11、题目要求
写一个脚本实现如下功能: 输入一个数字,然后运行对应的一个命令。
显示命令如下:
*cmd meau** 1 - date 2 - ls 3 - who 4 - pwd 当输入1时,会运行date, 输入2时运行ls, 以此类推。
核心要点
- case判断
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
echo "*cmd meau** 1 - date 2 - ls 3 - who 4 - pwd"
read -p "Please input a number: " n
if [ -z "$n" ]
then
echo "请输入一个纯数字,范围1-4."
exit
fi
n1=`echo $n|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`
if [ -n "$n1" ]
then
echo "请输入一个纯数字,范围1-4."
exit
fi
case $n in
1)
date
;;
2)
ls
;;
3)
who
;;
4)
pwd
;;
*)
echo "请输入1-4的数字"
;;
esac
注意 :
使用 -n "$n"判断一个变量是否为空
当一个数字 -z "$n" 为1时,输出1的指定命令
12、题目要求
用shell脚本实现如下需求:
添加user_00 – user_09 10个用户,并且给他们设置一个随机密码,密码要求10位包含大小写字母以及数字,注意需要把每个用户的密码记录到一个日志文件里。 提示:
-
随机密码使用命令 mkpasswd
-
在脚本中给用户设置密码,可以使用echo 然后管道passwd命令
核心要点
- seq实现数字递增
- mkpasswd产生随机字符
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
for i in `seq -w 00 09`
do
useradd user_$i
p=`mkpasswd -l 10 -s 0 `
echo "user_$i $p" >> /tmp/pass.tmp
echo $p |passwd --stdin user_$i
done注意 :
seq -w 00 09 #查找00到09之间的数字
mkpasswd -l 10 -s 0 #生成随机密码要求10位包含大小写字母以及数字
# echo "asdhdkjhakushd kjhskjd" | passwd --stdin user1 # 更新用户user的密码
使用命令 tail /etc/passwd 查看用户的随机密码,有没有生成。
使用命令 cat /tmp/pass.tmp 查看用户的随机密码,有没有生成。
在另一台机器上,测试用户的随机密码能不能登录
#ssh user_00@aming
password :输入密码
然后删除创建的用户的随机密码
# for i in 'seq -w 00 09 '; do userdel -r user_$i; done
使用命令 tail /etc/passwd 查看密码有没有删除成功
13、题目要求
在服务器上,写一个监控脚本,要求如下:
-
每隔10s去检测一次服务器上的httpd进程数,如果大于等于500的时候,就需要自动重启一下apache服务,并检测启动是否成功?
-
若没有正常启动还需再一次启动,最大不成功数超过5次则需要立即发邮件通知管理员,并且以后不需要再检测!
-
如果启动成功后,1分钟后再次检测httpd进程数,若正常则重复之前操作(每隔10s检测一次),若还是大于等于500,那放弃重启并需要发邮件给管理员,然后自动退出该脚本。假设其中发邮件脚本为之前使用的mail.py
核心要点
- pgrep -l httpd或者ps -C httpd --no-heading检查进程
- for循环5次计数器
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
check_service()
{
n=0
for i in `seq 1 5`
do
/usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl restart 2>/tmp/apache.err
if [ $? -ne 0 ]
then
n=$[$n+1]
else
break
fi
done
if [ $n -eq 5 ]
then
##下面的mail.py参考https://coding.net/u/aminglinux/p/aminglinux-book/git/blob/master/D22Z/mail.py
python mai.py "123@qq.com" "httpd service down" `cat /tmp/apache.err`
exit
fi
}
while true
do
t_n=`ps -C httpd --no-heading |wc -l`
if [ $t_n -ge 500 ]
then
/usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl restart
if [ $? -ne 0 ]
then
check_service
fi
sleep 60
t_n=`ps -C httpd --no-heading |wc -l`
if [ $t_n -ge 500 ]
then
python mai.py "123@qq.com" "httpd service somth wrong" "the httpd process is busy."
