文章目录
数据结构
数据结构是算法的基础
数据结构分为线性结构和非线性结构
2, 非线性结构
非线性结构包括:二维数组,多维数组,广义表,树结构,图结构
数组每次插入都需要复制当前数据到一个新的数据才能有类似扩容的功能。List其实是一种优化的数组,会尽量批量扩容,不会每次插入扩容,底层使用的还是数组。这种因素导致数组在插入的时候速度慢。
然后链表的话插入的时候速度就很快了,但是查找的时候,如果链表数据很多,就需要从头查找到尾部,其实相对而言查找速度就比较慢。
这就是学习树结构的原因。

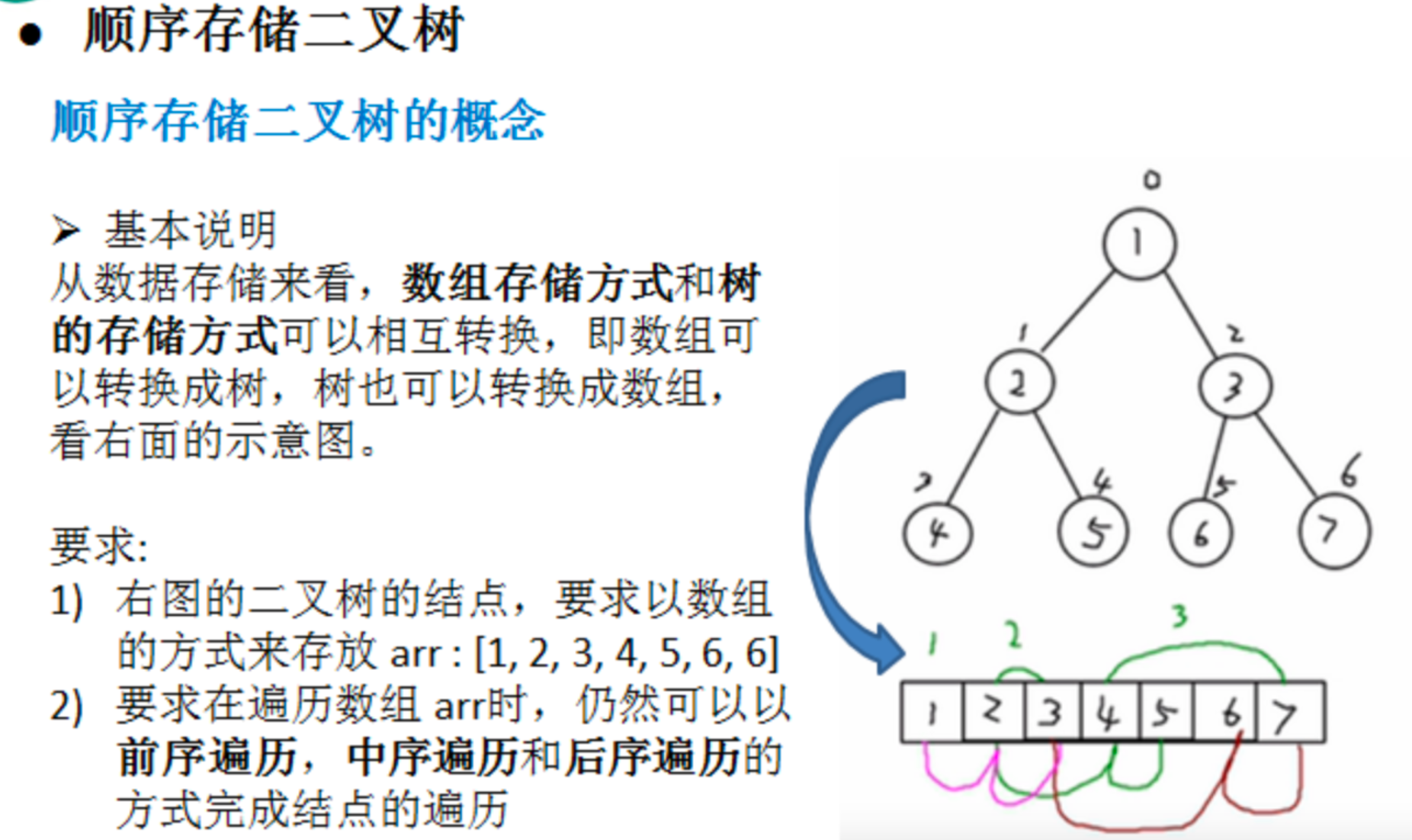
2.1, 二维数组
一维数组为线型结构,但是二维数组则为非线形结构
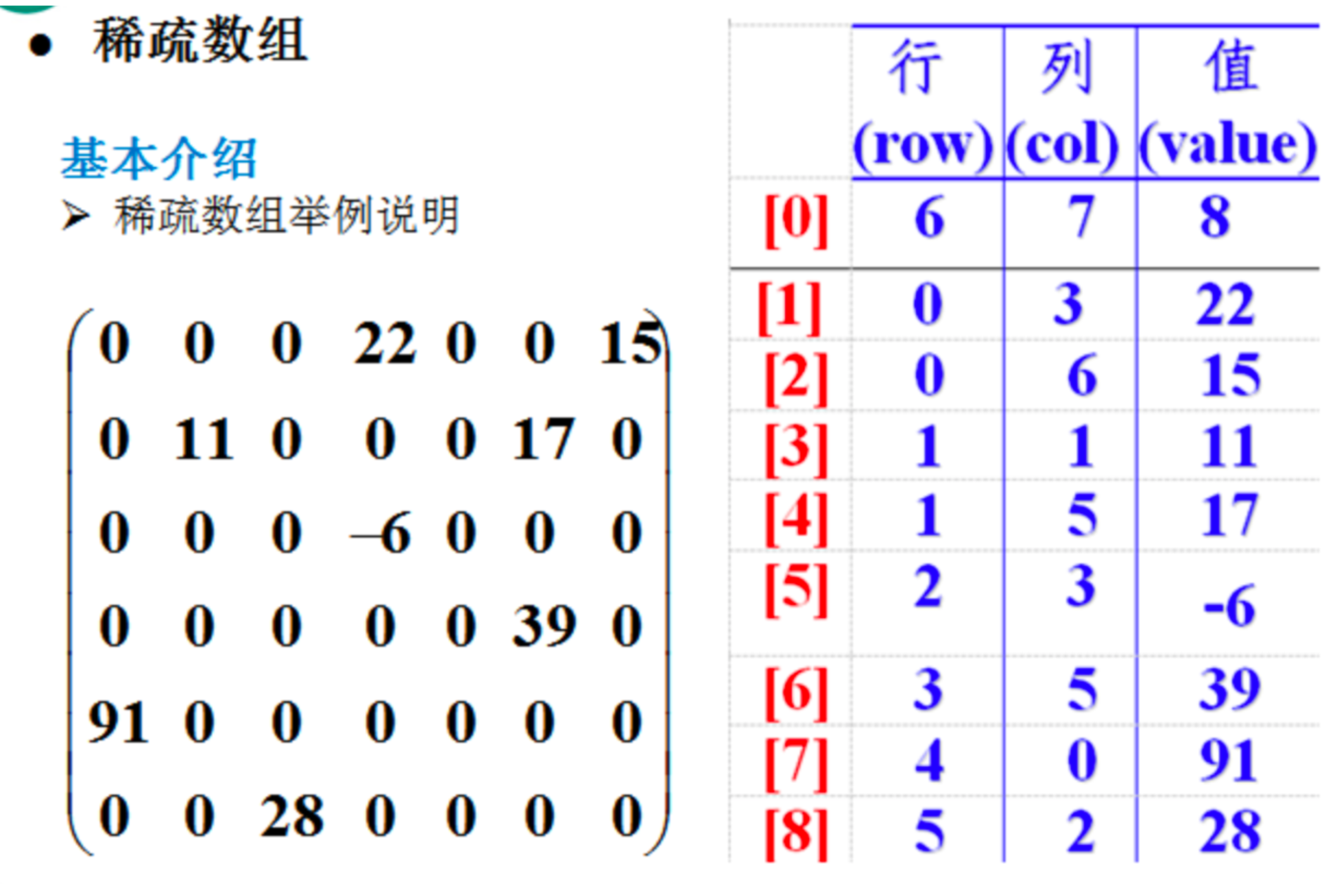
稀疏数组(sparseArray)
稀疏数组其实是一个二维数组,这里放在线性结构的数组里面并不合适。所以放入非线性结构的二维数组中记录
稀疏数组:数组中有多少个非0数字, 其转化成稀疏数组后, 对应的行数为数字个数+1,其列数固定为3列;
其中第0行:记录数组的总总行数列数以及对应的非0数字个数
第i行分别记录第i个不为的数字的行数,列数以及具体值
package im.bool;
/**
* #Author : ivanl001
* #Date : 2019/11/2 14:12
* #Desc : 稀疏数组-棋盘的应用
**/
public class a01_sparseArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//棋盘 11*11
//0表示没有棋子,1表示黑子, 2表示蓝子
int[][] chessArr = new int[11][11];
chessArr[1][2] = 1;
chessArr[2][3] = 2;
chessArr[2][4] = 2;
chessArr[3][4] = 2;
System.out.println("原始棋盘二维数组是:------------------------------------");
printArr(chessArr);
/*for (int[] row : chessArr) {
for (int num : row) {
System.out.printf(num + "\t");
}
System.out.println("\n");
}*/
System.out.println("开始转换成稀疏数组:-------------------------------------");
//1,先遍历二维数组,得到非0数据个数
