Installation of DNF
DNF in not available in the default repository of RHEL/CentOS 7. However Fedora 22 ships with DNF implemented officially.
To install DNF on RHEL/CentOS systems, you need to first install and enable epel-release repository.
# yum install epel-release
OR
# yum install epel-release -yThough it is not ethical to use ‘-y‘ with yum as it is recommended to see what is being installed in your system. However if this does not matter you much you may use ‘-y’ with yum to install everything automatically without user’s intervention.
Next, install DNF package using yum command from epel-release repository.
# yum install dnfAfter dnf installed successfully, it’s time to show you 27 practical usage of dnf commands with examples that will help you to manage packages in RPM based distribution easily and effectively.
1. Check DNF Version
Check the version of DNF installed on your System.
# dnf --version2. List Enabled DNF Repositories
The option ‘repolist‘ with dnf command, will display all enabled repositories under your system.
# dnf repolist3. List all Enabled and Disabled DNF Repositories
The option ‘repolist all‘ will print all the enabled/disabled repositories under your system.
# dnf repolist all4. List all Available and Installed Packages using DNF
The command “dnf list” will list all the available packages from all the repositories and installed packages on your Linux system.
# dnf list5. List all Installed Packages using DNF
While the “dnf list” command shows all the available/installed packages from all the repositories. However, you have the option to list only the installed packages using option “list installed” as shown below.
