一、前言说明
今天看到微信群里一道六年级数学题,如下图,求阴影部分面积

看起来似乎并不是很难,可是博主添加各种辅助线,写各种方法都没出来,不得已而改用写Python代码来求面积了
二、思路介绍
1.用Python将上图画在坐标轴上,主要是斜线函数和半圆函数

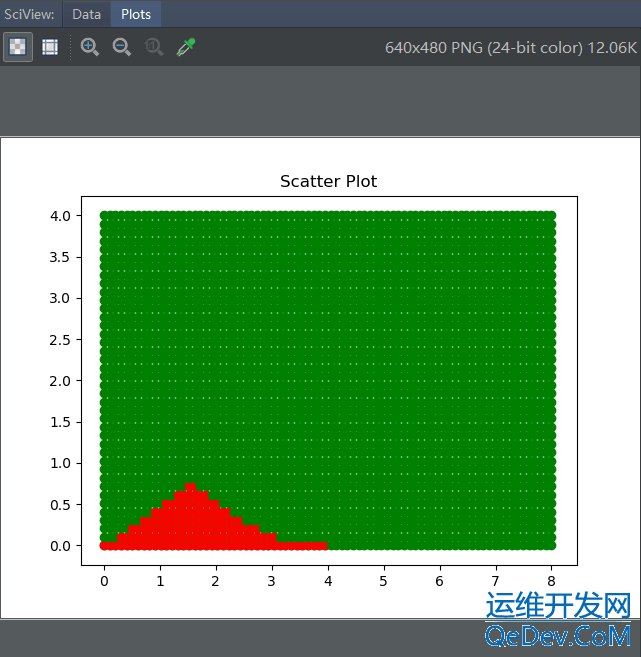
2.均匀的在长方形上面洒满豆子(假设是豆子),求阴影部分豆子占比*总面积
三、源码设计
1.做图源码
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def init():
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
fig = plt.gcf()
fig.set_facecolor('lightyellow')
fig.set_edgecolor("black")
ax = plt.gca()
ax.patch.set_facecolor("lightgray") # 设置ax区域背景颜色
ax.patch.set_alpha(0.1) # 设置ax区域背景颜色透明度
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
# 原下半函数
def f1(px, r, a, b):
return b - np.sqrt(r**2 - (px - a)**2)
# 斜线函数
def f2(px, m, n):
return px*n/m
# 斜线函数2
def f3(px, m, n):
return n-1*px*n/m
if __name__ == '__main__':
r = 4 # 圆半径
m = 8 # 宽
n = 4 # 高
a, b = (4, 4) # 圆心坐标
init()
x = np.linspace(0, m, 100*m)
y = np.linspace(0, n, 100*n)
# 半圆形
y1 = f1(x, r, a, b)
plt.plot(x, y1)
# 矩形横线
plt.plot((x.min(), x.max()), (y.min(), y.min()), 'g')
plt.plot((x.min(), x.max()), (y.max(), y.max()), 'g')
plt.plot((x.max(), x.max()), (y.max()+2, y.max()+2), 'g') # 画点(8,6)避免图形变形
# 矩形纵向
plt.plot((x.min(), x.min()), (y.min(), y.max()), 'g')
plt.plot((x.max(), x.max()), (y.min(), y.max()), 'g')
# 斜线方法
y2 = f2(x, m, n)
plt.plot(x, y2, 'purple')
# 阴影部分填充
xf = x[np.where(x <= 0.5*x.max())]
plt.fill_between(xf, y.min(), f1(xf, r, a, b), where=f1(xf, r, a, b) <= f2(xf, m, n),
facecolor='y', interpolate=True)
plt.fill_between(xf, y.min(), f2(xf, m, n), where=f1(xf, r, a, b) > f2(xf, m, n),
facecolor='y', interpolate=True)
# 半圆填充
plt.fill_between(x, y1, y.max(), facecolor='r', alpha=0.25)
plt.show()
Draw.py
2.计算源码,其中side是要不要计算图形边框上的点,理论上side只能为True;t设置越大运行时间越长也越精准
import numpy as np
def f1(px, r, a, b):
return b - np.sqrt(r**2 - (px - a)**2)
def f2(px, m, n):
return px*n/m
if __name__ == '__main__':
r = 4 # 圆半径
m = 8 # 宽
n = 4 # 高
a, b = (4, 4) # 圆心坐标
t = 100 # 精度
xs = np.linspace(0, m, 2*t*m)
ys = np.linspace(0, n, t*n)
# 半圆形
y1 = f1(xs, r, a, b)
# 斜线
y2 = f2(xs, m, n)
numin = 0
numtotel = 0
side = True # 是否计算边框
for x in xs:
for y in ys:
if not side:
if (x <= 0) | (x >= 8) | (y <= 0) | (y >= 4):
continue
numtotel += 1
if x >= 4:
continue
y1 = f1(x, r, a, b)
y2 = f2(x, m, n)
if y1 - y2 >= 0:
if y2 - y > 0:
numin += 1
if (y2 - y == 0) and side:
numin += 1
elif y2 - y1 > 0:
if y1 - y > 0:
numin += 1
if (y2 - y == 0) and side:
numin += 1
print(32*numin/numtotel)
calc.py
四、最后小结
1.此种算法t为100时,阴影面积为1.268;t为1000时,阴影面积为1.253,已经非常接近正确答案(正确答案1.252)
2.举一反三,类似于这种不规则的面积,只要可以写出来函数,就可以求解面积.
2.下面有三种求解方法,第三种表示比大学高数还难看懂,你们呢?
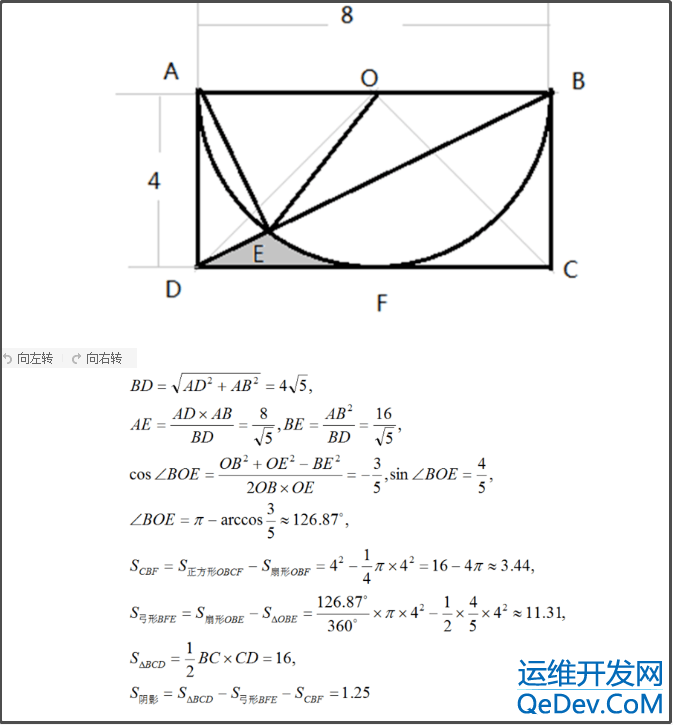

