实验一 信号的时域分析及Matlab实现
参考文章
题目
题目1代码实现
讲解
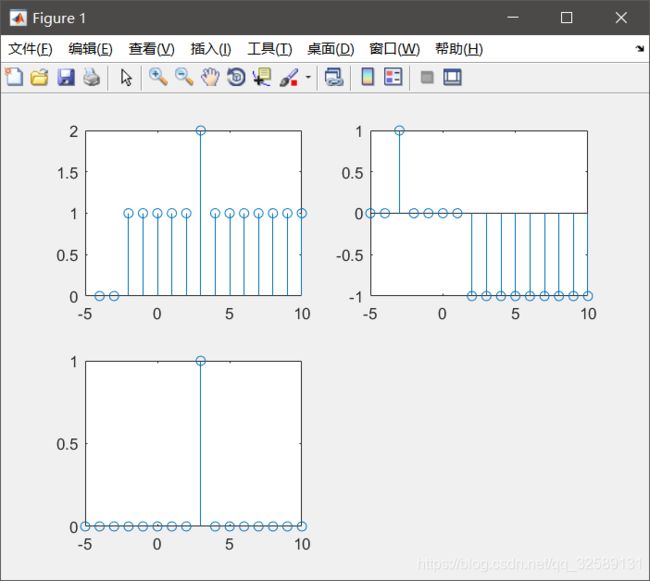
sinc(t)
Sa(t)
时移、翻转、展缩
subs(s,old,new)
ezplot() 绘画符号函数
题目2代码实现
讲解
题目3代码实现
新建函数
单位抽样序列
单位阶跃序列
离散信号的运算
参考文章
信号与系统实验指导
题目

题目1代码实现
syms t;
f=sym('sin(t)/t'); %定义符号函数 f(t)=sin(t)/t
f1=subs(f,t,(-3)*t+5); %对 f 进行移位
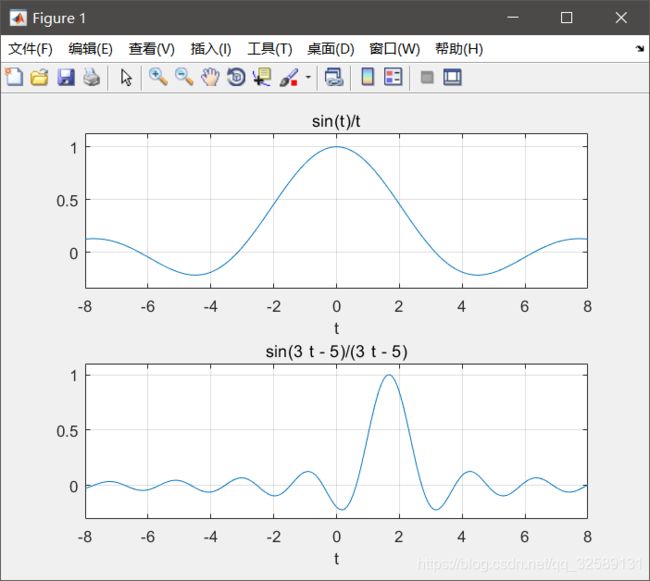
subplot(2,1,1);ezplot(f,[-8,8]);grid on;% ezplot 是符号函数绘图命令
subplot(2,1,2);ezplot(f1,[-8,8,-0.3,1.1]);grid on;
运行结果
讲解
sinc(t)

Sa(t)
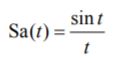
所以sinc (t/pi) = Sa(t)
时移、翻转、展缩
由 f (t)到
f ( − a t + b ) ( a > 0 ) f(-at+b)(a>0)f(−at+b)(a>0)
所用函数
subs(s,old,new)
returns a copy of s replacing all occurrences of old with new, and then evaluating s.
例:已知 f (t) = sin(t) / t ,试通过翻转、移位、展缩由 f (t)的波形得到 f (-2t + 3) 的波形。
syms t;
f=sym('sin(t)/t'); %定义符号函数 f(t)=sin(t)/t
f1=subs(f,t,t+3); %对 f 进行移位
f2=subs(f1,t,2*t); %对 f1 进行展缩
f3=subs(f2,t,-t); %对 f2 进行翻转
可以一步到位
syms t;
f=sym('sin(t)/t'); %定义符号函数 f(t)=sin(t)/t
f3 = subs(f, t, -2t+3);
ezplot() 绘画符号函数
ezplot(fun2,[xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax])
plots fun2(x,y) = 0 over xmin < x < xmax and ymin < y < ymax.
一般搭配使用
subplot(2,1,1);%divides the current figure into an m-by-n grid and creates an axes for a subplot in the position specified by p
ezplot(f,[-8,8,-0.3,1.1]);
grid on;%画网格与否
题目2代码实现
t=(-10:0.01:5);
f1= sin(2*pi*t)+exp(-3*t);
f2= sin(3*pi*t)-exp(-5*t);
f3= sin(2*pi*t).*exp(-3*t);
subplot(2,2,1);plot(t,f1);grid on;
subplot(2,2,2);plot(t,f2);grid on;
subplot(2,2,3);plot(t,f3);grid on;