exit
fi
fi
sleep 10
done注意 :
!$? -ne 0 # 表示输出的结果不等于0,
$n -eq 5 # 表示输出的结果等于5,表示重启不成功,发邮件给管理员。
/usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl restart 2>/tmp/apache.err #如果进程数为0 ,就重启,否则就输出到/tmp/apache.err 日志文件中
ps -C httpd --no-heading |wc -l` #统计进程数量
$t_n -ge 500 #如果apache重启一分钟后进程数,仍大于500,启动check_service,就登录服务器查看问题
14、题目要求
需求: 根据web服务器上的访问日志,把一些请求量非常高的ip给拒绝掉!并且每隔半小时把不再发起请求或者请求量很小的ip给解封。 假设:
-
一分钟内请求量高于100次的IP视为不正常请求。
-
访问日志路径为/data/logs/access_log。
用第2例中的1.log作为演示日志
核心要点
- 统计ip访问次数,排序
- 如何标记每隔半小时
- iptables计数器是一个重要的判断指标
- 函数(封IP、解封IP)
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
block_ip()
{
t1=`date -d "-1 min" +%Y:%H:%M`
log=/data/logs/access_log
egrep "$t1:[0-9]+" $log > /tmp/tmp_last_min.log
awk '{print $1}' /tmp/tmp_last_min.log |sort -n |uniq -c|sort -n |awk '$1>100 {print $2}' > /tmp/bad_ip.list
n=`wc -l /tmp/bad_ip.list|awk '{print $1}'`
if [ $n -ne 0 ]
then
for ip in `cat /tmp/bad_ip.list`
do
iptables -I INPUT -s $ip -j REJECT
done
fi
}
unblock_ip()
{
iptables -nvL INPUT|sed '1d' |awk '$1<5 {print $8}' > /tmp/good_ip.list
n=`wc -l /tmp/good_ip.list|awk '{print $1}'`
if [ $n -ne 0 ]
then
for ip in `cat /tmp/good_ip.list`
do
iptables -D INPUT -s $ip -j REJECT
done
fi
iptables -Z
}
t=`date +%M`
if [ $t == "00" ] || [ $t == "30" ]
then
unblock_ip
block_ip
else
block_ip
fi
注意 :
使用命令 :head 1.log 查看日志的内容
grep 2018:02:12:[0-9]+ 1.log #查看2018年的日志
实例 :
# t1='date -d "-1 min" +%Y:%H:%M' #指定一个变量
# echo $t1 #上一分钟,用变量的形式表示出来,
2019:12:12
# egrep "$t1:[0-9]+" 1.log # 截取出来1.log日志中上一分钟,所有的日志,
注意 :egrep 使用变量,使用双引号
sort -n |uniq -c|sort -n #表示排序,去重复,在排序
awk '$1>100 {print $2}' > /tmp/bad_ip.list #大于100的,写入/tmp/bad_ip.list中去
iptables -I INPUT -s $ip -j REJECT #把一些请求量非常高的ip给拒绝掉!
iptables -nvL INPUT|sed '1d' |awk '$1<5 {print $8}' > /tmp/good_ip.list #符合条件的IP,写入到/tmp/good_ip.list 文件中
#sed '1d' #过滤掉iptables -nvL INPU显示出来的 第一行
#print $8 #表示iptables -nvL INPU显示出来的,第八列,$8表示显示出来的IP地址
# iptbales -nvL INPUT #查看封掉的IP

# iptbales -Z INPUT #INPUT链里面的所有规则清空,重新计数。
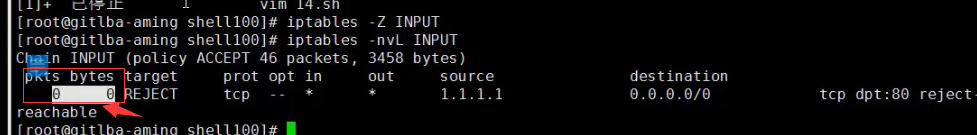
查看时间,22分钟之前的时间点
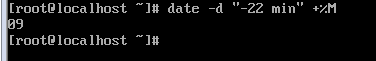
[ $t == "00" ] || [ $t == "30" ] #表示当时间为00分钟或者30分钟时,执行一次解封脚本。
15、题目要求
请仔细查看如下几个数字的规律,并使用shell脚本输出后面的十个数字。
10 31 53 77 105 141 …….
核心要点
- 计算两个数值之间的差值
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
x=10
y=21
for i in `seq 0 15`
do
echo $x
x=$[$x+$y]
z=$[2**$i]
y=$[$y+$z]
done
案例 :
# for i in 'seq 0 3'; do z=$[2**$i]; echo $z; done
1
2
4
8
# y=21; for i in 'seq 0 3'; do echo $y; z=$[2**$i]; y=$[$y+$z]; done
21
22
24
28
# x=10; y=21; for i in 'seq 0 3'; do echo $y; z=$[2**$i]; y=$[$y+$z]; done
10
31
53
z=$[2**$i] #表示2的$i次方
16、题目要求
写个shell,看看你的Linux系统中是否有自定义用户(普通用户),若是有,一共有几个?
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
v=`awk -F 'release ' '{print $2}' /etc/redhat-release |cut -d '.' -f1`
user()
{
if [ $1 -eq 0 ]
then
echo "系统没有自定义的用户"
else
echo "系统存在自定义用户,有$1个"
fi
}
case $v in
5|6)
n=`awk -F ':' '$3>=500' /etc/passwd|wc -l`
user $n
;;
7)
n=`awk -F ':' '$3>=1000' /etc/passwd|wc -l`
user $n
;;
*)
echo "脚本出错."
