在分布式系统中,负载均衡是必不可少的一个模块,dubbo 中提供了五种负载均衡的实现,在阅读这块源码之前,建议先学习负载均衡的基础知识。把看源码当做一个印证自己心中所想的过程,这样会得到事半功倍的效果
以下源码分析基于 dubbo 2.77 版本
类结构
先来看一下这一块的类结构图
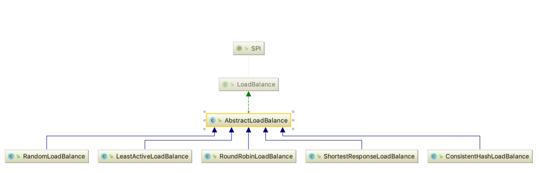
大部分算法都是在权重比的基础上进行负载均衡, RandomLoadBalance 是默认的算法
AbstractLoadBalance
AbstractLoadBalance 对一些通用的操作做了处理,是一个典型的模板方法模式的实现
select 方法只做一些简单的范围校验,具体的实现有子类通过 doSelect 方法去实现
@Override public Invoker select(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) { if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) { return null; } if (invokers.size() == 1) { return invokers.get(0); } return doSelect(invokers, url, invocation); }getWeight 方法封装了获取一个调用者的权重值的方法,并加入了 预热 处理
int getWeight(Invoker> invoker, Invocation invocation) { int weight; URL url = invoker.getUrl(); // Multiple registry scenario, load balance among multiple registries. // 注册中心不需要预热 if (REGISTRY_SERVICE_REFERENCE_PATH.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) { weight = url.getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY + "." + WEIGHT_KEY, DEFAULT_WEIGHT); } else { // 获取配置的权重值 weight = url.getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), WEIGHT_KEY, DEFAULT_WEIGHT); if (weight > 0) { // 获取服务提供者启动时的时间戳 long timestamp = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(TIMESTAMP_KEY, 0L); if (timestamp > 0L) { // 获取启动时长 long uptime = System.currentTimeMillis() - timestamp; // 当前时间小于服务提供者启动时间,直接给一个最小权重1 if (uptime < 0) { return 1; } // 获取预热时间 int warmup = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(WARMUP_KEY, DEFAULT_WARMUP); // 如果小于预热时间,计算权重 if (uptime > 0 && uptime < warmup) { weight = calculateWarmupWeight((int)uptime, warmup, weight); } } } } // 取与零比较的最大值,保证不会出现负值权重 return Math.max(weight, 0); }calculateWarmupWeight 方法用来计算权重,保证随着预热时间的增加,权重逐渐达到设置的权重
static int calculateWarmupWeight(int uptime, int warmup, int weight) { // 运行时间/(预热时间/权重) int ww = (int) ( uptime / ((float) warmup / weight)); // 保证计算的权重最小值是1,并且不能超过设置的权重 return ww < 1 ? 1 : (Math.min(ww, weight)); }RandomLoadBalance
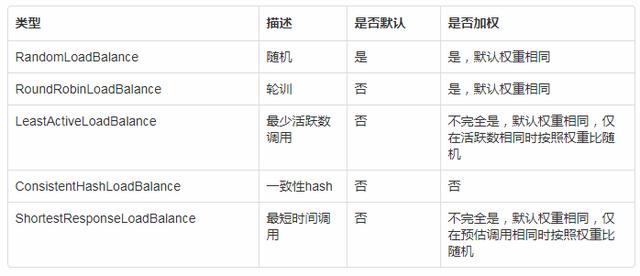
随机调用是负载均衡算法中最常用的算法之一,也是 dubbo 的默认负载均衡算法,实现起来也较为简单
随机调用的缺点是在调用量比较少的情况下,有可能出现不均匀的情况
@Override protected Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) { // Number of invokers int length = invokers.size(); // Every invoker has the same weight? boolean sameWeight = true; // the weight of every invokers int[] weights = new int[length]; // the first invoker's weight int firstWeight = getWeight(invokers.get(0), invocation); weights[0] = firstWeight; // The sum of weights int totalWeight = firstWeight; for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) { int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation); // save for later use // 依次把权重放到数组对应的位置 weights[i] = weight; // Sum // 累加权重 totalWeight += weight; // 如果出现权重不一样的,sameWeight 设为false if (sameWeight && weight != firstWeight) { sameWeight = false; } } if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) { // If (not every invoker has the same weight & at least one invoker's weight>0), select randomly based on totalWeight. // 在总权重里面随机选择一个偏移量 int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight); // Return a invoker based on the random value. for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { offset -= weights[i]; // 依次用偏移量减去当前权重,小于0说明选中 if (offset < 0) { return invokers.get(i); } } } // If all invokers have the same weight value or totalWeight=0, return evenly. // 如果所有的调用者有同样的权重或者总权重为0,则随机选择一个 return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length)); }RoundRobinLoadBalance