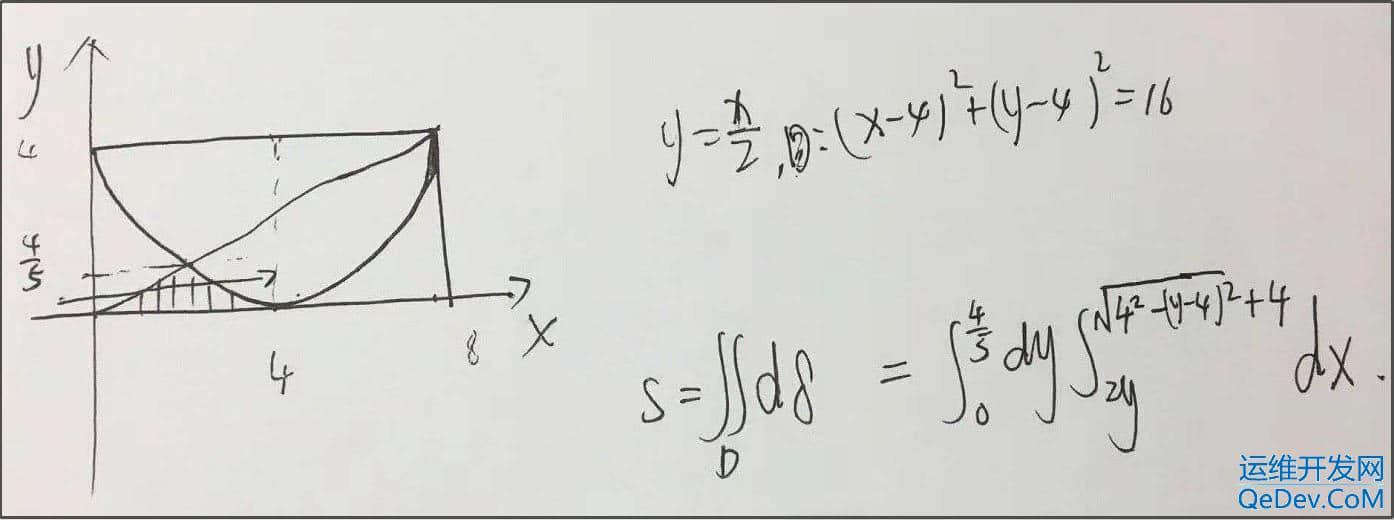
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对我们的支持。





















 1814
1814











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