讲解
f3= sin(2pit).exp(-3t);
如果你使用f3= sin(2pit)exp(-3t);而没加 .,建议学习一下matlab中数组乘法与矩阵乘法的区别
题目3代码实现
[x1,n]=delta(3,-4,10);
[x2,n]=step_seq(-2,-4,10);
subplot(2,2,1);
stem(n,x1+x2);
[x1,n]=delta(-3,-5,10);
[x2,n]=step_seq(2,-5,10);
subplot(2,2,2);
stem(n,x1-x2);
[x1,n]=delta(3,-5,10);
[x2,n]=step_seq(-2,-5,10);
subplot(2,2,3);
stem(n,x1.*x2);
新建函数
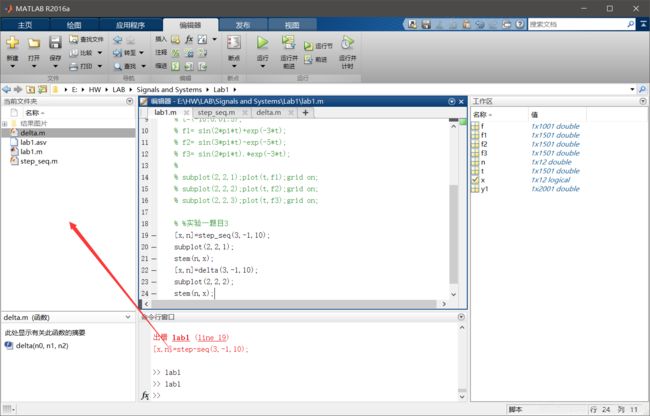
在空白处右键–》新建函数–》函数
修改函数名与文件名一致,最好保存在同一文件夹,到时候在同一个文件夹的其他 .m文件直接引用就ok
单位抽样序列
δ ( n − n 0 ) = { 1 , n = n 0 0 , n ≠ n 0 \delta(n-n0)=\left\{\begin{array}{lc}1,&n=n0\\0,&n\neq n0\end{array}\right.δ(n−n0)={1,0,n=n0n=n0
先根据上面新建一个函数,然后先定义delta函数,并保存。
function[x,n]=delta(n0,n1 ,n2)
n=[n1:n2];
x=[(n-n0)==0];
然后在主的.m文件
[x,n]=delta(3,-1,10);
stem(n,x);
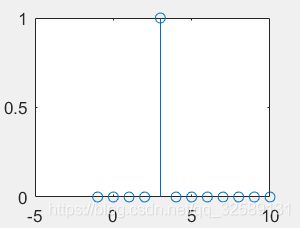
单位阶跃序列
u ( n − n 0 ) = { 1 , n > = n 0 0 , n < n 0 u(n-n0)=\left\{\begin{array}{lc}1,&n>=n0\\0,&nu(n−n0)={1,0,n>=n0n
先根据上面新建一个函数,然后先定义step_seq函数,并保存。
function[x,n]=step_seq(n0, n1, n2)
n=[n1:n2];
x=[(n-n0)>=0];
然后在主的.m文件
[x,n]=step_seq(3,-1,10);
stem(n,x);
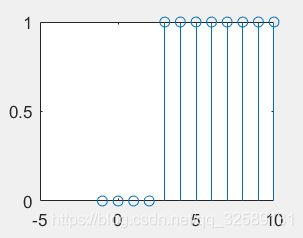
离散信号的运算
n一样,x不一样,在stem里面加
[x1,n]=delta(3,-4,10);
[x2,n]=step_seq(-2,-4,10);
stem(n,x1+x2);
如果是乘法,那么在**“*”前加“.”**





















 366
366











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