轮训算法避免了随机算法在小数据量产生的不均匀问题,我个人认为,轮训算法可以理解为随机算法的一种特例,在大量请求的情况下,从调用次数看,和随机并无区别,主要区别在于短时间内的调用分配上
加权轮训算法给人的直观感受,实现起来并不复杂,算出一权重总量,依次调用即可
例如A,B,C 三个节点的权重比依次 1,200,1000,如果依次轮训调用,就会出现先调用A 10 次,再调用B 200次,最后调用 C 1000次,不断重复前面的过程
但这样有一个问题,我们可以发现C 被练习调用1000次,会对C瞬间造成很大的压力
dubbo的新版本采用的是平滑加权轮询算法,轮训的过程中节点之间穿插调用,可以避免了上面说的问题,因此这块源码看起来会稍有难度
轮训算法 在dubbo 在升级的过程中,做过多次优化,有兴趣的可以去了解下该算法的优化过程,也是件很有意思的事情
public class RoundRobinLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance { public static final String NAME = "roundrobin"; private static final int RECYCLE_PERIOD = 60000; protected static class WeightedRoundRobin { // 权重值 private int weight; // 当前权重值 private AtomicLong current = new AtomicLong(0); // 最后一次使用该对象时间 private long lastUpdate; public int getWeight() { return weight; } public void setWeight(int weight) { this.weight = weight; current.set(0); } // 获取自增权重基数的当前权重值 public long increaseCurrent() { return current.addAndGet(weight); } public void sel(int total) { current.addAndGet(-1 * total); } public long getLastUpdate() { return lastUpdate; } // 设置最后一次更新时间戳 public void setLastUpdate(long lastUpdate) { this.lastUpdate = lastUpdate; } } private ConcurrentMap> methodWeightMap = new ConcurrentHashMap>(); /** * get invoker addr list cached for specified invocation * * for unit test only * * @param invokers * @param invocation * @return */ protected Collection getInvokerAddrList(List> invokers, Invocation invocation) { String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName(); Map map = methodWeightMap.get(key); if (map != null) { return map.keySet(); } return null; } @Override protected Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) { // {group}/{interfaceName}:{version} + methoName 获取当前消费者的唯一标示 String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName(); // 获取对应的 WeightedRoundRobin map,如果不存在,new 一个map放进去 ConcurrentMap map = methodWeightMap.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>()); int totalWeight = 0; long maxCurrent = Long.MIN_VALUE; long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); Invoker selectedInvoker = null; WeightedRoundRobin selectedWRR = null; for (Invoker invoker : invokers) { // 服务提供者在的唯一标识 String identifyString = invoker.getUrl().toIdentityString(); int weight = getWeight(invoker, invocation); WeightedRoundRobin weightedRoundRobin = map.computeIfAbsent(identifyString, k -> { WeightedRoundRobin wrr = new WeightedRoundRobin(); wrr.setWeight(weight); return wrr; }); // 如果权重改变了,更新 weightedRoundRobin 里面权重的值 if (weight != weightedRoundRobin.getWeight()) { //weight changed weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight); } // 当前权重自增自身权重 long cur = weightedRoundRobin.increaseCurrent(); // 设置最后一次更新时间戳 weightedRoundRobin.setLastUpdate(now); // 如果当前权重大于最大当前权重 if (cur > maxCurrent) { // 重置最大当前权重的值 maxCurrent = cur; // 把当前提供者设为选中的提供者 selectedInvoker = invoker; // 把当前轮训权重实例设为选中 selectedWRR = weightedRoundRobin; } // 累计总权重 totalWeight += weight; } // 提供者有变化 if (invokers.size() != map.size()) { // 超过60s没有使用,删除掉 map.entrySet().removeIf(item -> now - item.getValue().getLastUpdate() > RECYCLE_PERIOD); } if (selectedInvoker != null) { // 减去总权重 // 关于这个地方为什么要减去总权重,是一个很容易造成迷惑的地方 // 我的理解:每一次调用循环 每个提供者的 当前权重 都会自增自己的权重 // 因此在选中后(只有一个被选中),再减去总权重,正好保证了所有 WeightedRoundRobin 中当前权重之和永远等于0 selectedWRR.sel(totalWeight); return selectedInvoker; } // 理论上不会走到这个地方 // should not happen here return invokers.get(0); }}
LeastActiveLoadBalance
最少活跃数调用算法是指在调用时判断此时每个服务提供者此时正在处理的请求个数,选取最小的调用
dubbo 在实现该算法时的具体逻辑如下
- 选取所有活跃数最少的提供者
- 如果只有一个,直接返回
- 如果权重不同,加权随机选择一个
- 如果权重相同,随机选择一个