# dnf list installed6. List all Available Packages using DNF
Similarly, the “list available” option, will list all the packages available to be installed from all the enabled repositories.
# dnf list available7. Search for a Package using DNF
If incase, you’ve no idea about the package that you want install, in such situation you may use ‘search‘ option with dnf command to search for the package that matches the word or string (say nano).
# dnf search nano8. See what Provides a file/sub-package?
The dnf option “provides” find the name of the package that provides specific file/sub-package. For example, if you would like to find what provides ‘/bin/bash‘ on your system?
# dnf provides /bin/bash9. Get Details of a Package using DNF
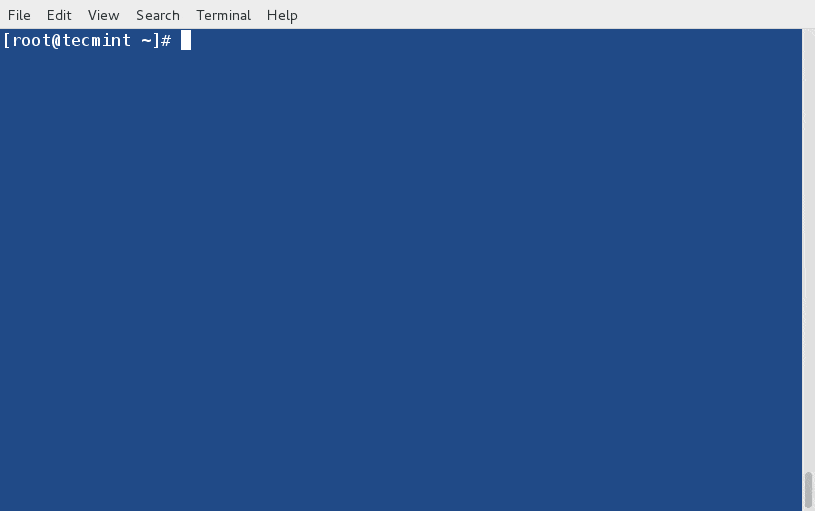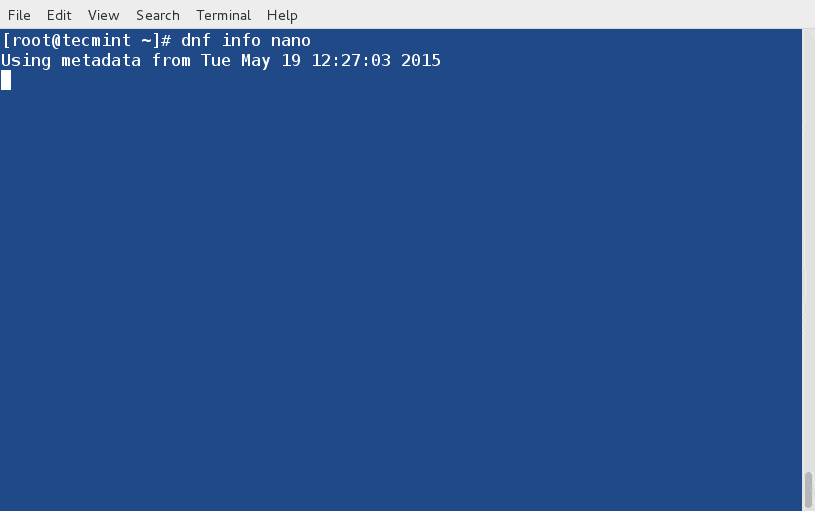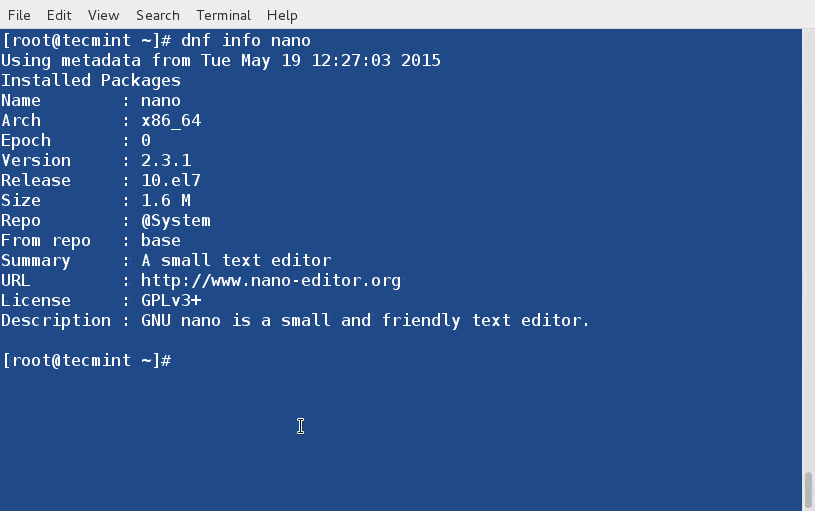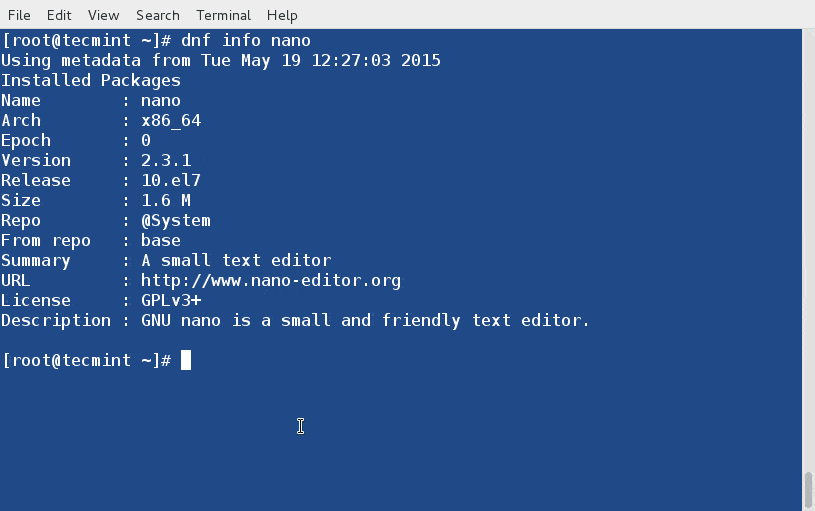
Let’s assume you want to know the information of a package before installing it on the system, you may use “info” switch to get a detailed information about a package (say nano) as below.
# dnf info nano10. Install a Package with DNF
To install a package called nano, just run the below command it will automatically resolve and install all required dependencies for package nano.
# dnf install nano11. Updating a Package using DNF
You may update only a specific package (say systemd) and leave everything on the system untouched.
# dnf update systemd12. Check for System Updates using DNF
Check updates for all the system packages installed into the system simply as.
# dnf check-update13. Update All System Packages using DNF
You may update the whole system including all the installed packages with following commands.
