二叉树的最大深度
leetcode https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
回溯基本思路
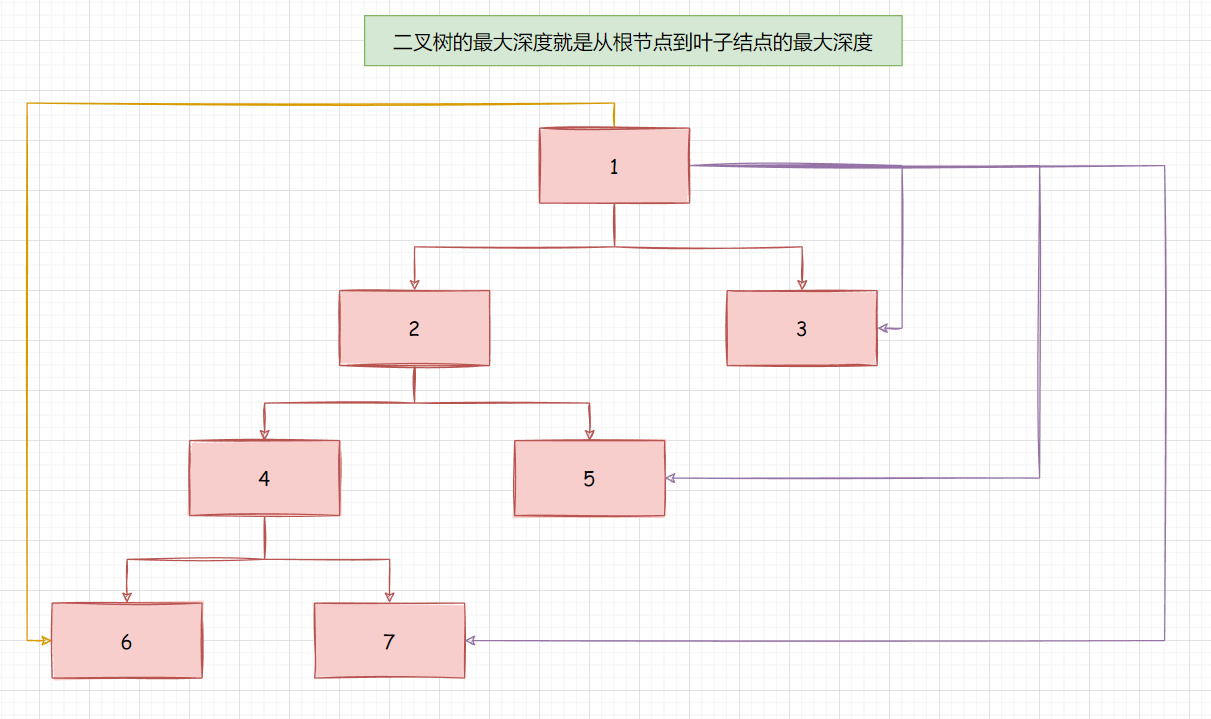
二叉树的最大深度就是 : 从根节点到叶子节点的最大的深度
- 定义一个全局变量 int res = 0 , 以及局部变量 depth 表示当前层的深度
- 当我们访问到根节点的时候(前序位置), 就让 depth++;
- 当我们执行到后续位置的时候, 就回溯, 让depth–;
- 当遇到叶子节点时, 就比较 res 和 当前层哪个大
回溯代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 需要有一个全局变量去存储
int res = 0 ;
public void getDepth(TreeNode node, int depth) {
if(node == null){
// 此时到叶子节点了
// 判断是否是最大
res = Math.max(depth, res);
return;
}
// 是回溯, 不是分治
// 最大深度就是从根节点到叶子节点经过的最大节点数
// 所以在前序位置累加
depth++;
getDepth(node.left, depth);
getDepth(node.right, depth);
// 撤销
depth--;
}
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
getDepth(root, 0);
return res;
}
}
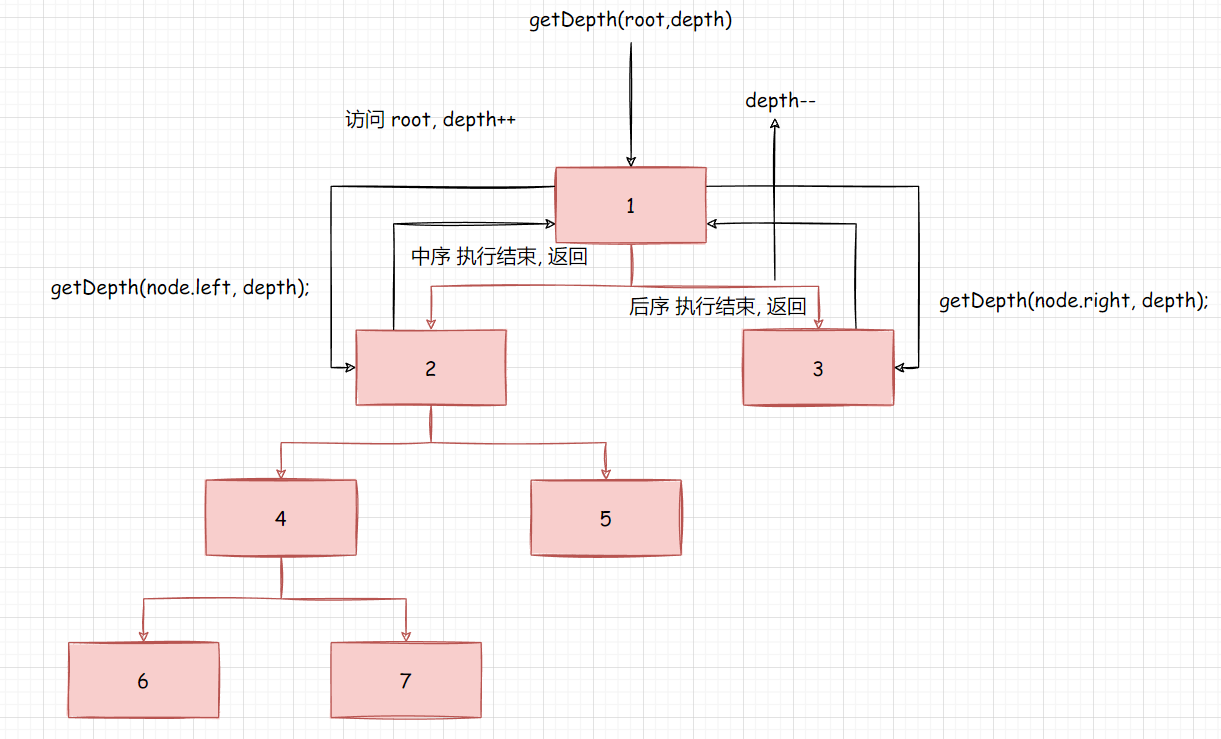
二叉树的最小深度
分治基本思路
我们不能使用计算二叉树的最大深度的那种方法区计算二叉树的最小深度, 原因如下 :
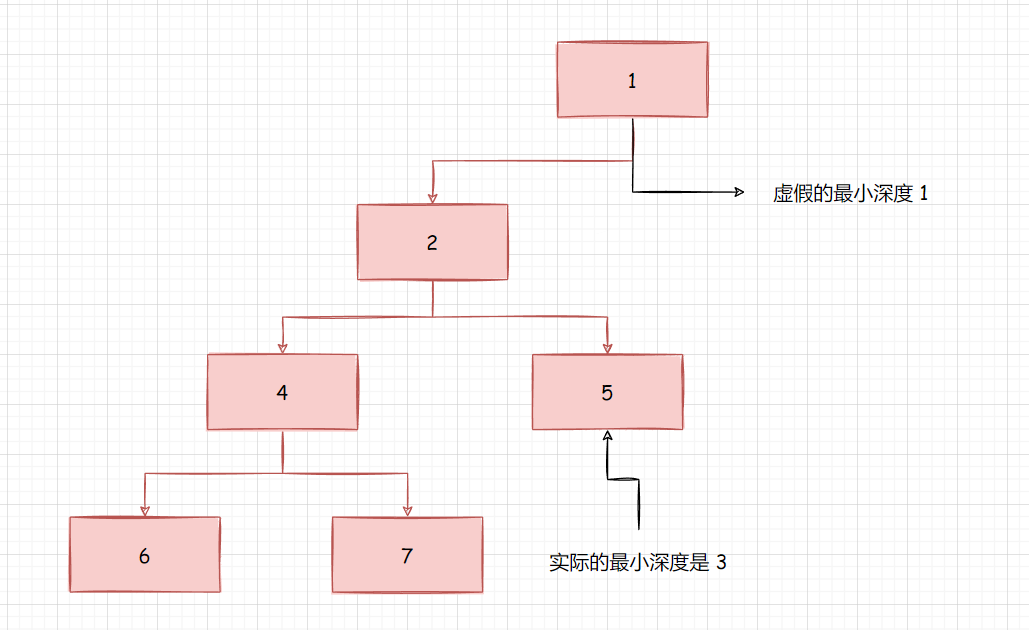
比如上面这个树, 右边完全是空的, 二叉树的最大深度判断叶子节点是 :
if(node == null) {
res = Math.max();
}
最大深度之所以ok是计算的是最大深度, 右边即使是1也不影响, 但是如果计算的是最小深度, 在比较时, 就无法真正获取最小深度
所以最小深度的计算思路是 :
- 根节点的最小深度 = 1 + min(左子树的最小深度, 右子树的最小深度)
- 假设左子树为空, 那么 根节点的最小深度 = 1 + 右子树的最小深度
- 假设右子树为空, 那么 根节点的最小深度 = 1 + 左子树的最小深度
- 假设都为空, 就是 null
- 这个其实是分治的思想
这个思路也可以处理最大深度, 也是一样的
递归三步 :
-
递归函数 :
public int getDepth(TreeNode root) -
