目录
使用决策树(Tree)模型对鸢尾花数据进行预测
1. 使用Model下的Tree
使用的数据集:鸢尾花数据集(这是很经典的机器学习的数据集 sklearn中的)是classification问题
Tree 模型,也就是常说的决策树模型,可处理离散型数据与连续型数据,可用于classification和Regression
英文介绍:
Tree is a simple algorithm that splits the data into nodes by class purity (information gain for categorical and MSE for numeric target variable). It is a precursor to Random Forest. Tree in Orange is designed in-house and can handle both categorical and numeric datasets.
2. 操作步骤
2.1 新建File,导入数据集

双击进入File,显示如下图所示:

鸢尾花数据集是Orange所带的,可以直接load,如果是自己的数据,可以直接选择自己的文件即可
从上图可看出,Feature有四个,分别为sepal length\sepal width\petal length\petal witdth,它们的类型为numeric(数值型)target为iris,value分别为Iris-virginica\vesicolor\setosa
点击Apply,进入下一步
2.2 查看数据
双击Data Table,即可进入到如下图所示的界面,整个数据集如下:

2.3 进入到Tree模型
双击进入到Tree模型

Tree parameters 介绍:
- Induce binary tree:build a binary tree 建立一个二叉树
- Min. number of instances in leaves: if checked, the algorithm will never construct a split which would put less than the specified number of training examples into any of the branches. 一个叶节点要存在所需要的最小样本量。一个节点在分支后的每一个子节点中,必须包含至少 Min. number of instances in leaves 个训练样本,否则分支就不会发生。这个参数可能会使得模型更平滑,尤其是在Regression中
- Do not split subsets smaller than: forbids the algorithm to split the nodes with less than the given number of instances 是一个中间节点要分支所需要的最小的样本量,如果一个节点包含的样本量小于Do not split subsets smaller than 中所填写的数字,这个节点分支就不会发生,也就是说,这个节点一定会成为一个叶子节点
- Limit the maximal tree depth: limits the depth of the classification tree to the specified number of node levels. 树的最大深度,这个参数越大,树的分支就会越多,计算量就会越大,会出现过拟合的现象,这个参数与Do not split subsets smaller than共同作用,先满足哪个限制条件,都会停止继续分支
- Stop when majority reaches [%]: stop splitting the nodes after a specified majority threshold is reached
2.4 进入到Tree Viewer
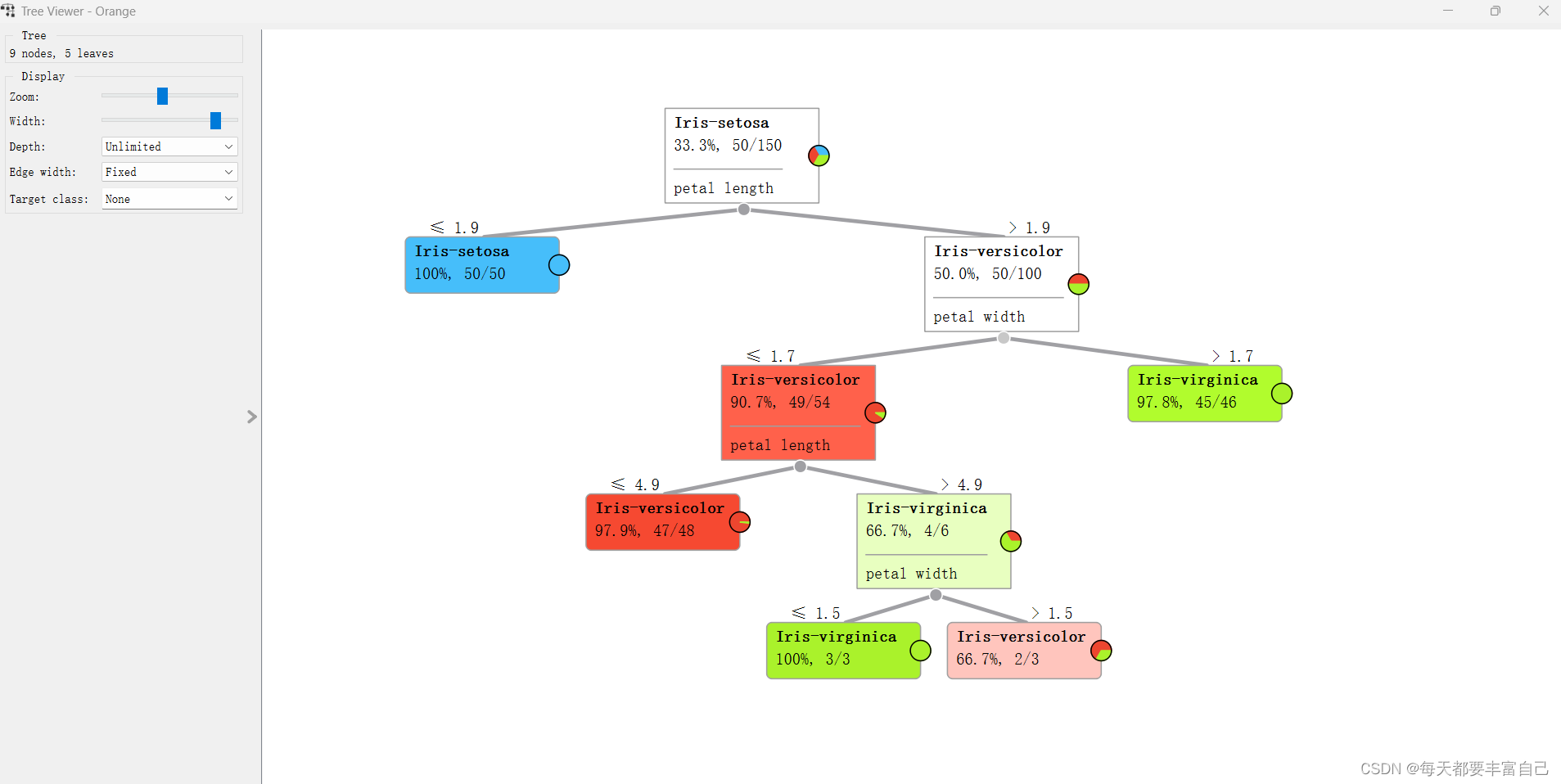
添加Tree Viewer到流程中,如下图所示:

如图左上角所示:
9 nodes, 5leaves: 说明分了九个节点,5个叶子(个人理解,如图中所示,蓝色的没有继续往下进行分支的为叶子,leaves是nodes的一种),可以调试Tree中的不同参数,看一下不同参数对这个Tree的影响
Zoom\width是调节显示的,可以自行调节看一下区别
Tree viewer可以接DataTable和Scatter Plot模块

在Tree Viewer后面是Selected data --->data
以Scatter Plot为例,双击之后显示如下图所示:
没有显示什么信息
这时,双击Selected data --->data,如下图所示,

拖拽中间线的起点终点即可改成下图:

此时,再双击Scatter Plot,显示如下图所示:
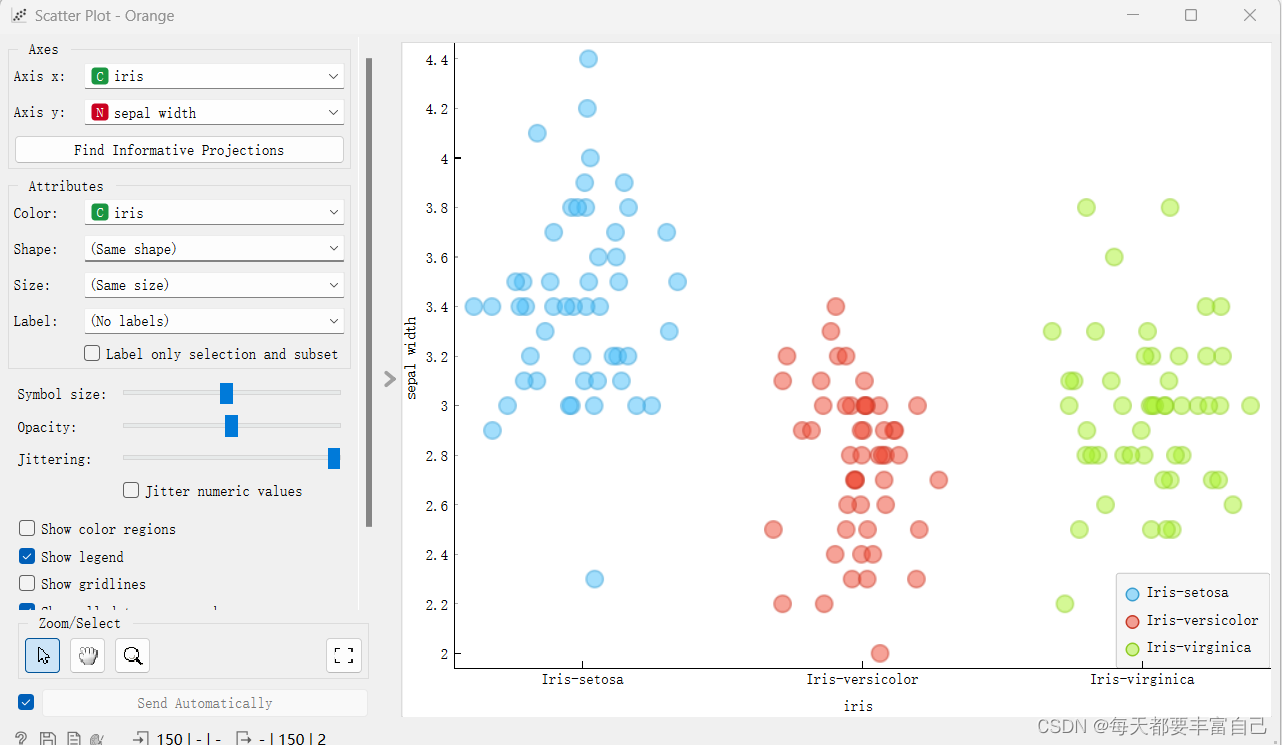
更改左侧的参数,调节不同显示效果
2.5 进行Test and Score
那么模型建好了,如何来看模型的效果呢?
这个时候,我们选用Test and Score 模块,我是基于之前的步骤,继续进行,添加Test and Score模块,如下图所示

双击Testa and Score,重要参数有cross validation 就是交叉验证,具体参数,这里不做详细介绍
number of folds 是指验证的次数

重要的结果参数:
- Area under ROC is the area under the receiver-operating curve.
- Classification accuracy is the proportion of correctly classified examples.
- F-1 is a weighted harmonic mean of precision and recall (see below).
- Precision is the proportion of true positives among instances classified as positive, e.g. the proportion of Iris virginica correctly identified as Iris virginica.
- Recall is the proportion of true positives among all positive instances in the data, e.g. the number of sick among all diagnosed as sick.
