最近的工作需要统计一些复杂的报表,为了提高效率,想用多线程去实现,但要在所有线程完成统计任务后,将结果汇总。所以在思考有没有什么办法解决,之所以是“系列一”是因为我想记录下我的思考过程。
1、首先设计一个Executer,负责任务的执行和汇总:
Java代码  public class Executer {
public class Executer {
//计算已经派发的任务数(条件谓词)
public static int THREAD_COUNT = 0;
//线程池
private Executor pool = null;
public Executer() {
this(1);
}
public Executer(int threadPoolSize) {
pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadPoolSize);
}
/**
* 任务派发
* @param job
*/
public void fork(Job job){
//将任务派发给线程池去执行
pool.execute(job);
THREAD_COUNT++;
}
/**
* 统计任务结果
*/
public void join(){
while(THREAD_COUNT > 0){
System.out.println("threadCount: "+THREAD_COUNT);
try {
wait();//如果任务没有全部完成,则挂起
} catch (Exception e) {}//这里总是抛异常,不知道为什么,好吧!先不管它
}
}
}
2、写一个抽象的Job类,负责执行具体的任务
Java代码  public abstract class Job implements Runnable {
public abstract class Job implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
this.execute();//执行子类具体任务
Executer.THREAD_COUNT--;
try{
notifyAll();//这里总是抛异常,不知道为什么,好吧!先不管它
}catch(Exception e){}
}
/**
* 业务处理函数
*/
public abstract void execute();
}
3、测试,先来一个具体的任务实现。
Java代码  public class MyJob extends Job {
public class MyJob extends Job {
@Override
public void execute() {
//模拟业务需要处理1秒.
try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println("running thread id = "+Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
}
4、测试。
Java代码  public class Test {
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化任务池
Executer exe = new Executer(5);
//初始化任务
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i
MyJob job = new MyJob();
exe.fork(job);//派发任务
}
//汇总任务结果
exe.join();
System.out.println("time: "+(System.currentTimeMillis() - time));
}
}
5、好吧,看一下结果
Java代码  threadCount: 10
threadCount: 10
......(表示有N多个)
threadCount: 10
running thread id = 8
running thread id = 9
running thread id = 11
running thread id = 10
running thread id = 12
threadCount: 5
......(表示有N多个)
threadCount: 5
running thread id = 9
running thread id = 10
running thread id = 12
running thread id = 8
running thread id = 11
threadCount: 3
time: 2032
哈哈,看来是可以了,最后汇总任务的处理时间是2032毫秒,看来是比单个任务顺序执行来的快。但是有几个问题:
1)如果没有catch那个超级Exception的话,就会抛下面的异常:
Java代码  java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException
java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException
at java.lang.Object.wait(Native Method)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Object.java:485)
at com.one.Executer.join(Executer.java:38)
at com.test.Test.main(Test.java:21)
2)为啥会打印N多个同样值threadCount呢?
于是和同事(河东)沟通,他说wait要放在synchronized里面才行,好吧,试一下,改进一下Executer和Job
Java代码  public class Executer {
public class Executer {
//计算已经派发的任务数(条件谓词)
public static int THREAD_COUNT = 0;
//条件队列锁
public static final Object LOCK = new Object();
//线程池
private Executor pool = null;
public Executer() {
this(1);
}
public Executer(int threadPoolSize) {
pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadPoolSize);
}
/**
* 任务派发
* @param job
*/
public void fork(Job job){
//将任务派发给线程池去执行
pool.execute(job);
//增加线程数
synchronized (LOCK) {
THREAD_COUNT++;
}
}
/**
* 统计任务结果
*/
public void join(){
synchronized (LOCK) {
while(THREAD_COUNT > 0){
System.out.println("threadCount: "+THREAD_COUNT);
try {
LOCK.wait();//如果任务没有全部完成,则挂起
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
Java代码  public abstract class Job implements Runnable {
public abstract class Job implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
this.execute();//执行子类具体任务
synchronized (Executer.LOCK) {
//处理完业务后,任务结束,递减线程数,同时唤醒主线程
Executer.THREAD_COUNT--;
Executer.LOCK.notifyAll();
}
}
/**
* 业务处理函数
*/
public abstract void execute();
}
6、测试一下:
Java代码  threadCount: 10
threadCount: 10
running thread id = 8
running thread id = 11
running thread id = 9
threadCount: 7
running thread id = 10
threadCount: 6
running thread id = 12
threadCount: 5
running thread id = 11
running thread id = 12
running thread id = 10
threadCount: 2
running thread id = 9
running thread id = 8
threadCount: 1
time: 2016
还真的行,谢谢河东哈!
但是原因是什么呢?回去查了查书《Java并发编程实践》,见附件!
Java代码  第14.2.1节这样说:
第14.2.1节这样说:
在条件等待中存在一种重要的三元关系,包括加锁、wait方法和一个条件谓词。在条件谓词中包含多个变量,而状态变量由一个锁来保护,因此在测试条件谓词之前必须先持有这个锁。锁对象与条件队列对象(即调用wait和notify等方法所在的对象)必须是同一个对象。
...
由于线程在条件谓词不为真的情况下也可以反复地醒来,因此必须在一个循环中调用wait,并在每次迭代中都测试条件谓词。
14.2.4节:
由于在调用notify或notifyAll时必须持有条件队列对象的锁,而如果这些等待中线程此时不能重新获得锁,那么无法从wait返回,因此发出通知的线程应该尽快地释放,从而确保正在等待的线程尽可能尽快的解除阻塞。
看来之前是不会用wait和notify,哈哈~!
感谢河东,和你交流收获很大!
顺便测试一下java多线程情况下,多核CPU的利用率,修改上面的线程池大小和任务数(2个线程处理1000000个任务,去掉MyJob的sleep(这样可以多抢些CPU时间),结果如下:
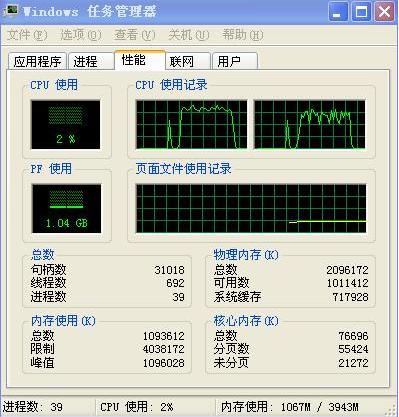
看来window下是可以利用多核的,虽然是一个JVM进程。之前和斯亮讨论的结论是错误的。
posted on 2012-07-15 01:20 mixer-a 阅读(3508) 评论(2) 编辑 收藏





















 537
537











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