终止条件 :
if(root == null) { return 0; } -
当前层处理逻辑
// 三种情况 : int leftDepth = getDepth(root.left); int rightDepth = getDepth(root.right); // 如果当前这棵树的左孩子不为null, 但是右孩子为null, // 此时不是叶子节点, 最小深度是 1 + 左子树的最小深度 if(root.left != null && root.right == null) { return 1 + leftDepth; }else if(root.left == null && root.right != null) { return 1 + rightDepth; }else{ // 左右都不为null1的情况 // 比较左子树的深度小还是右子树的深度小 int result = 1 + Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth); return result; }
分治代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int getDepth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
// 左右都不等于null
int leftDepth = getDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(root.right);
// 如果当前这棵树的左孩子不为null, 但是右孩子为null,
// 此时不是叶子节点, 最小深度是 1 + 左子树的最小深度
if(root.left != null && root.right == null) {
return 1 + leftDepth;
}else if(root.left == null && root.right != null) {
return 1 + rightDepth;
}else{
// 左右都不为null1的情况
// 比较左子树的深度小还是右子树的深度小
int result = 1 + Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return result;
}
}
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return getDepth(root);
}
}
回溯基本思路
递归三步 :
-
确定函数 :
public void getDepth(TreeNode node, int depth) -
终止条件 : 叶子节点, 特征是 左右子树为空
-
当前层逻辑 :
