本文分析 typeof 及 Javascript 类型相关的源码,版本为 V8 7.7.1。
typeof 源码分析
每一个 Javascript 对象都是 V8 中的 JSObject,JSObject 继承 JSReceiver:
// The JSObject describes real heap allocated JavaScript objects with
// properties.
class JSObject : public JSReceiver {
public:
static bool IsUnmodifiedApiObject(FullObjectSlot o);
// 后面略
}JSReceiver 继承 HeapObject:
// JSReceiver includes types on which properties can be defined, i.e.,
// JSObject and JSProxy.
class JSReceiver : public HeapObject {
public:
NEVER_READ_ONLY_SPACE
// Returns true if there is no slow (ie, dictionary) backing store.
inline bool HasFastProperties() const;
// 后面略
}所以每一个 Javascript 对象也是 HeapObject。
// HeapObject is the superclass for all classes describing heap allocated
// objects.
class HeapObject : public Object {
public:
// [map]: Contains a map which contains the object's reflective
// information.
inline Map map() const; // 本文的重点
inline void set_map(Map value);
inline MapWordSlot map_slot() const;
// 后面略
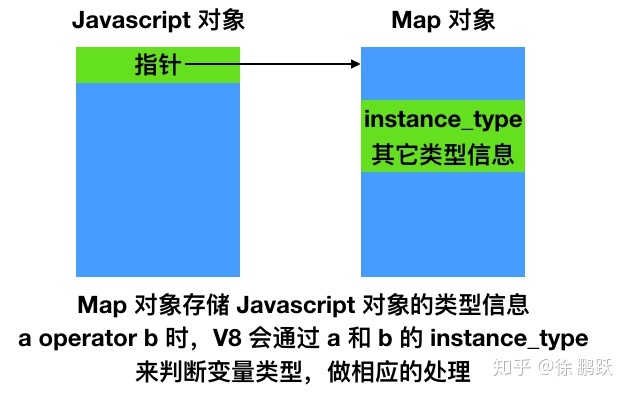
}HeapObject 偏移量为 0 的位置,是 Map 对象的指针,这里的 Map 不是 ES6 的 Map,而是 V8 中定义的一个 C++ 对象,本文的主角,声明如下:
// All heap objects have a Map that describes their structure.
// A Map contains information about:
// - Size information about the object
// - How to iterate over an object (for garbage collection)
//
// Map layout:
//
// 和类型相关的信息在此
// +----+----------+---------------------------------------------+
// | Int | The second int field |
// `---+----------+---------------------------------------------+
// | Short | [instance_type] 本文重点关注 |
// +----------+---------------------------------------------+
// | Byte | [bit_field] |
// | | - has_non_instance_prototype (bit 0) |
// | | - is_callable (bit 1) |
// | | - has_named_interceptor (bit 2) |
// | | - has_indexed_interceptor (bit 3) |
// | | - is_undetectable (bit 4) |
// | | - is_access_check_needed (bit 5) |
// | | - is_constructor (bit 6) |
// | | - has_prototype_slot (bit 7) |
// +----------+---------------------------------------------+
// | Byte | [bit_field2] |
// | | - is_extensible (bit 0) |
// | | - is_prototype_map (bit 1) |
// | | - unused bit (bit 2) |
// | | - elements_kind (bits 3..7) |
class Map : public HeapObject {
public:
// Instance size.
// Size in bytes or kVariableSizeSentinel if instances do not have
// a fixed size.
DECL_INT_ACCESSORS(instance_size)
// Size in words or kVariableSizeSentinel if instances do not have
// a fixed size.