;;
esac
案例 :
# cat /etc/redhat-release #查看系统版本
CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core)
# awk -F 'release' '{print $2}' /etc/redhat-release
7.4.1708 (Core)
# awk -F ':' '$3 >=500' /etc/passwd #查看大于500的自定义用户的个数
注意 :5,6,7代表的是得到的用户的个数结果是5,6,7,如果不是,表示脚本出错
17、题目要求
写一个shell脚本,检测所有磁盘分区使用率和inode使用率并记录到以当天日期为命名的日志文件里,当发现某个分区容量或者inode使用量大于85%时,发邮件通知你自己。
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
dir=/tmp/disk
d=`date +%F`
mail=123@123.com
[ -d $dir ] || mkdir $dir
df >> $dir/$d.log
df -i >> $dir/$d.log
df|sed '1d' |awk -F ' +|%' '$5>=85 {print $7}' > $dir/df.tmp
df -i|sed '1d' |awk -F ' +|%' '$5>=85 {print $7}' > $dir/df_i.tmp
n1=`wc -l $dir/df.tmp|awk '{print $1}'`
n2=`wc -l $dir/df_i.tmp|awk '{print $1}'`
tag=0
if [ $n1 -gt 0 ]
then
if [ $n2 -gt 0 ]
then
tag=11
else
tag=10
fi
else
if [ $n2 -gt 0 ]
then
tag=01
else
tag=00
fi
fi
case $tag in
11)
python mail.py $mail "磁盘空间和inode使用率高于85%" "`cat $dir/df.tmp $dir/df_i.tmp|xargs`"
;;
10)
python mail.py $mail "磁盘空间使用率高于85%" "`cat $dir/df.tmp|xargs`"
;;
01)
python mail.py $mail "磁盘inode使用率高于85%" "`cat $dir/df_i.tmp|xargs`"
;;
*)
;;
esac
实例 :
# df #查看的是空间使用量
# df -i #查看的是inode使用率
# df | awk '{print $5}' #查看df显示出来的,第五段信息磁盘使用率
# df | awk '{print $5}' |sed 's/%//' #查看df显示出来的,第五段信息磁盘使用率,去掉百分号;df | awk '{print $5}' |sed 's/[%.]//' 同一个意思
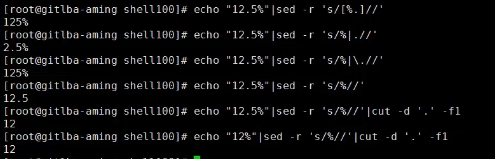
# df |sed '1d' | awk -F ' +|%' '$5<=85 {print $6}' #显示并打印出第六列,使用率大于85%的磁盘
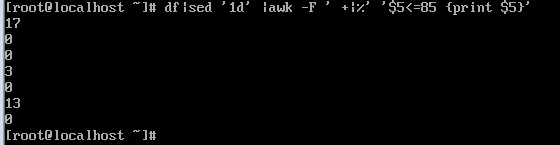
$n1 -gt 0 #当$n1等于0时,使用率大于等于85%,发邮件。
n2 -gt 0 #当$n2等于0时,innode大于等于85%,发邮件。
18、题目要求
有一台服务器作为web应用,有一个目录(/data/web/attachment)不定时地会被用户上传新的文件,但是不知道什么时候会上传。所以,需要我们每5分钟做一次检测是否有新文件生成。
请写一个shell脚本去完成检测。检测完成后若是有新文件,还需要将新文件的列表输出到一个按年、月、日、时、分为名字的日志里。
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
basedir=/data/web/attachment
t=`date +%Y%m%d%H%M`
find $basedir/ -type f -mmin -5 > /tmp/file.list
n=`wc -l /tmp/file.list|awk '{print $1}'`
if [ $n -lt 0 ]
then
mv /tmp/file.list /tmp/$t.list
fi
案例 :
find $basedir/ -type f -mmin -5 > /tmp/file.list #小于5分钟生成的新文件写入到 /tmp/file.list 文件中去 。
$n -lt 0 #如果大于零的,把文件移到/tmp/file.list /tmp/$t.list文件中去
19、题目要求
写一个shell脚本来看看你使用最多的命令是哪些,列出你最常用的命令top10。
参考答案
cat ~/.bash_history |sort |uniq -c |sort -nr |head
20、题目要求
假如需要每小时都去执行一个脚本。在脚本中实现这样的功能,当时间是0点和12点时,需要将目录/data/log/下的文件全部清空,
注意只能清空文件内容而不能删除文件。而其他时间只需要统计一下每个文件的大小,一个文件一行,输出到一个按日期和时间为名字的日志里。
需要考虑/data/log/目录下的二级、三级、… 等子目录里面的文件。
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
dir=/tmp/log_stat
t=`date +%d%H`
t1=`date +%H`
logdir=/data/log
[ -d $dir ] || mkdir $dir
[ -f $dir/$t.log ] && rm -f $dir/$t.log
if [ $t == "00" -o $t1 == "12" ]
then
for f in `find $logdir/ -type f`
do
> $f
done
else
for f in `find $logdir/ -type f`
do
du -sh $f >> $dir/$t.log
done
fi
案例 :
先创建 目录
# mkdir -p /data/log/
再执行脚本
来源 : https://github.com/aminglinux/shell100/blob/master/11.md





















 349
349











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