int sum = 0;
for (int[] ints : chessArr) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
if (anInt != 0) {
sum++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("遍历之后获取到非零数据个数:" + sum);
//2, 创建稀疏数组
int[][] sparseArr = new int[1 + sum][3];
//3, 给稀疏数组赋值
//-------第一行是整体描述---------
//说明原先数组有11行
sparseArr[0][0] = 11;
//说明原先数组有11列
sparseArr[0][1] = 11;
//说明原先数组有sum个不为零到数字
sparseArr[0][2] = sum;
//-------其余行是非零描述--------
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chessArr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chessArr[i].length; j++) {
if (chessArr[i][j] != 0) {
count ++;
sparseArr[count][0] = i;
sparseArr[count][1] = j;
sparseArr[count][2] = chessArr[i][j];
}
}
}
//打印稀疏数组
System.out.println("稀疏数组是:");
printArr(sparseArr);
System.out.println("把稀疏数组转换回原始二维数组:----------------------------");
int rowNum = sparseArr[0][0];
int columnNum = sparseArr[0][1];
int[][] theOriginalArr = new int[rowNum][columnNum];
for (int i = 1; i < sparseArr.length; i++) {
theOriginalArr[sparseArr[i][0]][sparseArr[i][1]] = sparseArr[i][2];
}
System.out.println("恢复后的二维数组是:---------------------------");
printArr(theOriginalArr);
}