DECL_INT_ACCESSORS(instance_size_in_words)
// 后面略
}从 Map 的注释可以知道,Map 存储了关于 Javascript 对象的大小、垃圾回收和类型相关的信息。和类型关系最密切的是 instance_type。
最近知乎偶尔会向笔者推送一些前端培训班的文章,有的文章说 Javascript 有 6 种类型,有的文章说 Javascript 有 7 种类型。这里笔者以 Javascript 的第 8 种类型 BigInt 举例,当在 d8 中执行以下代码:
let big = 2n
typeof big // bigintd8 会打印出变量 big 的类型,即 bigint。typeof 运算符核心代码如下:
Node* CodeStubAssembler::Typeof(Node* value) {
VARIABLE(result_var, MachineRepresentation::kTagged);
Label return_number(this, Label::kDeferred), if_oddball(this),
return_function(this), return_undefined(this), return_object(this),
return_string(this), return_bigint(this), return_result(this);
GotoIf(TaggedIsSmi(value), &return_number);
Node* map = LoadMap(value); // 1.获取 map 对象
GotoIf(IsHeapNumberMap(map), &return_number);
Node* instance_type = LoadMapInstanceType(map);// 2.获取 instance_type 字段
// 3.通过 instance_type 判断 value 是不是函数、对象、字符串、bigint、symbol...,并跳转,返回相应类型的字符串表示
GotoIf(InstanceTypeEqual(instance_type, ODDBALL_TYPE), &if_oddball);// 先拦截掉奇葩,比如 null
Node* callable_or_undetectable_mask = Word32And(
LoadMapBitField(map),
Int32Constant(Map::IsCallableBit::kMask | Map::IsUndetectableBit::kMask));
GotoIf(Word32Equal(callable_or_undetectable_mask,
Int32Constant(Map::IsCallableBit::kMask)),
&return_function);
GotoIfNot(Word32Equal(callable_or_undetectable_mask, Int32Constant(0)),
&return_undefined);
GotoIf(IsJSReceiverInstanceType(instance_type), &return_object);
GotoIf(IsStringInstanceType(instance_type), &return_string);
// 4.由于 2n 是 BigInt 类型,执行下面一行后,跳转 &return_bigint
GotoIf(IsBigIntInstanceType(instance_type), &return_bigint);
CSA_ASSERT(this, InstanceTypeEqual(instance_type, SYMBOL_TYPE));
result_var.Bind(HeapConstant(isolate()->factory()->symbol_string()));
Goto(&return_result);
BIND(&return_number);
{
result_var.Bind(HeapConstant(isolate()->factory()->number_string()));
Goto(&return_result);
}
BIND(&if_oddball);
{
Node* type = LoadObjectField(value, Oddball::kTypeOfOffset);
result_var.Bind(type);
Goto(&return_result);
}
BIND(&return_function);
{
result_var.Bind(HeapConstant(isolate()->factory()->function_string()));
Goto(&return_result);
}
BIND(&return_undefined);
{
result_var.Bind(HeapConstant(isolate()->factory()->undefined_string()));
Goto(&return_result);
}
BIND(&return_object);
{
result_var.Bind(HeapConstant(isolate()->factory()->object_string()));
Goto(&return_result);
}
BIND(&return_string);
{
result_var.Bind(HeapConstant(isolate()->factory()->string_string()));
Goto(&return_result);
}
BIND(&return_bigint);
{
// 5.BigInt 类型执行到这里
result_var.Bind(HeapConstant(isolate()->factory()->bigint_string()));
Goto(&return_result);
}
BIND(&return_result);
return result_var.value();
}CodeStubAssembler::Typeof 的主要逻辑很简单。既然要获取变量的类型,而且已知每一个 Javascript 对象都有一个与之关联的描述类型的 Map 对象,第一步当然是要拿到 Map 对象。V8 调用 LoadMap 来获取 Map,LoadMap 源码如下:
TNode<Map> CodeStubAssembler::LoadMap(SloppyTNode<HeapObject> object) {
return UncheckedCast<Map>(LoadObjectField(object, HeapObject::kMapOffset,
MachineType::TaggedPointer()));
}HeapObject::kMapOffset 是 V8 通过 C++ 的宏定义的枚举,值是 0,LoadMap 实质上是取参数 object 偏移量为 0 处的指针,也是是 Map 对象的地址。
拿到 Map 对象的地址后,开始从 Map 对象取 instance_type 字段,源码如下:
TNode<Int32T> CodeStubAssembler::LoadMapInstanceType(SloppyTNode<Map> map) {
return UncheckedCast<Int32T>(
LoadObjectField(map, Map::kInstanceTypeOffset, MachineType::Uint16()));
