Skia深入分析7——区域解码
1、概述
-当图片很大时,解码速度缓慢,占用内存很高,并且,当图片超过一定尺寸时,无法做纹理上传和显示(这跟GPU能力有关,一般的GPU是8192*8192)。这时只好做下采样,但会牺牲图片显示的质量。
-对于图库等需要清晰浏览图片的应用,不可能设置一个下采样率去解决这一问题,因此,Google加入了区域解码这个功能,使我们可以从原始的图片文件中,解出一部分区域完整的图片内容。
-区域解码的难点主要在于定位像素区域所对应的文件位置,这个需要图像编码时有一定的连续性,所幸,主流图像格式都是这样的。
-目前区域解码主要实现了png、jpeg、webp类型图片的支持。本篇过一下区域解码的框架,并介绍一下最常用的jpeg格式的区域解码实现。
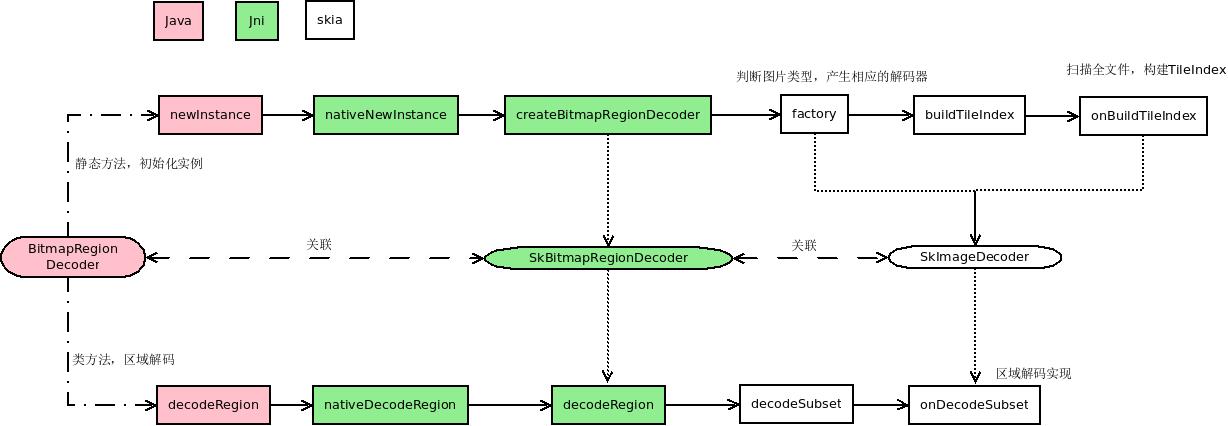
2、区域解码总流程
如图所示在Framework侧创建 BitmapRegionDecoder时,创建对应类型的SkImageDecoder扫描全文件,调用其onBuildTileIndex方法构建tileIndex,嵌入其关联的SkImageDecoder之中,在后续的 decodeRegion调用时,使用 SkImageDecoder的 onDecodeSubset 方法做区域解码。
3、Jpeg的区域解码
#ifdef SK_BUILD_FOR_ANDROID
bool SkJPEGImageDecoder::onBuildTileIndex(SkStreamRewindable* stream, int *width, int *height) {
SkAutoTDelete<SkJPEGImageIndex> imageIndex(SkNEW_ARGS(SkJPEGImageIndex, (stream, this)));
jpeg_decompress_struct* cinfo = imageIndex->cinfo();
skjpeg_error_mgr sk_err;
set_error_mgr(cinfo, &sk_err);
// All objects need to be instantiated before this setjmp call so that
// they will be cleaned up properly if an error occurs.
if (setjmp(sk_err.fJmpBuf)) {
return false;
}
// create the cinfo used to create/build the huffmanIndex
if (!imageIndex->initializeInfoAndReadHeader()) {
return false;
}
if (!imageIndex->buildHuffmanIndex()) {
return false;
}
// destroy the cinfo used to create/build the huffman index
imageIndex->destroyInfo();
// Init decoder to image decode mode
if (!imageIndex->initializeInfoAndReadHeader()) {
return false;
}
// FIXME: This sets cinfo->out_color_space, which we may change later
// based on the config in onDecodeSubset. This should be fine, since
// jpeg_init_read_tile_scanline will check out_color_space again after
// that change (when it calls jinit_color_deconverter).