# dnf update
OR
# dnf upgrade14. Remove/Erase a Package using DNF
To remove or erase any unwanted package (say nano), you may use “remove” or “erase” switch with dnf command to remove it.
# dnf remove nano
OR
# dnf erase nano15. Remove Orphan Packages using DNF
Those packages that were installed to satisfy dependency may be useless if not being used by other applications. To remove those orphan packages execute the below command.
# dnf autoremove16. Remove Cached Packages using DNF
A lot of time we encounter out-of-date headers and unfinished transactions which results into error while executing dnf. We may clean all the cached packages and headers containing remote package information simply by executing.
# dnf clean all17. Get Help on Specific DNF Command
You may get help of any specific dnf command (say clean) just by executing the below command.
# dnf help clean18. List all DNF Commands and Options
To list help on all available dnf commands and option simply type.
# dnf help19. View History of DNF
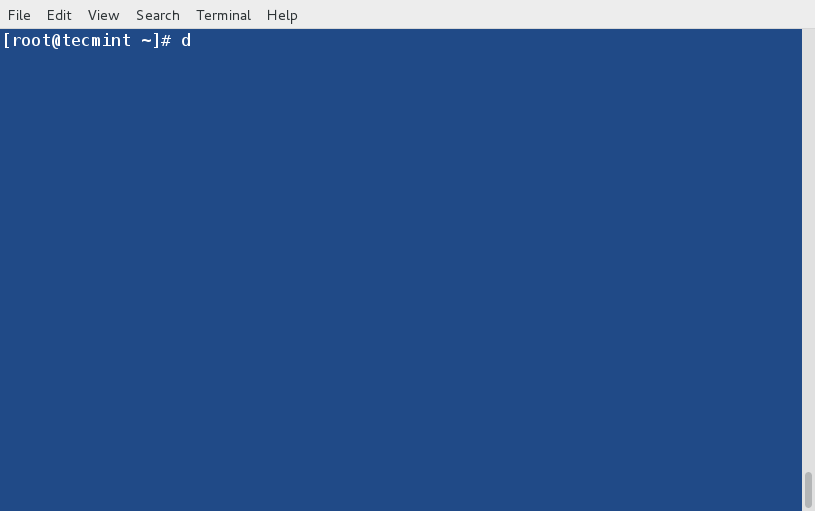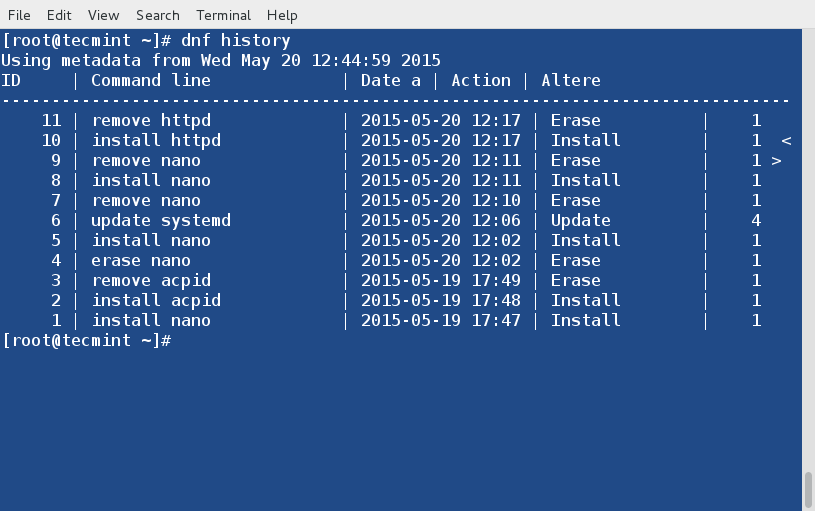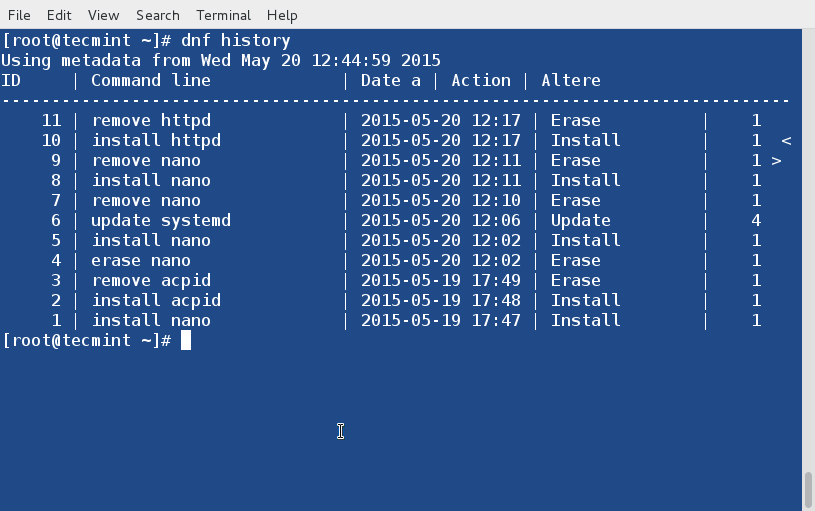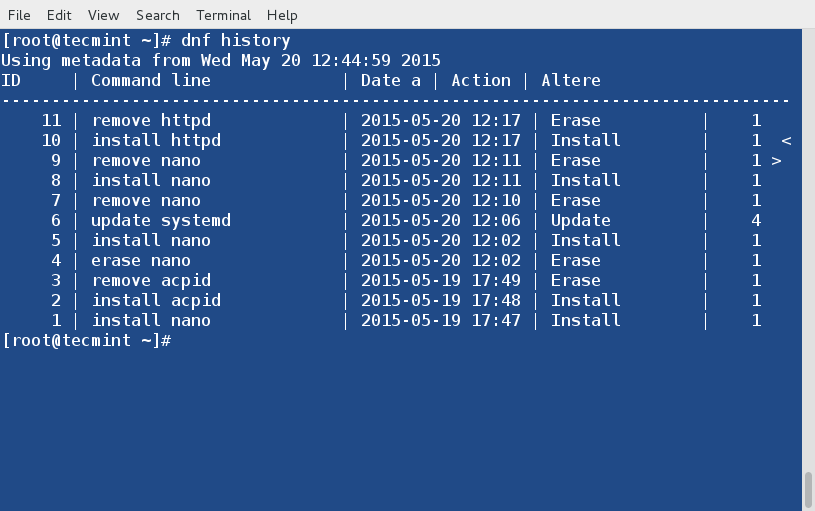
You may call dnf history to look at the list of already executed dnf commands. This way you can be aware of what was installed/removed with time stamp.
# dnf history20. List all Group Packages
The command “dnf grouplist” will print all available or installed packages, if nothing is mentioned, it will list all known groups.
# dnf grouplist21. Install a Group Package using DNF
To install a Group of packages bundled together as group package (say Educational Software) simply as.