}Map::kInstanceTypeOffset 的值是 12,表示 instance_type 字段在 Map 对象上的偏移量。CodeStubAssembler::LoadMapInstanceType 的功能是从 Map 对象上取出 instance_type,instance_type 占用 16 bit 的空间。
取出 instance_type 后,其实也就知道了变量的类型,把 instance_type 和函数、对象、字符串、bigint 和 symbol 等类型的 instance_type 做比较,判断当前变量具体是哪种类型,然后跳转到不同的分支。如果用高级语言描述,CodeStubAssembler::Typeof 大多数逻辑相当于一个有多个分支的 switch case 语句。
因为 let big = 2n,所以 big 的类型是 BigInt,跳过前面的多个分支,下面这行代码会执行:
GotoIf(IsBigIntInstanceType(instance_type), &return_bigint);IsBigIntInstanceType 的定义很简单,判断 instance_type 和 BIGINT_TYPE 是否相等,BIGINT_TYPE 的值是 66。
TNode<BoolT> CodeStubAssembler::IsBigIntInstanceType(
SloppyTNode<Int32T> instance_type) {
return InstanceTypeEqual(instance_type, BIGINT_TYPE);
}
TNode<BoolT> CodeStubAssembler::InstanceTypeEqual(
SloppyTNode<Int32T> instance_type, int type) {
return Word32Equal(instance_type, Int32Constant(type));
}big 是 BigInt 类型的变量,IsBigIntInstanceType 返回 true,程序跳转到了标号 &return_bigint 处执行,并最终返回字符串 bigint。
BIND(&return_bigint);
{
result_var.Bind(HeapConstant(isolate()->factory()->bigint_string()));
Goto(&return_result);
}在 V8 中,每一个 Javascript 对象都有一个与之关联的 Map 对象,Map 对象描述 Javascript 对象类型相关的信息,类似元数据
Map 对象主要使用 16 bit 的 instance_type 字段来描述对应 Javascript 对象的类型
typeof 的两个坑
typeof document.all 等于 undefined

结果有些出乎意料,再看一下 Map 的注释:
// +----+----------+---------------------------------------------+
// | Int | The second int field |
// `---+----------+---------------------------------------------+
// | Short | [instance_type] 本文重点关注 |
// +----------+---------------------------------------------+
// | Byte | [bit_field] |
// | | - has_non_instance_prototype (bit 0) |
// | | - is_callable (bit 1) |
// | | - has_named_interceptor (bit 2) |
// | | - has_indexed_interceptor (bit 3) |
// document.all,null,undefined的 is_undetectable 为 1 |
// | | - is_undetectable (bit 4)
// | | - is_access_check_needed (bit 5) |
// | | - is_constructor (bit 6) |
// | | - has_prototype_slot (bit 7) |
// +----------+---------------------------------------------+
// | Byte | [bit_field2] |
// | | - is_extensible (bit 0) |
// | | - is_prototype_map (bit 1) |
// | | - unused bit (bit 2) |
// | | - elements_kind (bits 3..7) |Map 对象的 instance_type 相邻的字节定义了一些 bit,比如 is_callable,is_undetectable 和 is_constructor 等。null 和 undefined 的 is_undetectable bit 是 1,这点很容易理解。但同时也要看到,这些 bit 不是互斥的,document.all 虽然不是一个空对象,但它的 Map 对象的 is_undetectable 也是 1,所以才会有 typeof document.all 等于 undefined 的不合理情况。
typeof null 等于 object
至于前端“经典”的 typeof null === 'object',由于 null 和 undefinde 的 is_undetectable bit 同为 1,null 和 undefined 的流程应该是一样的,从源码的写法来看,为了避免出现 typeof null === 'undefined' 这种不合规范的情况,V8 对 null 提前做了一层判断,就在 CodeStubAssembler::Typeof 函数比较早的一行。
GotoIf(InstanceTypeEqual(instance_type, ODDBALL_TYPE), &if_oddball);null 的 instance_type 是 ODDBALL_TYPE(值为 67),跳转到 if_oddball 标号执行。完美避开了后续的判断,ODDBALL_TYPE 如果翻译成中文的话,可能会叫奇怪类型。至少从 ODDBALL_TYPE 的命名来看,V8 也认为 null 是一个不走寻常路的类型。
前端社区有很多人很多文章讨论 typeof null 等于 object 的问题,笔者认为这是个历史包袱,而且不合逻辑,这个问题没有什么为什么,也不具备讨论的价值。如果在 V8 中把下面这一行代码删掉,typeof null 会返回 undefined。
GotoIf(InstanceTypeEqual(instance_type, ODDBALL_TYPE), &if_oddball) 这一行代码出现的太早,和其它代码比较起来显得生硬,像是突然插进去的。明显 V8 是在填 typeof null 的坑,人生苦短,本节完。
null 和 undefined 虽然不是 Javascript 对象,却是 C++ 对象
null 和 undefined 的共同点是 is_undetectable bit 是 1,区别点在于 null 的 instance_type 是 ODDBALL_TYPE,CodeStubAssembler::Typeof 对 ODDBALL_TYPE(暂译为奇葩类型)做了特殊处理,提前返回
为什么 1 + 1 = 2,1 + '1' = '11'?

