1、什么是多态?
从属于不同的类对象 , 调用相同的函数(同名函数),最终会具体调用不同的代码,实现不同的功能, 这就是多态
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class point
{
private:
int xres;
int yres;
public:
//点类的构造函数
point(int x, int y)
{
//cout<<"point constructor"<<endl;
xres = x;
yres = y;
}
virtual void display() //定义为虚函数
{
cout<<"xres: "<<xres<<" "<<"yres: "<<yres<<endl;
}
};
class rectangle : public point
{
private:
int xres;
int yres;
int width;
int height;
public:
rectangle(int x, int y, int w, int h):point(x,y)
{
xres = x;
yres = y;
width = w;
height = h;
}
void display()
{
cout<<"rec_xres: "<<xres<<" "<<"rec_yres: "<<yres<<endl;
cout<<"width: "<<width<<" "<<"height: "<<height<<endl;
}
};
class circle : public point
{
private:
int xres;
int yres;
int radus;
public:
//基类中有构造函数,编译过程中分配了空间,需要对其初始化。若不要初始化,就不要出现构造函数
circle(int x, int y, int r):point(x,y) //如果去掉point(x,y)会报错,可以删掉基类的构造函数或者基类成员。
{
xres = x;
yres = y;
radus = r;
}
void display()
{
cout<<"cir_xres: "<<xres<<" "<<"cir_yres: "<<yres<<endl;
cout<<"cir_r: "<<radus<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
/*测试1
point p(10, 20);
point *ptr = &p;
ptr->display(); //调用的是基类的成员函数
rectangle rec(100, 200, 300, 400);
ptr = &rec;
ptr->display(); //调用的是基类的成员函数
*/
//测试点
rectangle rec(100, 200, 300, 400);
circle cir(10, 20, 80);
point *ptr;
//调用矩形打印
ptr = &rec;
ptr->display(); //在基类中定义为虚函数之后,这里调用的是rectangle派生类的成员函数
ptr = ○
ptr->display(); //在基类中定义为虚函数之后,这里调用的是circle派生类的成员函数
return 0;
}
2、纯虚函数
1)什么是纯虚函数
在基类中定义虚函数
virtual void dispaly();
基类一定要定义,但是基类不应该:
a、定义数据成员
b、构造函数
c、虚函数有必要存在,但是不能有具体实现内容
所以最终基类,只能用来声明虚函数存在,并且可以写成
virtual void dispaly(); //纯虚函数
示例函数:
#if 0
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
#define pi 3.14
class Shape // 定义图形
{public:
virtual string getName() = 0; // 定义第一个纯虚函数
virtual float getArea() = 0; // 定义第二个纯虚函数
};
class Circle : public Shape
{public:
Circle(string n, int x, int y, int r)
{ name = n;
xres = x;
yres = y;
radius = r;
}
string getName(void)
{ return name;
}
float getArea(void)
{ return pi*radius*radius;
}
private:
string name;
float xres;
float yres;
float radius;
};
class Rectangle : public Shape
{public:
Rectangle(string n, float x, float y, float w, float h)
{ name = n;
xres = x;
yres = y;
width= w;
height = h;
}
string getName()
{ return name;
}
float getArea()
{ return width*height;
}
private:
string name;
float xres;
float yres;
float width;
float height;
};
class Triangle : public Shape
{public:
Triangle(string n, float x, float y, float z)
{ name = n;
a = x;
b = y;
c = z;
}
string getName()
{ return name;
}
float getArea()
{ float s = (a + b + c)/2;
return sqrt(s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c));
}
private:
string name;
float a;
float b;
float c;
};
int main()
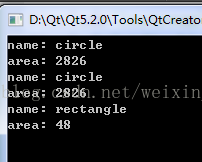
{ Circle c("circle",100,100,30); Shape *ptr = NULL;
ptr = &c;
cout<<"name: "<<ptr->getName()<<endl;
cout<<"area: "<<ptr->getArea()<<endl;
//Shape *ptr = NULL;
ptr = new Circle("circle",100, 100, 30); cout<<"name: "<<ptr->getName()<<endl;
cout<<"area: "<<ptr->getArea()<<endl;
ptr = new Rectangle("rectangle",10,20,8,6); cout<<"name: "<<ptr->getName()<<endl;
cout<<"area: "<<ptr->getArea()<<endl;
delete ptr;
//ptr = NULL;
return 0;
}
#endif
3、错误示范

当运行代码出现这类问题的时候是:在基类中定义了纯虚函数,但是没有实现,在子类中实现了,当子类创建对象的时候就会出现这个问题。























 4820
4820











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








