一、说下HashMap中存储元素的基本原理
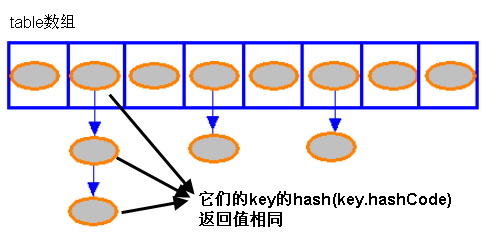
在 HashMap 中,是采用 Hash 算法来决定集合中元素的存储位置,当系统开始初始化 HashMap 时,系统会创建一个长度为 capacity(16) 的 Entry 数组,这个数组里可以存储元素的位置被称为“桶(bucket)”,每个 bucket 都有其指定索引,系统可以根据其索引快速访问该 bucket 里存储的元素。 无论何时,HashMap 的每个“桶”只存储一个元素(也就是一个 Entry),由于 Entry 对象可以包含一个引用变量(就是 Entry 构造器的的最后一个参数)用于指向下一个 Entry,因此可能出现的情况是:HashMap 的 bucket 中只有一个 Entry,但这个 Entry 指向另一个 Entry ——这就形成了一个 Entry 链,如下图所示:
二、HashMap的读取实现:
当 HashMap 的每个 bucket 里存储的 Entry 只是单个 Entry ——也就是没有通过指针产生 Entry 链时,此时的 HashMap 具有最好的性能:当程序通过 key 取出对应 value 时,系统只要先计算出该 key 的 hashCode() 返回值,在根据该 hashCode 返回值找出该 key 在 table 数组中的索引,然后取出该索引处的 Entry,最后返回该 key 对应的 value 即可。看 HashMap 类的 get(K key)方法代码:
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
/**
* Offloaded version of get() to look up null keys. Null keys map
* to index 0. This null case is split out into separate methods
* for the sake of performance in the two most commonly used
* operations (get and put), but incorporated with conditionals in
* others.
*/
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the
* HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for the key.
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}从源码中可以看出,如果 HashMap 的每个 bucket 里只有一个 Entry 时,HashMap 可以根据索引、快速地取出该 bucket 里的 Entry;在发生“Hash 冲突”的情况下,单个 bucket 里存储的不是一个 Entry,而是一个 Entry 链,系统只能必须按顺序遍历每个 Entry,直到找到想搜索的 Entry 为止——如果恰好要搜索的 Entry 位于该 Entry 链的最末端(该 Entry 是最早放入该 bucket 中),那系统必须循环到最后才能找到该元素。
三、说下HashMap的扩容原理
public class HashMap<K,V>extends AbstractMap<K,V>implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable1、HashMap 的实例有两个参数影响其性能:初始容量和加载因子--容量是哈希表中桶的数量,初始容量只是哈希表在创建时的容量;加载因子是哈希表在其容量自动增加之前可以达到多满的一种尺度。此实现假定哈希函数将元素适当地分布在各桶之间,可为基本操作(get 和 put)提供稳定的性能,迭代 collection 视图所需的时间与 HashMap 实例的“容量”(桶的数量)及其大小(键-值映射关系数)成比例,所以,如果迭代性能很重要,则不要将初始容量设置得太高(或将加载因子设置得太低)。当哈希表中的条目数超出了加载因子与当前容量的乘积时,则要对该哈希表进行 rehash 操作(即重建内部数据结构),从而哈希表将具有大约两倍的桶数。
2、通常,默认加载因子 (0.75) 在时间和空间成本上寻求一种折衷,加载因子过高虽然减少了空间开销,但同时也增加了查询成本(在大多数 HashMap 类的操作中,包括 get 和 put 操作,都反映了这一点),在设置初始容量时应该考虑到映射中所需的条目数及其加载因子,以便最大限度地减少 rehash 操作次数,如果初始容量大于最大条目数除以加载因子,则不会发生 rehash 操作,如果很多映射关系要存储在 HashMap 实例中,则相对于按需执行自动的 rehash 操作以增大表的容量来说,使用足够大的初始容量创建它将使得映射关系能更有效地存储。 new HashMap()构造一个具有默认初始容量 (16) 和默认加载因子 (0.75) 的空 HashMap。
建议:如果能明确数据的个数:初始容量就比较好办,如果无法明确,那么要考虑他的每次增长是*2






















 1906
1906

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