本文只讨论 1 + '1' = '11' 的情况。
既然已经知道每个 Javascript 对象都有与之关联的 Map 对象来描述类型信息,那么只要知道左右两个操作数的类型,就可以判断是做加法还是做字符串相连。从 V8 加法的字节码处理函数一路追起,加法核心代码如下,有删减。
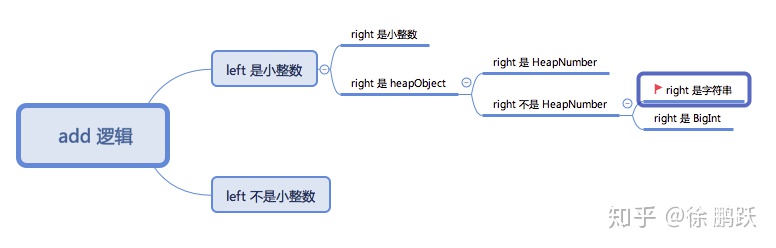
TF_BUILTIN(Add, AddStubAssembler) {
Node* context = Parameter(Descriptor::kContext);
// 1.取得两个参数var_left、var_left
VARIABLE(var_left, MachineRepresentation::kTagged,
Parameter(Descriptor::kLeft));
VARIABLE(var_right, MachineRepresentation::kTagged,
Parameter(Descriptor::kRight));
// We might need to loop several times due to ToPrimitive, ToString and/or
// ToNumeric conversions.
VARIABLE(var_result, MachineRepresentation::kTagged);
Variable* loop_vars[2] = {&var_left, &var_right};
Label loop(this, 2, loop_vars),
string_add_convert_left(this, Label::kDeferred),
string_add_convert_right(this, Label::kDeferred),
do_bigint_add(this, Label::kDeferred);
Goto(&loop);
BIND(&loop);
{
Node* left = var_left.value();
Node* right = var_right.value();
Label if_left_smi(this), if_left_heapobject(this);
// 2.根据 left 的类型,跳转不同的分支,本文 left 是一个小整数,跳转 BIND(&if_left_smi)
Branch(TaggedIsSmi(left), &if_left_smi, &if_left_heapobject);
BIND(&if_left_smi);
{
Label if_right_smi(this), if_right_heapobject(this);
// 3.根据 right 的类型,跳转不同的分支,本文 right 是字符串,跳转 BIND(&if_right_heapobject) 执行
Branch(TaggedIsSmi(right), &if_right_smi, &if_right_heapobject);
BIND(&if_right_smi);
{
Label if_overflow(this);
TNode<Smi> result = TrySmiAdd(CAST(left), CAST(right), &if_overflow);
Return(result);
BIND(&if_overflow);
{
var_left_double.Bind(SmiToFloat64(left));
var_right_double.Bind(SmiToFloat64(right));
Goto(&do_double_add);
}
} // if_right_smi
BIND(&if_right_heapobject);
{
Node* right_map = LoadMap(right);
Label if_right_not_number(this, Label::kDeferred);
GotoIfNot(IsHeapNumberMap(right_map), &if_right_not_number);
// {right} is a HeapNumber.
var_left_double.Bind(SmiToFloat64(left));
var_right_double.Bind(LoadHeapNumberValue(right));
Goto(&do_double_add);
BIND(&if_right_not_number);
{
CodeStubAssembler::Print("if_right_not_number");
Node* right_instance_type = LoadMapInstanceType(right_map);
// 4.right 是字符串,跳转 BIND(&string_add_convert_left);
GotoIf(IsStringInstanceType(right_instance_type),
&string_add_convert_left);
GotoIf(IsBigIntInstanceType(right_instance_type), &do_bigint_add);
ConvertAndLoop(&var_right, right_instance_type, &loop, context);
}
} // if_right_heapobject
} // if_left_smi
}
BIND(&string_add_convert_left);
{
// Convert {left} to a String and concatenate it with the String {right}.
// 5.最后执行到了这里,left 转成字符串后,与 right 进行字符串连接
TailCallBuiltin(Builtins::kStringAdd_ConvertLeft, context, var_left.value(),
var_right.value());
}
}代码逻辑很简单,总体来说是个分支嵌套,首先判断左边操作数的类型,是小整数。然后判断右面操作数的类型,是字符串,最后代码把左边的小整数转换成字符串,与右面操作数做字符串连接的逻辑。
总结







 本文深入分析了V8引擎中typeof运算符的实现,探讨了为何typeof document.all等于undefined以及typeof null等于object的问题。通过对V8源码的解析,揭示了对象类型判断的细节,同时也解释了1 + 1 = 2,而1 + '1' = '11'的原因。
本文深入分析了V8引擎中typeof运算符的实现,探讨了为何typeof document.all等于undefined以及typeof null等于object的问题。通过对V8源码的解析,揭示了对象类型判断的细节,同时也解释了1 + 1 = 2,而1 + '1' = '11'的原因。














 5542
5542

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