@Override protected Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) { // Number of invokers int length = invokers.size(); // The least active value of all invokers // 最少活跃数量 int leastActive = -1; // The number of invokers having the same least active value (leastActive) // 有同样活跃值的提供者数量 int leastCount = 0; // The index of invokers having the same least active value (leastActive) int[] leastIndexes = new int[length]; // the weight of every invokers // 每一个提供者的权重 int[] weights = new int[length]; // The sum of the warmup weights of all the least active invokers // 最少活跃提供者的总权重 int totalWeight = 0; // The weight of the first least active invoker int firstWeight = 0; // Every least active invoker has the same weight value? // 所有的最少活跃提供者是否拥有同样的权重值 boolean sameWeight = true; // Filter out all the least active invokers for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { Invoker invoker = invokers.get(i); // Get the active number of the invoker // 活跃数量 int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive(); // Get the weight of the invoker's configuration. The default value is 100. // 获取权重值 int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation); // save for later use // 保存权重留着后面用 weights[i] = afterWarmup; // If it is the first invoker or the active number of the invoker is less than the current least active number // 如果是第一个提供者,或者当前活跃数量比最少的少 if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) { // Reset the active number of the current invoker to the least active number // 重置最少活跃数量 leastActive = active; // Reset the number of least active invokers // 重置最少活跃提供者的数量 leastCount = 1; // Put the first least active invoker first in leastIndexes // 把最少活跃提供者的索引保存起来 leastIndexes[0] = i; // Reset totalWeight // 重置总权重 totalWeight = afterWarmup; // Record the weight the first least active invoker // 记录第一个最少活跃提供者的权重 firstWeight = afterWarmup; // Each invoke has the same weight (only one invoker here) // 每个最少活跃提供者是否有同样的权重??? sameWeight = true; // If current invoker's active value equals with leaseActive, then accumulating. // 如果当前活跃数量等于最少活跃数量 } else if (active == leastActive) { // Record the index of the least active invoker in leastIndexes order // 最少活跃提供者的索引依次放入 leastIndexes leastIndexes[leastCount++] = i; // Accumulate the total weight of the least active invoker // 累计最少活跃提供者的总权重 totalWeight += afterWarmup; // If every invoker has the same weight? // 如果当前权重和第一个最少活跃的权重不同,sameWeight 设为false if (sameWeight && afterWarmup != firstWeight) { sameWeight = false; } } } // Choose an invoker from all the least active invokers // 最少活跃提供者只有一个,直接返回 if (leastCount == 1) { // If we got exactly one invoker having the least active value, return this invoker directly. return invokers.get(leastIndexes[0]); } // 如拥有不同的权重,在权重的基础上随机选取一个,可以参考 RandomLoadBalance,有同样的写法 if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) { // If (not every invoker has the same weight & at least one invoker's weight>0), select randomly based on // totalWeight. int offsetWeight = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight); // Return a invoker based on the random value. for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) { int leastIndex = leastIndexes[i]; offsetWeight -= weights[leastIndex]; if (offsetWeight < 0) { return invokers.get(leastIndex); } } } // 权重相同,随机选取一个 // If all invokers have the same weight value or totalWeight=0, return evenly. return invokers.get(leastIndexes[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(leastCount)]); }ShortestResponseLoadBalance
最短时间调用调用算法是指预估出来每个处理完请求的提供者所需时间,然后又选择最少最短时间的提供者进行调用,整体处理逻辑和最少活跃数算法基本相似
dubbo 在实现该算法时的具体逻辑如下
