本节目标:数据结构
1,文件共享
打开文件内核数据结构
一个进程两次打开同一个文件
两个进程打开同一个文件
2,复制文件描述符(dup、dup二、fcntl)
一,文件共享app
1,一个进程打开两个文件内核数据结构ide
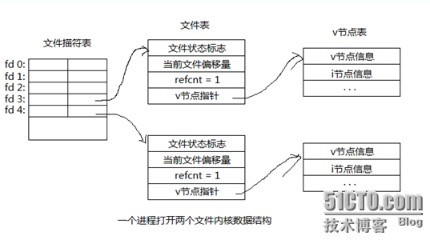
说明:ui
文件描述符表:每一个进程都有一张,彼此独立,每一个文件描述符表项都指向一个文件表,文件描述符0(STDIN_FILENO)、1(STDOUT_FILENO)、2(STDERR_FILENO),默认已经打开,分别表示:标准输入,标准输出,标准错误设备。this
文件表:每打开一个文件就对应一张文件表,文件表能够共享,当多个文件描述符指向同一个文件表时,文件表中的spa
refcnt字段会相应变化。文件状态标识:文件的打开模式(R,W,RW,APPEND,NOBLOCK,等),当前文件偏移量,refcnt:被引用数量,3d
v节点指针:指向一个v节点表。指针
v节点表:每一个文件对应一个,不管被被多少个进程打开都只有一个,它包括v节点信息(主要是stat结构体中的信息),i节点信息。code
每一个进程默认只能打开1024个文件描述符,当一个进程打开一个文件时,默认会从0开始查找未被使用的描述符,因为0,1,2默认被占用,全部通常从3开始使用。orm
二、一个进程两次打开同一个文件
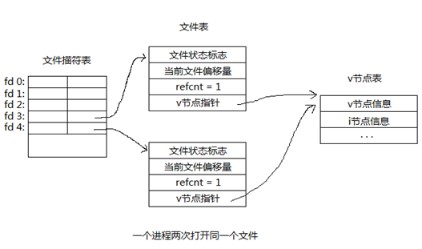
当一个进程屡次打开同一个文件时,首先会在描述符表顺序查找未被使用的描述符,而后每打开一次创建一张文件表,但各文件表中的v节点指针都指向同一个v节点表。
示例程序:
#include #include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do\
{ \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
}while(0)int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{intfd1;intfd2;char buf1[1024] = {0};char buf2[1024] = {0};
fd1= open("test.txt", O_RDONLY);if (fd1 == -1)
ERR_EXIT("open error");
read(fd1, buf1,5);
printf("buf1=%s\n", buf1);
fd2= open("test.txt", O_RDWR);if (fd2 == -1)
ERR_EXIT("open error");
read(fd2, buf2,5);
printf("buf2=%s\n", buf2);
write(fd2,"AAAAA", 5);
memset(buf1,0, sizeof(buf1));
read(fd1, buf1,5);
printf("buf1=%s\n", buf1);
close(fd1);
close(fd2);return 0;
}
运行结果:

说明:先建立test.txt文件写入hello,再同一个进程两次打开该文件,可见每打开一次文件就参数一张文件表,不共享偏移量,都开始位置读取,以后利用第二个文件描述符写入AAAAA,在利用第一个描述符能够读取出,代表都指向同一个v节点表,操做同一个文件。
3,两个不一样进程打开同一个文件
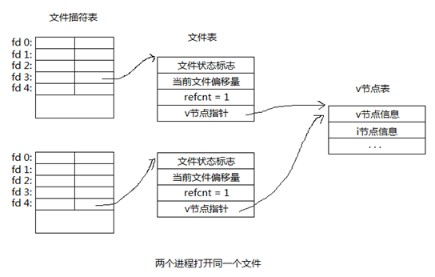
当不一样进程打开同一个文件时,每一个进程首先在它们各自的文件描述符表中顺序查找未被使用的描述符,最终得到的文件描述符可能相同也可能不一样,每一个fd指向各自的文件表,但一样,每一个文件表中的v节点指针都指向同一个v节点表。
2、复制文件描述符
复制前:

