abstract
graph embedding is a method to embed a high dimensional graph into a much lower dimensiona vector space while maximally preserving the structural information of the original network.
we address a real-time and distributed graph embedding algorithm (RTDGE) : distributively embedding a graph in a streaming fashion contain : 1) a graph partition scheme 2)a dynamic negative sampling method 3)unsupervised global aggregation
================================================================================================
limitations of the existing method :
1) can not perform real-time streaming data
2) most of the model are centralized ,which means that they can not handle big data
============================================================================
three steps of this model : 1) graph partition 2) dynamic graph embedding 3) graph aggregation
contributions:
1) divide edges into non-overlapping subgraphs
2) distributed sugraphs adaptively update the embedded vectors with incoming edges
3) contruct a distrubuted big-data real-time processing platform to evaluate our model
==============================================================================
model :
![]() : directed link from vertex vi to vj , weight wij
: directed link from vertex vi to vj , weight wij
optimization : ![]() (1)
(1)
![]() are the embedded vectors for vi and vj
are the embedded vectors for vi and vj
s( ) is the predifined similarity function (this paper use the function defined in LINE , first-order and second-order proximity)
================================================================================================
problem formulation :
1) first-order similarity : 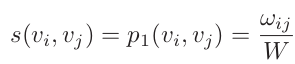 (2) W : the total weight of edges
(2) W : the total weight of edges
after mebedding : 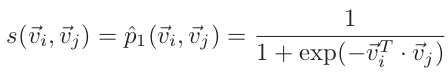 (3)
(3)
d( ) is the KL distance (1) can be written as : ![]() (4)
(4)
plug (2) (3) into (4) and apply KL distance : 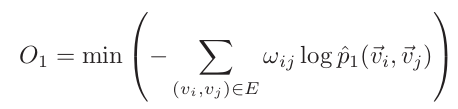 (5) ???????
(5) ???????
KL distance : https://www.cnblogs.com/ywl925/p/3554502.html
2) second-order similarity :

![]() N(vi) : vi's neighborhood
N(vi) : vi's neighborhood
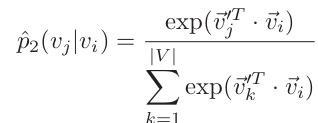 0
0
(1) can be written as : 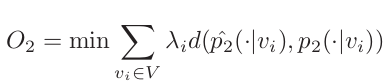
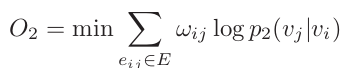
===============================================================================================
graph parittion :
1) initially, all K subgraphs are open will be closed, if its capacity is reached (maximal number of edges)
2)an incomming edge e=(u,v) will be assigned to the subgraph who has the minimal weight among all subgraphs containing vertex u or v
3) te is defined to balance the number of edges : ![]()
===============================================================================================
dynamic graph embedding :
for a vertex :
1) positive samples : vertices directly connected to it
2) negative samples : without direct connections to it
the optimization problem become :
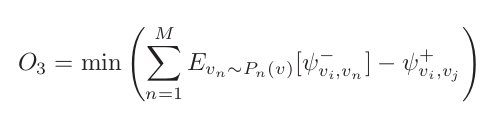
where : ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
f(v) the weight sum of the selected negative samples ![]()
α is the smoothing parameter
未完 待续。。。





















 1318
1318











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