- 其实就是选择, 先去遍历下左子树, 看看有没有最小深度, 逐层向下时, depth++, 重新回到根节点时, 得撤回
- 否则, 当我去遍历右子树, 看看有没有最小深度时, 就执行了两次 depth++;
if(node.left != null) { depth++; getDepth(node.left, depth); // 撤销选择, 为啥要撤销, // 因为还要选择右子树 depth--; } if(node.right != null) { depth++; // 这要是不撤销, 如果执行了 getDepth(node.left, depth) 就累加两次了 getDepth(node.right, depth); depth--; }
回溯代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public void getDepth(TreeNode node, int depth){
if(node.left == null && node.right == null) {
res = Math.min(res, depth);
return;
}
if(node.left != null) {
depth++;
getDepth(node.left, depth);
// 撤销选择, 为啥要撤销,
// 因为还要选择右子树
depth--;
}
if(node.right != null) {
depth++;
// 这要是不撤销, 如果执行了 getDepth(node.left, depth) 就累加两次了
getDepth(node.right, depth);
depth--;
}
}
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
getDepth(root,1);
return res;
}
}
迭代基本思想
思路很简单 : 层序遍历, 每走一层, depth+1, 第一次遇到叶子节点就是最小深度
迭代代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int depth = 0;
boolean flag = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
if(node.left == null && node.right == null) {
// 叶子节点
depth++;
return depth;
}
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}























 9029
9029











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