复制后:
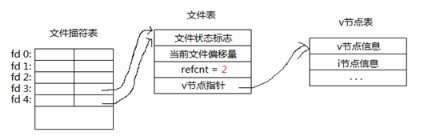
复制后,两个文件描述符都指向了同一个文件表,refcnt=2。
复制文件描述符有三种方法:
1,dup
2,dup2
#include
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
DESCRIPTION
These system calls create a copy of the file descriptor oldfd.
dup() uses the lowest-numbered unused descriptor for the new descriptor.
dup2() makes newfd be the copy of oldfd, closing newfd first if necessary, but note
the following:
* If oldfd is not a valid file descriptor, then the call fails, and newfd is not closed.
* If oldfd is a valid file descriptor, and newfd has the same value as
oldfd, then dup2() does nothing, and returns newfd.
After a successful return from one of these system calls, the old and new file descriptors may be used interchangeably. They refer to the same open file description (see open(2)) and thus share file offset and file status flags; for example, if the file offset is modified by using lseek(2) on one of the descriptors, the offset is also changed for the other.
RETURN VALUE
On success, these system calls return the new descriptor. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
示例程序:
#include #include#include#include
int main(void)
{intfd;
fd= open("test.txt",O_WRONLY);if( fd == -1){
perror("open error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}intfd2;
fd2=dup(fd);if(fd2 == -1){
perror("dup error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("oldfd = %d\n",fd);
printf("newfd = %d\n",fd2);intfd3;
close(0); //或者close(STDIN_FILENO)
fd3 =dup(fd);if(fd3 == -1){
perror("dup error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("after close stdin,the newfd = %d\n",fd3);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
运行结果:
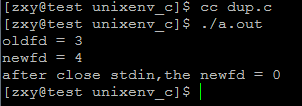
用dup进行文件描述符的复制时,顺序查找即从0开始查找能够文件描述符
示例2:
#include #include#include#include
int main(void)
{intfd;
fd= open("test.txt",O_WRONLY);if( fd == -1){
perror("open error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}intfd2;
fd2= dup2(fd,0);if(fd2 == -1){
perror("dup error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("oldfd = %d\n",fd);
printf("newfd = %d\n",fd2);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
运行结果:
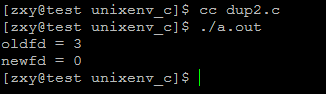
用dup2进行文件描述符复制时,指定须要复制的新的描述符,若是该描述符已经被占用,则先关闭它在从新复制,相似于先调用close再dup
3,fcntl
功能:操纵文件描述符,改变已打开的文件的属性
#include
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );
DESCRIPTION
fcntl() performs one of the operations described below on the open file
descriptor fd. The operation is determined by cmd.
fcntl() can take an optional third argument. Whether or not this argu-
ment is required is determined by cmd. The required argument type is
indicated in parentheses after each cmd name (in most cases, the
required type is long, and we identify the argument using the name
arg), or void is specified if the argument is not required.
由第二个参数指定操做类型,后面点的可变参数指定该命令所需的参数
这里咱们进行文件描述符复制,可将cmd 设为: F_DUPFD (long),该命令表示:
Find the lowest numbered available file descriptor greater than
or equal to arg and make it be a copy of fd. This is different
from dup2(2), which uses exactly the descriptor specified.
On success, the new descriptor is returned.
示例程序:
#include #include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do\
{ \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
}while(0)int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{intfd;
fd= open("test.txt", O_WRONLY);if (fd == -1)
ERR_EXIT("open error");
close(1);if (fcntl(fd, F_DUPFD, 0) < 0)
ERR_EXIT("dup fd error");
printf("-----------\n");//进行重定向,将不会显示在标准输出,
return 0;
}
运行结果:
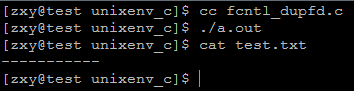





















 1147
1147











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








