一、概述
1.1 EventLoop
EventLoop(事件循环对象) 本质是一个单线程执行器(同时维护了一个 Selector),里面有 run 方法处理 Channel 上源源不断的 io 事件。
它的继承关系比较复杂
- 一条线是继承自 j.u.c.ScheduledExecutorService 因此包含了线程池中所有的方法
- 另一条线是继承自 netty 自己的 OrderedEventExecutor,
- 提供了 boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread) 方法判断一个线程是否属于此 EventLoop
- 提供了 parent 方法来看看自己属于哪个 EventLoopGroup
1.2 EventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup(事件循环组) 是一组 EventLoop,Channel 一般会调用 EventLoopGroup 的 register 方法来绑定其中一个 EventLoop,后续这个 Channel 上的 io 事件都由此 EventLoop 来处理(保证了 io 事件处理时的线程安全)
- 继承自 netty 自己的 EventExecutorGroup
- 实现了 Iterable 接口提供遍历 EventLoop 的能力
- 另有 next 方法获取集合中下一个 EventLoop
主要有以下两种EventLoopGroup:
(1)NioEventLoopGroup:处理IO事件,普通任务,定时任务
(2)DefaultEventLoopGroup:处理普通任务,定时任务
这里先给出一个结论,EventLoopGroup当中的每一个EventLoop,和客户端Channel实际是绑定的:简单来说,就是一个channel发送的内容,会被同一个线程处理。
二、使用示例
2.1 遍历EventLoopGroup
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutor;
public class TestEventLoopGroup {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//构造方法可以指定线程数,默认不设置会首先根据Netty的环境变量,否则根据线程核心数*2,最小为1
NioEventLoopGroup nioEventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(2);
//使用next方法,获取内部的EventLoop
System.out.println(nioEventLoopGroup.next());
System.out.println(nioEventLoopGroup.next());
System.out.println(nioEventLoopGroup.next());
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
//for循环获取内部的EventLoop
for (EventExecutor group:nioEventLoopGroup){
System.out.println(group);
}
}
}
输出结果
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@56cbfb61
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@1134affc
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@56cbfb61
-------------------------------------
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@56cbfb61
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@1134affc
2.2 普通任务和定时任务
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
public class EventLoopGroupDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 创建一个EventLoopGroup,它是一个接口
* 有两种实现方式:
* - NioEventLoopGroup:它可以处理io事件,普通任务,定时任务
* - DefaultEventLoop:它可以处理普通任务,定时任务。适用于一些没有io事件发生的场景
*/
EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//获取下一个EventLoopGroup对象
eventLoopGroup.next();
eventLoopGroup.next().execute(() -> {
log.debug("执行普通任务");
});
// 执行定时任务 scheduleAtFixedRate(任务对象,初始延迟时间,间隔时间,时间单位)
// 下面的含义是,刚开始等待1秒执行,然后接下来每隔两秒执行一次
eventLoopGroup.next().scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
log.debug("执行定时任务");
},1,2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
运行结果
10:08:29.438 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG com.lilinchao.netty.eventloop.EventLoopGroupDemo - 执行普通任务
10:08:30.441 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-2] DEBUG com.lilinchao.netty.eventloop.EventLoopGroupDemo - 执行定时任务
10:08:32.448 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-2] DEBUG com.lilinchao.netty.eventloop.EventLoopGroupDemo - 执行定时任务
10:08:34.453 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-2] DEBUG com.lilinchao.netty.eventloop.EventLoopGroupDemo - 执行定时任务
10:08:36.446 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-2] DEBUG com.lilinchao.netty.eventloop.EventLoopGroupDemo - 执行定时任务
10:08:38.445 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-2] DEBUG com.lilinchao.netty.eventloop.EventLoopGroupDemo - 执行定时任务
10:08:40.449 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-2] DEBUG com.lilinchao.netty.eventloop.EventLoopGroupDemo - 执行定时任务
2.3 执行IO任务
其实所谓IO任务就是,客户端和服务端的通信。
- 服务端代码
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
@Slf4j
public class EventLoopGroupDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel sc) throws Exception {
// 这里就没有定义处理ByteBuf和字符串转换的Handler,仅仅定义一个,现在自己进行转换
sc.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
log.debug("接收客户端的消息为:" + byteBuf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
}
});
}
}).bind(8080);
}
}
- 客户端代码
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class EventLoopGroupClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//1.启动类
Channel channel = new Bootstrap()
//2.添加EventLoop
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
//3.选择客户端 channel实现
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
//4.添加处理器
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
// 在连接建立后被调用
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
//5.连接到服务器
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080))
.sync()
.channel();
System.out.println(channel);
System.out.println("");
}
}
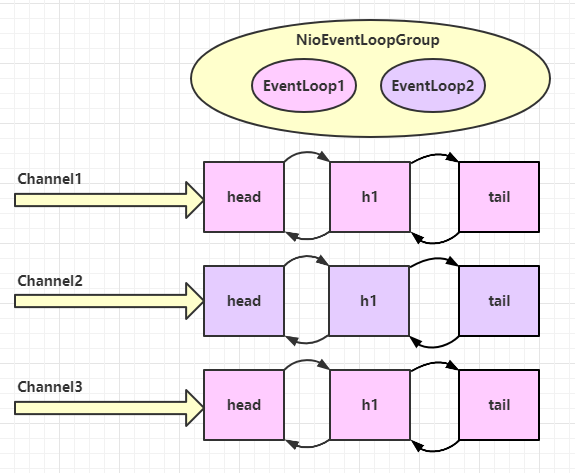
需要注意的是:一旦客户端和服务端建立连接,channel就和事件循环组中的某一个eventloop进行绑定了,即之后的该channel的读写事件都由这个eventloop负责,下面的图说明了这一过程,每个channel的所有事件都被同一个EventLoop处理。
2.4 分工细化
- 细化一
可以把事件循环组的EventLoop分工得更加细一些,即让一个EventLoop处理accept事件,其他的EventLoop处理读写事件。
Bootstrap的group()方法可以传入两个EventLoopGroup参数,分别负责处理不同的事件。
两个Group,分别为 Boss 负责serversocketchannel上的Accept事件,Worker 负责socketchannel上的读写事件
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(1), new NioEventLoopGroup(2))
...
