *Math.log10(sum);309 }310 }311 returnL;312 }313
314 /**
315 * 输出每篇文档在各个主题上的概率分布316 *317 *@paramoutFile318 */
319 private void outputPzd(double[][] Pz_d, String outFile) {320 BufferedWriter bw = null;321 try{322 bw = new BufferedWriter(newFileWriter(outFile));323 for (int i = 0; i < this.M; i++) {324 String docName = this.dataset.getDataAt(i).docName;325 bw.write(docName);326 for (int j = 0; j < this.K; j++) {327 bw.write("\t");328 bw.write(String.valueOf(Pz_d[i][j]));329 }330 bw.newLine();331 }332 } catch(IOException e) {333 e.printStackTrace();334 } finally{335 if (bw != null) {336 try{337 bw.close();338 } catch(IOException e) {339 }340 }341 }342 }343
344 /**
345 * 输出每个主题下的top100的词346 *347 *@paramoutFile348 */
349 private void outputPwz(double[][] Pw_z, String outFile) {350 BufferedWriter bw = null;351 try{352 bw = new BufferedWriter(newFileWriter(outFile));353 for (int i = 0; i < Pw_z.length; i++) {354 Map wordWeight = new HashMap();//词在该主题下的权重
355 for (int j = 0; j < Pw_z[i].length; j++) {356 String word = this.dataset.features.get(j);357 wordWeight.put(word, Pw_z[i][j]);358 }359 List> wordWeightList = new ArrayList>(360 wordWeight.entrySet());361 Collections.sort(wordWeightList, new Comparator>() {362 @Override363 public int compare(Entry o1, Entryo2) {364 if (o1.getValue() >o2.getValue()) {365 return -1;366 } else if (o1.getValue()
391 public static voidmain(String[] args) {392 int nTopic = 50;393 int nIter = 100;394 PLSA plsa = newPLSA();395 if (args.length < 1) {396 System.err.println("train data in docs/user2vec");397 plsa.doPLSA("docs/user2vec", nTopic, nIter);398 } else{399 System.out.println("train data in " + args[0]);400 if (args.length >= 2) {401 nTopic = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);402 }403 if (args.length >= 3) {404 nIter = Integer.parseInt(args[2]);405 }406 plsa.doPLSA(args[0], nTopic, nIter);407 }408 System.out.println("end PLSA");409
410 String docVecFile = "model/doc_topic." + (nIter - 1);411 plsa.test(docVecFile);412 }413 //nohup java -cp .:plsa.jar plsa.PLSA /data/orisun/cf/data/user_graph.txt 50 100 &
414 }
View Code
Dataset.java


1 packageplsa;2
3 importjava.io.BufferedReader;4 importjava.io.File;5 importjava.io.FileReader;6 importjava.io.IOException;7 importjava.util.ArrayList;8 importjava.util.HashMap;9 importjava.util.List;10 importjava.util.Map;11
12 /**
13 * 文档集合14 *15 *@authororisun16 * @date 2016年7月10日17 */
18 public classDataset {19
20 /**文档集合 **/
21 List datas = new ArrayList();22 /**记录每个词的编号 **/
23 Map featureIndex = new HashMap();24 List features = new ArrayList();25
26 intsize() {27 returndatas.size();28 }29
30 intgetFeatureNum() {31 returnfeatureIndex.size();32 }33
34 Data getDataAt(inti) {35 returndatas.get(i);36 }37
38 /**
39 *40 *@paramdataDir41 * 如果dataDir是文档集所在的目录。文档格式:每行存储一个词及词在文件中的权重,空格分隔。每篇文档中词可以有重复。
42 * 如果所有文档都放在dataDir这一个文件里面,则文件每行的格式为:文件名\t词:权重\t词:权重……43 *@throwsIOException44 */
45 Dataset(String dataDir) throwsIOException {46 File path = newFile(dataDir);47 if(path.exists()) {48 int featureNum = 0;49 if(path.isDirectory()) {50 File[] files =path.listFiles();51 for(File file : files) {52 Data data = newData();53 data.docName =file.getName();54 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(newFileReader(file));55 String line = null;56 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {57 String[] arr = line.trim().split("\\s+");58 if (arr.length == 2) {59 String word = arr[0];60 double weight = Double.parseDouble(arr[1]);61 Integer index =featureIndex.get(word);62 if (index == null) {63 featureIndex.put(word, featureNum);64 features.add(word);65 index =featureNum;66 featureNum++;67 }68 Feature feature = newFeature(index, weight);69 data.features.add(feature);70 }71 }72 br.close();73 datas.add(data);74 }75 } else if(path.isFile()) {76 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(newFileReader(path));77 String line = null;78 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {79 String[] arr = line.trim().split("\\s+");80 if (arr.length >= 2) {81 Data data = newData();82 data.docName = arr[0];83 for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {84 String[] brr = arr[i].split(":");85 if (brr.length == 2) {86 String word = brr[0];87 double weight = Double.parseDouble(brr[1]);88 Integer index =featureIndex.get(word);89 if (index == null) {90 featureIndex.put(word, featureNum);91 features.add(word);92 index =featureNum;93 featureNum++;94 }95 Feature feature = newFeature(index, weight);96 data.features.add(feature);97 }98 }99 datas.add(data);100 }101 }102 br.close();103 }104 }105 }106
107 }
View Code
Data.java


1 packageplsa;2
3 importjava.util.ArrayList;4 importjava.util.List;5
6 /**
7 * 文档8 *9 *@authororisun10 * @date 2016年7月10日11 */
12 public classData {13
14 /**文档中的所有词 **/
15 List features = new ArrayList();16 /**文档名称 **/
17 String docName;18
19 intsize() {20 returnfeatures.size();21 }22
23 Feature getFeatureAt(inti) {24 returnfeatures.get(i);25 }26 }
View Code
Feature.java


1 packageplsa;2
3 /**
4 * 词5 *6 *@authororisun7 * @date 2016年7月10日8 */
9 public classFeature {10
11 /**该词在所有词中的编号 **/
12 intdim;13 /**该词在指定文档中的权重 **/
14 doubleweight;15
16 Feature(int index, doubleweight) {17 this.dim =index;18 this.weight =weight;19 }20 }
View Code
Posting.java


1 packageplsa;2
3 /**
4 * 倒排索引5 *6 *@authororisun7 * @date 2016年7月10日8 */
9 public classPosting {10
11 /**文档编号 **/
12 intdocID;13 /**词在文档中的位置 **/
14 intpos;15
16 Posting(int docID, intpos) {17 this.docID =docID;18 this.pos =pos;19 }20 }
View Code





















 3745
3745











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