# dnf groupinstall 'Educational Software'22. Update a Group Package
Let’s update a Group Package (say Educational Software) by executing the below command.
# dnf groupupdate 'Educational Software'23. Remove a Group Package
We can remove the group Package (say Educational Software) as.
# dnf groupremove 'Educational Software'24. Install a Package from Specific Repository
DNF makes it possible to install any specific package (say phpmyadmin) from a repo (epel) as simply as,
# dnf --enablerepo=epel install phpmyadmin25. Synchronize Installed Packages to Stable Release
The command “dnf distro-sync” will provides necessary options to synchronize all installed packages to most recent stable version available from any enabled repository. If no package is selected, all installed packages are synchronized.
# dnf distro-sync26. Reinstall a Package
The command “dnf reinstall nano” will reinstall an already installed package (say nano).
# dnf reinstall nano27. Downgrade a Package
The option “downgrade” will downgrades the named package (say acpid) to lower version if possible.
# dnf downgrade acpidSample Output
Using metadata from Wed May 20 12:44:59 2015
No match for available package: acpid-2.0.19-5.el7.x86_64
Error: Nothing to do.My observation: DNF does not downgraded the package as it is supposed to. It has also been reported as bug.
转自:http://www.tecmint.com/dnf-commands-for-fedora-rpm-package-management/














































 8681
8681

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