}
}
- 细化2
EventLoop虽然可以做到多路复用,但是如果有一个读写事件耗时过长,会影响这个EventLoop下的其他事件的进行,因此可以创建一个独立的EventLoopGroup处理耗时较长的事件,当有的任务需要较长的时间处理时,可以使用非NioEventLoopGroup,避免同一个NioEventLoop中的其他Channel在较长的时间内都无法得到处理。
那么就会有个问题,创建的事件循环组如何与耗时较长的handle联系起来?
在调用addLast()方法时可以传递进来,addLast()有三个参数:事件循环组(空则默认为上方建立的),循环组名称,处理函数。
下面以一个例子来说明,假设服务器端接收客户端的消息后需要6s去处理(休眠6s),那么这个休眠的事件可以放在新的EventLoopGroup中去处理,此外连续打开10个客户端连接服务端测试效果,客户端代码与上方的客户端类似。
下面是服务端代码,加入了两个handler,第一个是默认的EventLoopGroup(当前ServerBootstrap的EventLoopGroup),并且使用ctx.fireChannelRead(msg)将msg传给第二个handler,第二个使用的是新建的EventLoopGroup去处理耗时较长的事件。
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class EventLoopGroupServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup(3);
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(), new NioEventLoopGroup(2))
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("nioHandler",new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("nioHandler"+Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 将消息传递给下一个handler
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}).addLast(group,"myhandler",new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("myhandler"+Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}
- 如何切换
上面说到了在处理事件时可以从一个EventLoopGroup切换到另一个EventLoopGroup,另一个handler专门处理耗时较长的事件,降低对其他事件造成的影响,那么netty内部是怎么做到不同的EventLoopGroup切换呢?
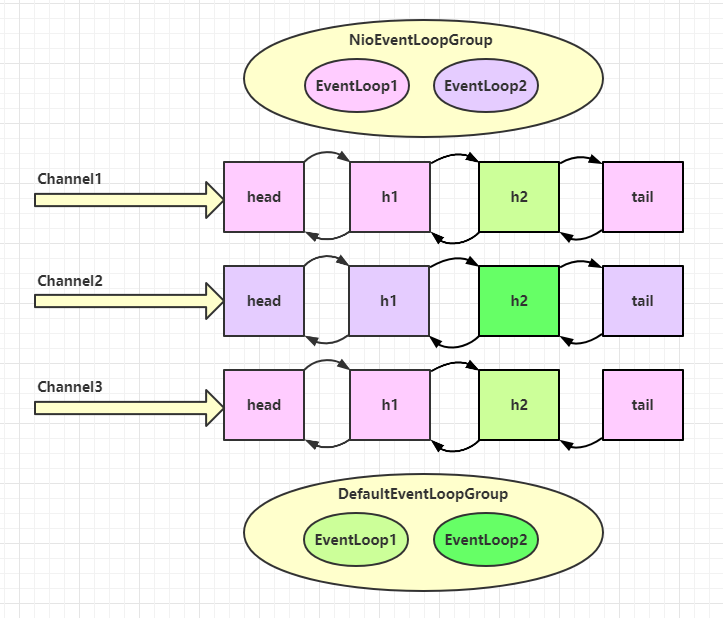
上面的图描述的就是切换EventLoopGroup,当handler中绑定的EventLoopGroup不同时,需要切换EventLoopGroup来执行不同的任务,具体来说netty是使用下面这个方法进行切换:
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {
final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor(); // 获得下一个EventLoop, excutor 即为 EventLoopGroup
// 如果下一个EventLoop 在当前的 EventLoopGroup中
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {//当前handler中的线程是否和eventloop是同一个线程
// 使用当前 EventLoopGroup 中的 EventLoop 来处理任务
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
} else {
// 否则让另一个 EventLoopGroup 中的 EventLoop 来创建任务并执行
executor.execute(new Runnable() {//此时需要在下一个线程中执行
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
});
}
}
```java
- 如果两个 handler 绑定的是同一个线程,那么就直接调用
- 否则,把要调用的代码封装为一个任务对象,由下一个 handler 的线程来调用
// 否则让另一个 EventLoopGroup 中的 EventLoop 来创建任务并执行
executor.execute(new Runnable() {//此时需要在下一个线程中执行
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
});
}
}
- 如果两个 handler 绑定的是同一个线程,那么就直接调用
- 否则,把要调用的代码封装为一个任务对象,由下一个 handler 的线程来调用





















 329
329











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