- 选取所有预估处理时间最短的提供者
- 如果只有一个,直接返回
- 如果权重不同,加权随机选择一个
- 如果权重相同,随机选择一个
@Override protected Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) { // Number of invokers int length = invokers.size(); // Estimated shortest response time of all invokers // 最少响应时间 long shortestResponse = Long.MAX_VALUE; // The number of invokers having the same estimated shortest response time // 最少响应时间的提供者数量 int shortestCount = 0; // The index of invokers having the same estimated shortest response time int[] shortestIndexes = new int[length]; // the weight of every invokers int[] weights = new int[length]; // The sum of the warmup weights of all the shortest response invokers // 最少响应时间的提供者的总权重 int totalWeight = 0; // The weight of the first shortest response invokers // 第一个最少响应时间的权重 int firstWeight = 0; // Every shortest response invoker has the same weight value? // 所有的最少响应时间提供者是否拥有同样的权重值 boolean sameWeight = true; // Filter out all the shortest response invokers for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { Invoker invoker = invokers.get(i); RpcStatus rpcStatus = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()); // Calculate the estimated response time from the product of active connections and succeeded average elapsed time. // 平均响应成功时间 long succeededAverageElapsed = rpcStatus.getSucceededAverageElapsed(); // 活跃的连接连接数量 int active = rpcStatus.getActive(); // 预估响应时间 long estimateResponse = succeededAverageElapsed * active; // 获取权重值 int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation); // 保存权重留着后面用 weights[i] = afterWarmup; // Same as LeastActiveLoadBalance // 如果预估时间小于最少的响应时间 if (estimateResponse < shortestResponse) { // 重置最少响应时间 shortestResponse = estimateResponse; // 最少响应时间的提供者数量设为1 shortestCount = 1; // 保存提供者下标 shortestIndexes[0] = i; // 重置最少响应时间的提供者的总权重 totalWeight = afterWarmup; // 重置第一个最少响应时间的权重 firstWeight = afterWarmup; sameWeight = true; // 如果当前最少响应时间等于最少响应时间 } else if (estimateResponse == shortestResponse) { // 最少最少响应时间的下标依次放入 shortestIndexes shortestIndexes[shortestCount++] = i; // 累计最少响应时间的总权重 totalWeight += afterWarmup; // 如果当前权重和第一个最少响应时间的权重不同,sameWeight 设为false if (sameWeight && i > 0 && afterWarmup != firstWeight) { sameWeight = false; } } } // 最少最少响应时间只有一个,直接返回 if (shortestCount == 1) { return invokers.get(shortestIndexes[0]); } // 如拥有不同的权重,在权重的基础上随机选取一个,可以参考 RandomLoadBalance,有同样的写法 if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) { int offsetWeight = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight); for (int i = 0; i < shortestCount; i++) { int shortestIndex = shortestIndexes[i]; offsetWeight -= weights[shortestIndex]; if (offsetWeight < 0) { return invokers.get(shortestIndex); } } } // 权重相同,随机选取一个 return invokers.get(shortestIndexes[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(shortestCount)]); }ConsistentHashLoadBalance
一致性hash算法是一种广泛应用于分布式缓存中的算法,该算法的优势在于新增和删除节点后,只有少量请求发生变动,大部分请求仍旧映射到原来的节点
为了防止节点过少,造成节点分布不均匀,一般采用虚拟节点的方式,dubbo默认的是160个虚拟节点
网上关于一致性hash算法的文章有很多,这里就不再多赘述,以下是dubbo中的实现,需要说明的是, 一致性hash算法中权重配置不起作用
@Override protected Invoker doSelect(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) { String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation); // {group}/{interfaceName}:{version} + methoName 获取当前消费者的唯一标示 String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + methodName; // using the hashcode of list to compute the hash only pay attention to the elements in the list int invokersHashCode = invokers.hashCode(); // 获取当前消费者的一致性hash选择器 ConsistentHashSelector selector = (ConsistentHashSelector) selectors.get(key); // 如果 selector 还没初始化,或者 