一、原理流程
1、用java代码控制事务,本质上就是利用数据库本身的事务,有可能是JDBC,也有可能是JTA、JMS。先不管,反正是用了别人的连接。
2、AOP,切面增强,生成代理对象来进行事务的控制
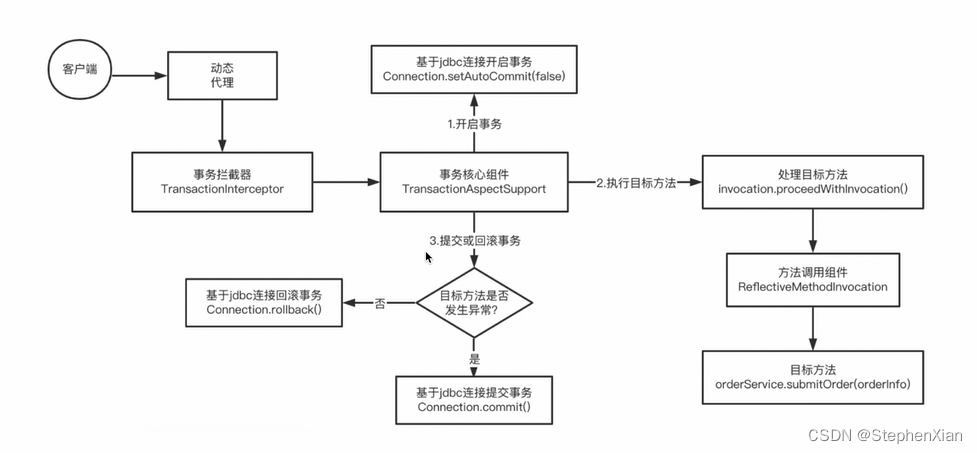
二、源码解读分析
先不管动态代理这一部分是怎么实现的。
读取@Transaction注解上的元信息,生成一个TransactionAttribute
总之会获取到注解上的信息,然后将生成代理对象,用反射的代理对象,增强目标方法
TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser类里面获取到一个很重要的类TransactionInterceptor
@Override
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return TransactionInterceptor.class;
}
TransactionInterceptor 继承自TransactionAspectSupport,并且实现了AOP的MethodInterceptor,需要方法调用invoke方法。
public class TransactionInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
重点就是在 invokeWithinTransaction方法里面藏着事务控制的方法,会尝试获取事务的一些属性信息,判断事务是否开启,如果没有开启,那么就会执行createTransactionIfNecessary方法,而诸如事务的传播属性判断之类的就是在createTransactionIfNecessary之中,
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
//获取到transaction attribute
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
//这里面开启事务
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
//执行目标方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
//如果事务存在,那么就执行该事务
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
return invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
}
}
关注status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager中的getTransaction包含着事务的属性设置等诸多内容
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException {
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
// Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks.
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (definition == null) {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
}
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition);
}
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
doBegin(transaction, definition);
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + definition);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
doBegin(transaction, definition);这个方法就是连接数据库,用数据库的或者orm框架的连接来做事务控制,如JMS,JPA,Heibernate,JDBC
下面是JDBC的dobegin方法
@Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try {
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
}
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,
// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
// configured the connection pool to set it already).
if (con.getAutoCommit()) {
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
}
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
// Bind the connection holder to the thread.
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
}
}
三、具体使用
| 属性名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| name | 当在配置文件中有多个 TransactionManager , 可以用该属性指定选择哪个事务管理器。 |
| propagation | 事务的传播行为,默认值为 REQUIRED |
| isolation | 事务的隔离度,默认值采用 DEFAULT |
| timeout | 事务的超时时间,默认值为-1。如果超过该时间限制但事务还没有完成,则自动回滚事务 |
| read-only | 指定事务是否为只读事务,默认值为 false;为了忽略那些不需要事务的方法,比如读取数据,可以设置 read-only 为 true |
| rollback-for | 用于指定能够触发事务回滚的异常类型,如果有多个异常类型需要指定,各类型之间可以通过逗号分隔 |
| no-rollback- for | 抛出 no-rollback-for 指定的异常类型,不回滚事务 |
因此使用的时候,一般是用声明式事务,指定相应的参数
事务隔离级别
隔离级别是指若干个并发的事务之间的隔离程度。TransactionDefinition 接口中定义了五个表示隔离级别的常量:
TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT:这是默认值,表示使用底层数据库的默认隔离级别。对大部分数据库而言,通常这值就是TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED。
TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED:该隔离级别表示一个事务可以读取另一个事务修改但还没有提交的数据。该级别不能防止脏读,不可重复读和幻读,因此很少使用该隔离级别。比如PostgreSQL实际上并没有此级别。
TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED:该隔离级别表示一个事务只能读取另一个事务已经提交的数据。该级别可以防止脏读,这也是大多数情况下的推荐值。
TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ:该隔离级别表示一个事务在整个过程中可以多次重复执行某个查询,并且每次返回的记录都相同。该级别可以防止脏读和不可重复读。
TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE:所有的事务依次逐个执行,这样事务之间就完全不可能产生干扰,也就是说,该级别可以防止脏读、不可重复读以及幻读。但是这将严重影响程序的性能。通常情况下也不会用到该级别。
事务传播行为
所谓事务的传播行为是指,如果在开始当前事务之前,一个事务上下文已经存在,此时有若干选项可以指定一个事务性方法的执行行为。在TransactionDefinition定义中包括了如下几个表示传播行为的常量:
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则创建一个新的事务。这是默认值。
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:创建一个新的事务,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起。
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则以非事务的方式继续运行。
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起。
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则抛出异常。
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则创建一个事务作为当前事务的嵌套事务来运行;如果当前没有事务,则该取值等价于 TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED。
事务超时
所谓事务超时,就是指一个事务所允许执行的最长时间,如果超过该时间限制但事务还没有完成,则自动回滚事务。在 TransactionDefinition 中以 int 的值来表示超时时间,其单位是秒。
默认设置为底层事务系统的超时值,如果底层数据库事务系统没有设置超时值,那么就是none,没有超时限制。
事务只读属性
只读事务用于客户代码只读但不修改数据的情形,只读事务用于特定情景下的优化,比如使用Hibernate的时候。
默认为读写事务。
spring事务回滚规则
指示spring事务管理器回滚一个事务的推荐方法是在当前事务的上下文内抛出异常。spring事务管理器会捕捉任何未处理的异常,然后依据规则决定是否回滚抛出异常的事务。
默认配置下,spring只有在抛出的异常为运行时unchecked异常时才回滚该事务,也就是抛出的异常为RuntimeException的子类(Errors也会导致事务回滚),而抛出checked异常则不会导致事务回滚。可以明确的配置在抛出那些异常时回滚事务,包括checked异常。也可以明确定义那些异常抛出时不回滚事务。
还可以编程性的通过setRollbackOnly()方法来指示一个事务必须回滚,在调用完setRollbackOnly()后你所能执行的唯一操作就是回滚。
面试问题:
1、失效场景
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41356873/article/details/109368337
2、如何配置,怎么写
3、传播属性和隔离级别






















 6070
6070











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