(void) this->getBitmapColorType(cinfo);
turn_off_visual_optimizations(cinfo);
// instead of jpeg_start_decompress() we start a tiled decompress
if (!imageIndex->startTileDecompress()) {
return false;
}
SkASSERT(1 == cinfo->scale_num);
fImageWidth = cinfo->output_width;
fImageHeight = cinfo->output_height;
if (width) {
*width = fImageWidth;
}
if (height) {
*height = fImageHeight;
}
SkDELETE(fImageIndex);
fImageIndex = imageIndex.detach();
return true;
}
bool SkJPEGImageDecoder::onDecodeSubset(SkBitmap* bm, const SkIRect& region) {
if (NULL == fImageIndex) {
return false;
}
jpeg_decompress_struct* cinfo = fImageIndex->cinfo();
SkIRect rect = SkIRect::MakeWH(fImageWidth, fImageHeight);
if (!rect.intersect(region)) {
// If the requested region is entirely outside the image return false
return false;
}
skjpeg_error_mgr errorManager;
set_error_mgr(cinfo, &errorManager);
if (setjmp(errorManager.fJmpBuf)) {
return false;
}
int requestedSampleSize = this->getSampleSize();
cinfo->scale_denom = requestedSampleSize;
set_dct_method(*this, cinfo);
const SkColorType colorType = this->getBitmapColorType(cinfo);
adjust_out_color_space_and_dither(cinfo, colorType, *this);
int startX = rect.fLeft;
int startY = rect.fTop;
int width = rect.width();
int height = rect.height();
jpeg_init_read_tile_scanline(cinfo, fImageIndex->huffmanIndex(),
&startX, &startY, &width, &height);
int skiaSampleSize = recompute_sampleSize(requestedSampleSize, *cinfo);
int actualSampleSize = skiaSampleSize * (DCTSIZE / cinfo->min_DCT_scaled_size);
SkScaledBitmapSampler sampler(width, height, skiaSampleSize);
SkBitmap bitmap;
// Assume an A8 bitmap is not opaque to avoid the check of each
// individual pixel. It is very unlikely to be opaque, since
// an opaque A8 bitmap would not be very interesting.
// Otherwise, a jpeg image is opaque.
bitmap.setInfo(SkImageInfo::Make(sampler.scaledWidth(), sampler.scaledHeight(), colorType,
kAlpha_8_SkColorType == colorType ?
kPremul_SkAlphaType : kOpaque_SkAlphaType));
// Check ahead of time if the swap(dest, src) is possible or not.
// If yes, then we will stick to AllocPixelRef since it's cheaper with the
// swap happening. If no, then we will use alloc to allocate pixels to
// prevent garbage collection.
int w = rect.width() / actualSampleSize;
int h = rect.height() / actualSampleSize;
bool swapOnly = (rect == region) && bm->isNull() &&
(w == bitmap.width()) && (h == bitmap.height()) &&
((startX - rect.x()) / actualSampleSize == 0) &&
((startY - rect.y()) / actualSampleSize == 0);
if (swapOnly) {
if (!this->allocPixelRef(&bitmap, NULL)) {
return return_false(*cinfo, bitmap, "allocPixelRef");
}
} else {
if (!bitmap.allocPixels()) {
return return_false(*cinfo, bitmap, "allocPixels");
}
}
SkAutoLockPixels alp(bitmap);
#ifdef ANDROID_RGB
/* short-circuit the SkScaledBitmapSampler when possible, as this gives
a significant performance boost.
*/
if (skiaSampleSize == 1 &&
((kN32_SkColorType == colorType && cinfo->out_color_space == JCS_RGBA_8888) ||
(kRGB_565_SkColorType == colorType && cinfo->out_color_space == JCS_RGB_565)))
{
JSAMPLE* rowptr = (JSAMPLE*)bitmap.getPixels();
INT32 const bpr = bitmap.rowBytes();
int rowTotalCount = 0;
while (rowTotalCount < height) {
int rowCount = jpeg_read_tile_scanline(cinfo,
fImageIndex->huffmanIndex(),
&rowptr);
// if rowCount == 0, then we didn't get a scanline, so abort.
// onDecodeSubset() relies on onBuildTileIndex(), which
// needs a complete image to succeed.
if (0 == rowCount) {
return return_false(*cinfo, bitmap, "read_scanlines");
}
if (this->shouldCancelDecode()) {
return return_false(*cinfo, bitmap, "shouldCancelDecode");
}
rowTotalCount += rowCount;
rowptr += bpr;
}
if (swapOnly) {
bm->swap(bitmap);
} else {
cropBitmap(bm, &bitmap, actualSampleSize, region.x(), region.y(),
region.width(), region.height(), startX, startY);
}
return true;
}
#endif
// check for supported formats
SkScaledBitmapSampler::SrcConfig sc;
int srcBytesPerPixel;
if (!get_src_config(*cinfo, &sc, &srcBytesPerPixel)) {
return return_false(*cinfo, *bm, "jpeg colorspace");
}
if (!sampler.begin(&bitmap, sc, *this)) {
return return_false(*cinfo, bitmap, "sampler.begin");
}
SkAutoMalloc srcStorage(width * srcBytesPerPixel);
uint8_t* srcRow = (uint8_t*)srcStorage.get();
// Possibly skip initial rows [sampler.srcY0]
if (!skip_src_rows_tile(cinfo, fImageIndex->huffmanIndex(), srcRow, sampler.srcY0())) {
return return_false(*cinfo, bitmap, "skip rows");
}
// now loop through scanlines until y == bitmap->height() - 1
for (int y = 0;; y++) {
JSAMPLE* rowptr = (JSAMPLE*)srcRow;
int row_count = jpeg_read_tile_scanline(cinfo, fImageIndex->huffmanIndex(), &rowptr);
// if row_count == 0, then we didn't get a scanline, so abort.
