注:关于排序算法,博主写过【数据结构排序算法系列】数据结构八大排序算法,基本上把所有的排序算法都详细的讲解过,而之所以单独将java集合中的排序算法拿出来讲解,是因为在阿里巴巴内推面试的时候面试官问过我,让我说说java集合框架中用的哪种排序算法,当时回答错了,(关于面试详细过程请参看:【阿里内推一面】记我人生的处女面)面试结束后看了一下java源码,用的是折半插入排序算法,本来早就打算写此博客,但是因为准备鹅厂的在线考试,而鹅厂在我心中的地位是最高的,为了准备鹅厂的在线考试,自己基本上把所有事情都搁置起来了,把全部的精力都投入到复习中去了,所以一直没动手写。既然java的天才程序员都采用了折半插入排序,那么“此人必有过人之处”,因此得好好了解一下折半插入排序。
我们先从c语言中的折半插入排序算法看起,在此基础之上在来看java集合框架中的源码。
#include
using namespace std;
const int len=7;
void binaryInsertSort(int * array,int len)
{
for(int i=1;i
{
int x=array[i];
int low=0,high=i-1;//low与high的初始化很重要,因为i从1开始,所以low=0,high=i-1,这样就能保证数组中的每一个
//元素参与排序,教材上的low=1是错误的,因为教材上将数组中的第0位作为监视哨而未参与排序。
while(low<=high)//寻找待插入的位置
{
int mid=(low+high)/2;
if(x
high=mid-1;
else
low=mid+1;
}
for(int j=i-1;j>=low;j--)//将记录向后移动
{
array[j+1]=array[j];
}
array[low]=x;//插入记录
}
}
int main()
{
int a[len]={7,0,4,5,1,2,3};
binaryInsertSort(a,len);
for(int i=0;i
cout<
cout<
}可以看到折半插入排序的思想是基于折半查找的,即对有序表进行折半查找,其性能较好,所以可将折半查找的思路运用到排序中一个数组中的元素虽然刚开始不是有序的,但是可以通过折半查找的同时构造有序表,即折半插入排序算法即是通过折半查找构造有序序列,然后在已构造的部分有序序列中运用折半查找插入元素,最终直至整个表排好序为止。
程序运行结果如下:
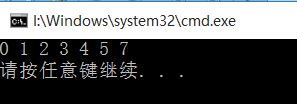
经过上述c语言代码的讲解,下面我们来看一下java的那些天才设计者们是如何java实现该算法的以及分析一个为何那些天才们看上的不是我们普通程序员最喜欢的快速排序而是折半插入排序。
下面是java中TimSort类中的sort源码,而java集合中的类调用的sort方法最终会调用它
static void sort(T[] a, int lo, int hi, Comparator super T> c,
T[] work, int workBase, int workLen) {
assert c != null && a != null && lo >= 0 && lo <= hi && hi <= a.length;
int nRemaining = hi - lo;
if (nRemaining < 2)
return; // Arrays of size 0 and 1 are always sorted
// If array is small, do a "mini-TimSort" with no merges
if (nRemaining < MIN_MERGE) {
int initRunLen = countRunAndMakeAscending(a, lo, hi, c);
binarySort(a, lo, hi, lo + initRunLen, c);
return;
}可以看到在TimSort类中最终会调用binarySort方法,即折半插入排序,我们来看一下其源码:
/**
* Sorts the specified portion of the specified array using a binary
* insertion sort. This is the best method for sorting small numbers
* of elements. It requires O(n log n) compares, but O(n^2) data
* movement (worst case).
*
* If the initial part of the specified range is already sorted,
* this method can take advantage of it: the method assumes that the
* elements from index {@code lo}, inclusive, to {@code start},
* exclusive are already sorted.
*
* @param a the array in which a range is to be sorted
* @param lo the index of the first element in the range to be sorted
* @param hi the index after the last element in the range to be sorted
* @param start the index of the first element in the range that is
* not already known to be sorted ({@code lo <= start <= hi})
* @param c comparator to used for the sort
*/
@SuppressWarnings("fallthrough")
private static void binarySort(T[] a, int lo, int hi, int start,
Comparator super T> c) {
assert lo <= start && start <= hi;
if (start == lo)
start++;
for ( ; start < hi; start++) {
T pivot = a[start];
// Set left (and right) to the index where a[start] (pivot) belongs
int left = lo;
int right = start;
assert left <= right;
/*
* Invariants:
* pivot >= all in [lo, left).
* pivot < all in [right, start).
*/
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) >>> 1;
if (c.compare(pivot, a[mid]) < 0)
right = mid;
else
left = mid + 1;
}
assert left == right;
/*
* The invariants still hold: pivot >= all in [lo, left) and
* pivot < all in [left, start), so pivot belongs at left. Note
* that if there are elements equal to pivot, left points to the
* first slot after them -- that's why this sort is stable.
* Slide elements over to make room for pivot.
*/
int n = start - left; // The number of elements to move
// Switch is just an optimization for arraycopy in default case
switch (n) {
case 2: a[left + 2] = a[left + 1];
case 1: a[left + 1] = a[left];
break;
default: System.arraycopy(a, left, a, left + 1, n);
}
a[left] = pivot;
}
}可以看到其实其代码一点也不复杂,与我们上面分析的c语言代码几乎完全相同,只不过它所排序的元素不再是简单的int型,比较规则也不再是简单的比较数的大小,而是通过java中的Comparator接口来规定的,可以看到注释远远多于代码量,一方面这是因为那些天才们用其高超的艺术大大的简化了代码,另一方面也是为了解释关于选择折半插入排序的原因:
/**
* Sorts the specified portion of the specified array using a binary
* insertion sort. This is the best method for sorting small numbers
* of elements. It requires O(n log n) compares, but O(n^2) data
* movement (worst case).
/*
* The invariants still hold: pivot >= all in [lo, left) and
* pivot < all in [left, start), so pivot belongs at left. Note
* that if there are elements equal to pivot, left points to the
* first slot after them -- that's why this sort is stable.
* Slide elements over to make room for pivot.
*/从我截取的这两段注释来看,可以知道:
1折半插入排序是最好的算法对于排序小数量的元素This is the best method for sorting small numbers of elements.
2它只需要O(nlogn)的比较次数,但是其移动次数仍然为 O(n^2)。It requires O(n log n) compares, but O(n^2) data movement (worst case).
3它是稳定的排序算法。that's why this sort is stable.而快速排序不是稳定的排序。
分析到这我们就可以知道为何会选择折半插入排序,其中1和3是最主要的原因。




















 1073
1073











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








