转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_26525215
本文源自【大学之旅_谙忆的博客】
这篇博客讲了AOP代理-通知的3种方式:
1、MethodBeforeAdvice-前置通知
2、AfterReturningAdvice-正常返回后通知
3、MethodInterceptor-环绕通知
【框架】[Spring]纯Java的方式实现AOP切面(拦截)技术
现在本篇博客再详细讲解一下ThrowsAdvice-异常通知。
顾明思议,就是被代理的原型对象出异常了,就会运行到实现此接口中的一个方法。
这个和AfterReturningAdvice互补哦。
被代理的类:
package cn.hncu.javaImpl;
public class Person {
public void run(){
System.out.println("我在run...");
}
public void run(int i){
System.out.println("我在run"+i+"...");
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
public void say(){
System.out.println("我在say...");
}
}
实现ThrowsAdvice的方法:
package cn.hncu.javaImpl;
import org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice;
public class ThrowException implements ThrowsAdvice{
public void afterThrowing(Exception e) throws Throwable{
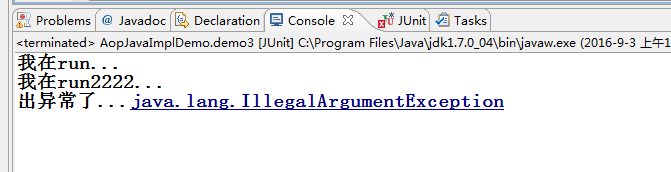
System.out.println("出异常了..."+e);
}
}运行的方法:
@Test
public void demo3(){
ProxyFactoryBean factory = new ProxyFactoryBean();
factory.setTarget(new Person());//给代理工厂一个原型对象
//切面 = 切点 + 通知
//切点
JdkRegexpMethodPointcut cut = new JdkRegexpMethodPointcut();
cut.setPatterns(new String[]{".*run.*",".*say.*"});//可以配置多个正则表达式
Advice throwsAdvice = new ThrowException();
//切面 = 切点 + 通知
Advisor throwsAdviceAdvisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(cut, throwsAdvice);
factory.addAdvisors(throwsAdviceAdvisor);
Person p2 = (Person) factory.getObject();//从代理工厂中获取一个代理后的对象
p2.run();
p2.run(2222);
}运行结果:
有几个需要注意的地方:
1、就是原型对象的异常不能抓!一旦抓取就无法运行afterThrowing。
也就是只有出异常了,且没被抓,才会运行这个方法。
2、不能在运行的方法中直接new ThrowsAdvice然后实现afterThrowing方法,这样因为出异常,线程挂了,也会无法运行这个afterThrowing方法。
也就是不能在测试的方法中直接:
Advice throwsAdvice = new ThrowsAdvice() {
public void afterThrowing(Exception e) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("出异常了..."+e);
}
};这样也无法实现原型对象处异常拦截。
ThrowsAdvice源代码分析:
直接看ThrowsAdvice接口的源代码:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2008 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.aop;
/**
* Tag interface for throws advice.
*
* <p>There are not any methods on this interface, as methods are invoked by
* reflection. Implementing classes must implement methods of the form:
*
* <pre class="code">void afterThrowing([Method, args, target], ThrowableSubclass);</pre>
*
* <p>Some examples of valid methods would be:
*
* <pre class="code">public void afterThrowing(Exception ex)</pre>
* <pre class="code">public void afterThrowing(RemoteException)</pre>
* <pre class="code">public void afterThrowing(Method method, Object[] args, Object target, Exception ex)</pre>
* <pre class="code">public void afterThrowing(Method method, Object[] args, Object target, ServletException ex)</pre>
*
* The first three arguments are optional, and only useful if we want further
* information about the joinpoint, as in AspectJ <b>after-throwing</b> advice.
*
* <p><b>Note:</b> If a throws-advice method throws an exception itself, it will
* override the original exception (i.e. change the exception thrown to the user).
* The overriding exception will typically be a RuntimeException; this is compatible
* with any method signature. However, if a throws-advice method throws a checked
* exception, it will have to match the declared exceptions of the target method
* and is hence to some degree coupled to specific target method signatures.
* <b>Do not throw an undeclared checked exception that is incompatible with
* the target method's signature!</b>
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @see AfterReturningAdvice
* @see MethodBeforeAdvice
*/
public interface ThrowsAdvice extends AfterAdvice {
}
你会发现里面并没有一个抽象方法!也行会有小伙伴迷茫,那为什么我们要实现那个方法啊。
没办法,因为我们是用Spring的框架,Spring内部用类反射来匹配了的,实现这个接口必须要实现这4个方法中的一个:
public void afterThrowing(Exception ex)
public void afterThrowing(RemoteException)
public void afterThrowing(Method method, Object[] args, Object target, Exception ex)
public void afterThrowing(Method method, Object[] args, Object target, ServletException ex)它的源代码有解释的,英文好一点就能看懂啦。
至于为什么不直接在这个接口中写这4个抽象类,可能怕代码太冗余吧。
毕竟,我们实现这个接口,我们用到的方法只会有一个,而如果都被声明成抽象方法了,那么,用户实现接口也必须实现这4个方法,显得冗余了。
所以估计Spring就干脆定义成标识接口了吧。
本文章由[谙忆]编写, 所有权利保留。
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_26525215
本文源自【大学之旅_谙忆的博客】





















 615
615

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