// onDecodeSubset() relies on onBuildTileIndex(), which
// needs a complete image to succeed.
if (0 == row_count) {
return return_false(*cinfo, bitmap, "read_scanlines");
}
if (this->shouldCancelDecode()) {
return return_false(*cinfo, bitmap, "shouldCancelDecode");
}
if (JCS_CMYK == cinfo->out_color_space) {
convert_CMYK_to_RGB(srcRow, width);
}
sampler.next(srcRow);
if (bitmap.height() - 1 == y) {
// we're done
break;
}
if (!skip_src_rows_tile(cinfo, fImageIndex->huffmanIndex(), srcRow,
sampler.srcDY() - 1)) {
return return_false(*cinfo, bitmap, "skip rows");
}
}
if (swapOnly) {
bm->swap(bitmap);
} else {
cropBitmap(bm, &bitmap, actualSampleSize, region.x(), region.y(),
region.width(), region.height(), startX, startY);
}
return true;
}
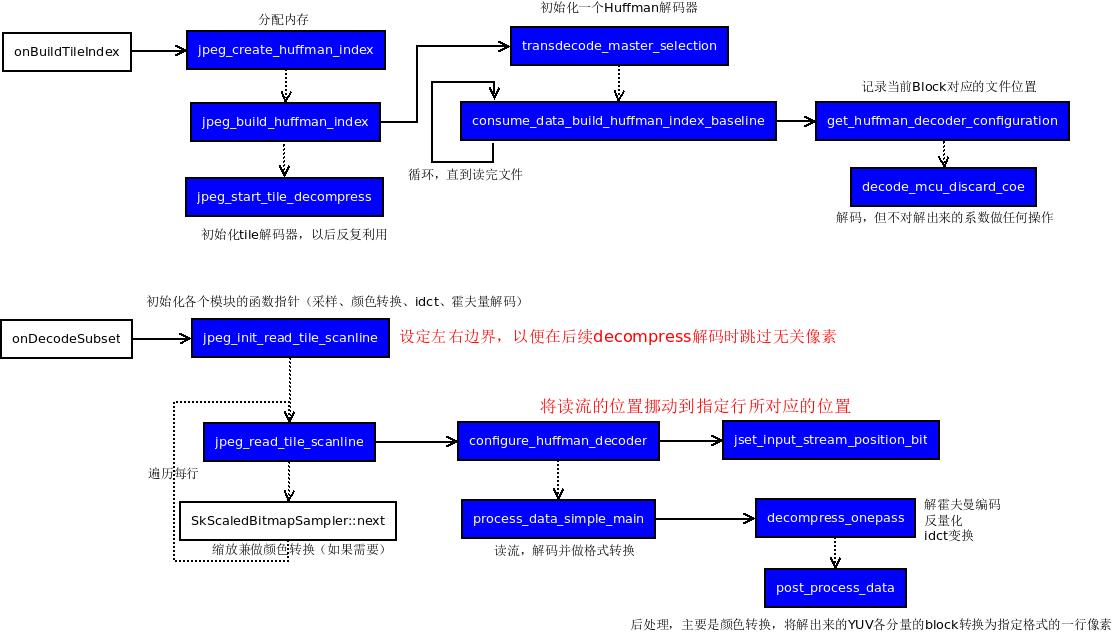
#endif在 onBuildTileIndex 时,创建了huffman_index,其中的内容主要是一系列的huffman_offset,记录每个block对应的偏移量。在解码时,先移到对应block的位置,然后解出像素。
GLOBAL(JDIMENSION)
jpeg_read_tile_scanline (j_decompress_ptr cinfo, huffman_index *index,
JSAMPARRAY scanlines)
{
// Calculates the boundary of iMCU
int lines_per_iMCU_row = cinfo->max_v_samp_factor * DCTSIZE;
int lines_per_iMCU_col = cinfo->max_h_samp_factor * DCTSIZE;
int sample_size = DCTSIZE / cinfo->min_DCT_scaled_size;
JDIMENSION row_ctr = 0;
if (cinfo->progressive_mode) {
(*cinfo->main->process_data) (cinfo, scanlines, &row_ctr, 1);
} else {
if (cinfo->output_scanline % (lines_per_iMCU_row / sample_size) == 0) {
// Set the read head to the next iMCU row
int iMCU_row_offset = cinfo->output_scanline /
(lines_per_iMCU_row / sample_size);
int offset_data_col_position = cinfo->coef->MCU_column_left_boundary /
index->MCU_sample_size;
huffman_offset_data offset_data =
index->scan[0].offset[iMCU_row_offset][offset_data_col_position];
(*cinfo->entropy->configure_huffman_decoder) (cinfo, offset_data);
}
(*cinfo->main->process_data) (cinfo, scanlines, &row_ctr, 1);
}
cinfo->output_scanline += row_ctr;
return row_ctr;
}






















 895
895

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








