java的注解处理器类主要是AnnotatedElement接口的实现类实现,为位于java.lang.reflect包下。由下面的class源码可知AnnotatedElement接口是所有元素的父接口,这时我们通过反射获得一个类的AnnotatedElement对象后,就可以通过下面表格的几个方法,访问Annotation信息。
public final class Class<T> implements java.io.Serializable, GenericDeclaration, Type, AnnotatedElement {
总结AnnotatedElement的常用方法 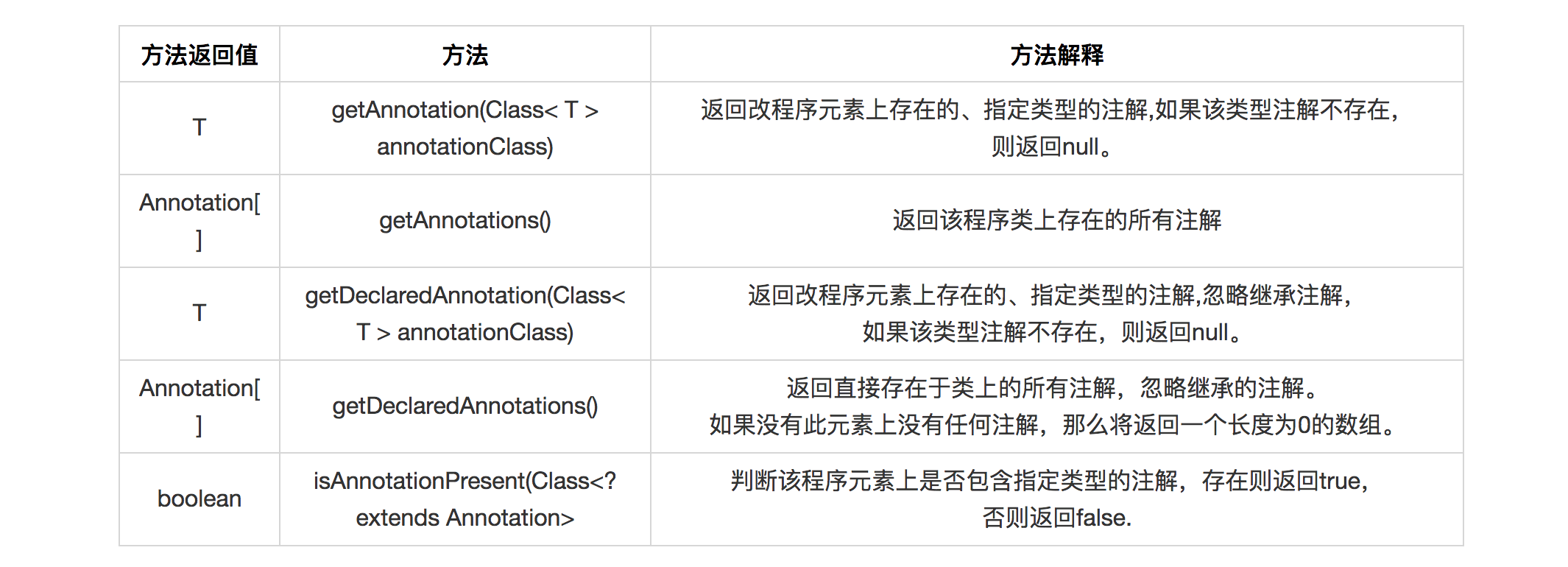
注意:getDeclaredAnnotations和getAnnotations得到的都是当前类上面所有的注解(不包括方法上注解和属性上注解),不同的是,前者不包括继承的。而getAnnotations得到的是包括继承的所有注解。
注解处理器使用示例
新建自定注解@ReqMapping
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Description:
* Created by gaowei on 2018/1/3.
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ReqMapping {
ReqMethod [] method() default {};
String[] val() default "";
}
新建一个枚举类
public enum ReqMethod {
GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, TRACE
}
新建自定义注解@ReqValue
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Description:
* Created by gaowei on 2018/1/4.
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ReqValue {
String value1() default "";
String value2() default "";
}
使用自定义注解
@ReqMapping(method = ReqMethod.POST,val = "类")
public class User {
@ReqValue(value1 = "张三")
private String userName;
@ReqValue(value2 = "密码")
private String pswd;
@ReqMapping(method = ReqMethod.GET)
public void get(){
}
@ReqMapping(method = ReqMethod.POST)
public void post(){
}
@ReqMapping(val={"a","b"})
public void other(){
}
}
注解处理器测试
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Description:
* Created by gaowei on 2018/1/2.
*/
public class TestAnnotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<User> clazz = User.class;
//获得clazz(User)里面所有方法信息
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
//获得clazz(User)里面所有属性信息
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
System.out.println("methods注解个数:"+methods.length);
System.out.println("declaredFields注解个数:"+declaredFields.length);
//遍历循环所有方法信息
for (Method method : methods) {
//判断method是否含有指定元素的注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(ReqMapping.class)) {
//返回当前方法上的注解对象
ReqMapping reqMapping = method.getAnnotation(ReqMapping.class);
//获得注解的值
System.out.println("方法注解值:"+reqMapping.method());
//如果一个注解有多个值,通过遍历取出(特别注意:reqMapping.val(),这个val()是你定义注解的成员)
String[] values = reqMapping.val();
for (String value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
//获得类里面所有方法的注解信息
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
if(declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(ReqValue.class)){
ReqValue reqValue = declaredField.getAnnotation(ReqValue.class);
System.out.println("属性注解值:"+reqValue.value1());
System.out.println("属性注解值:"+reqValue.value2());
}
}
//获得类上的所有注解
Annotation[] declaredAnnotations = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotations();
for (Annotation declaredAnnotation : declaredAnnotations) {
System.out.println("类注解值:"+ declaredAnnotation);
}
}
}
其他博文
深入理解Java自定义注解(一):入门:https://my.oschina.net/itgaowei/blog/1600525
深入理解Java自定义注解(二)-使用自定义注解:https://my.oschina.net/itgaowei/blog/1602277






















 8142
8142

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