invokers 已经变化,重新初始化 selector if (selector == null || selector.identityHashCode != invokersHashCode) { selectors.put(key, new ConsistentHashSelector(invokers, methodName, invokersHashCode)); selector = (ConsistentHashSelector) selectors.get(key); } return selector.select(invocation); } // 一致性hash选择器 private static final class ConsistentHashSelector { // 存储hash环的数据结构 节点 -> 提供者 private final TreeMap> virtualInvokers; // 虚拟节点数量 private final int replicaNumber; // 用来标示所有提供者是唯一标示 private final int identityHashCode; // 用来存储计算hash值参数下标的数组,例如计算第一个和第三个参数 该数组为[0,2] private final int[] argumentIndex; ConsistentHashSelector(List> invokers, String methodName, int identityHashCode) { this.virtualInvokers = new TreeMap>(); this.identityHashCode = identityHashCode; URL url = invokers.get(0).getUrl(); // 虚拟节点数量,默认 160 this.replicaNumber = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_NODES, 160); // 默认只对第一个参数进行hash String[] index = COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_ARGUMENTS, "0")); argumentIndex = new int[index.length]; for (int i = 0; i < index.length; i++) { argumentIndex[i] = Integer.parseInt(index[i]); } for (Invoker invoker : invokers) { String address = invoker.getUrl().getAddress(); // 关于这个地方为什么要除以4,我理解的是md5后为16字节的数组,计算hash值只需要用到四个字节,所以可以用四次 // 因此除以4,算是一个性能优化点 for (int i = 0; i < replicaNumber / 4; i++) { // md5, 获得一个长度为16的字节数组 byte[] digest = md5(address + i); for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) { // 如果h=0,则用第0,1,2,3四个字节进行位运算,得出一个0-2^32-1的值 // 如果h=1,则用第4,5,6,7四个字节进行位运算,得出一个0-2^32-1的值 // 如果h=2,则用第8,9,10,11四个字节进行位运算,得出一个0-2^32-1的值 // 如果h=3,则用第12,13,14,15四个字节进行位运算,得出一个0-2^32-1的值 long m = hash(digest, h); virtualInvokers.put(m, invoker); } } } } public Invoker select(Invocation invocation) { String key = toKey(invocation.getArguments()); byte[] digest = md5(key); return selectForKey(hash(digest, 0)); } // 根据配置生成计算hash值的key private String toKey(Object[] args) { StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(); for (int i : argumentIndex) { if (i >= 0 && i < args.length) { buf.append(args[i]); } } return buf.toString(); } private Invoker selectForKey(long hash) { // 找到hash值在hash环上的位置 // ceilingEntry 方法返回大于或者等于当前key的键值对 Map.Entry> entry = virtualInvokers.ceilingEntry(hash); // 如果返回为空,说明落在了hash环中2的32次方-1的最后,直接返回第一个 if (entry == null) { entry = virtualInvokers.firstEntry(); } return entry.getValue(); } // 得出一个0-2^32-1的值, 四个字节组成一个长度为32位的二进制数字并转化为long值 private long hash(byte[] digest, int number) { return (((long) (digest[3 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 24) | ((long) (digest[2 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 16) | ((long) (digest[1 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 8) | (digest[number * 4] & 0xFF)) & 0xFFFFFFFFL; } private byte[] md5(String value) { MessageDigest md5; try { md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5"); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } md5.reset(); byte[] bytes = value.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); md5.update(bytes); return md5.digest(); } }总结
以上就是dubbo负载均衡源码的全部解析,如果还是不明白,可以看下官方文档的解析
http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/source_code_guide/loadbalance.html
dubbo的负载均衡算法总体来说并不复杂,代码写的也很优雅,简洁,看起来很舒服,而且有很多细节的处理值得称赞,例如预热处理,轮训算法的平滑处理等。
我们平时使用时,可以根据自己的业务场景,选择适合自己的算法,当然,一般情况下,默认的的随机算法就能满足我们的日常需求,而且随机算法的性能足够好。
如果觉得dubbo提供的五种算法都不能满足自己的需求,还可以通过dubbo的SPI机制很方便的扩展自己的负载均衡算法。
来源:https://www.tuicool.com/articles/Jj2iYze




















 119
119











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