- Specificity is the proportion of true negatives among all negative instances, e.g. the number of non-sick among all diagnosed as non-sick.
- LogLoss or cross-entropy loss takes into account the uncertainty of your prediction based on how much it varies from the actual label.
目前我也只了解CA (Classification accuracy)这个数,越大越精准,后续随着学习,会对这方面做一个更明晰的解释。可看出,该模型预测准确度在95.3%
在Test and Score之后,可添加Condfusion Matrix,看可视化的再现模拟的结果

双击Confusion Matrix,如下图所示,Actual代表实际的真实的,Predicted代表模型预测的
Iris-setosa实际有50个,模型预测50个
Iris-versicolor实际50个,模型预测结果是51个,其中包括47个Iris-versicolor和4个错误的Iris-virginica
Iris-virginica实际50个,模型预测结果是49个,其中包括46个Iris-virginica和3个错误的Iris-versicolor

2.6 保存一下文件
3 结语
今日份学习到此结束










 本文介绍了使用Orange数据可视化工具构建决策树模型的过程,针对鸢尾花数据集进行分类预测。首先,通过File导入数据集,然后在Tree模型中设置参数,如最小样本量、最大树深度等。接着,使用TreeViewer展示决策树结构,并通过TestandScore模块进行模型效果验证,得到约95.3%的分类准确率。最后,通过ConfusionMatrix展示了模型的分类混淆情况。
本文介绍了使用Orange数据可视化工具构建决策树模型的过程,针对鸢尾花数据集进行分类预测。首先,通过File导入数据集,然后在Tree模型中设置参数,如最小样本量、最大树深度等。接着,使用TreeViewer展示决策树结构,并通过TestandScore模块进行模型效果验证,得到约95.3%的分类准确率。最后,通过ConfusionMatrix展示了模型的分类混淆情况。

















 676
676

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