private static void printArr(int[][] arr){
for (int[] row : arr) {
for (int num : row) {
System.out.printf(num + "\t");
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
}
}
2.2, 多维数组
# 跳过不表
2.3, 树结构
# 为什么需要树结构?
# 1, 数组查询速度快,但是插入速度慢,因为插入的时候实际是进行数组的复制
# 2, 链表插入速度快,但是查询的时候需要重头开始遍历,速度又会有一定限制
# 如果使用树结构,可以实现查询速度较快,插入速度也较快
满二叉树:所有的叶子结点都是在最后一级
-
遍历的时候看主节点,先遍历主节点就是前序遍历,中间遍历主节点,是中序遍历,最后遍历主节点,是后序遍历
-
前序遍历: 先遍历主节点,然后遍历左节点,最后遍历右节点
-
中序遍历: 先遍历左节点, 然后遍历主节点,最后遍历右节点
-
后序遍历: 先遍历左节点,然后遍历右节点,最后遍历主节点
1, 二叉树的遍历/查找/删除
package im.bool.a09_tree;
/**
* @author : 不二
* @date : 2021/5/8-下午8:25
* @desc : 二叉树代码重写
* 包括二叉树前中后三种遍历方式
* 以及二叉树的前中后三种查找方式
* 以及二叉树的元素删除
**/
public class a09_01_BinaryTreeDemo_v1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 首先构造一个数类并添加节点元素
StudentBinaryTree binaryTree = new StudentBinaryTree();
StudentNode heroNode00 = new StudentNode(0, "1");
StudentNode heroNode01 = new StudentNode(1, "1");
StudentNode heroNode02 = new StudentNode(2, "2");
StudentNode heroNode03 = new StudentNode(3, "3");
StudentNode heroNode04 = new StudentNode(4, "4");
StudentNode heroNode05 = new StudentNode(5, "5");
StudentNode heroNode06 = new StudentNode(6, "6");
StudentNode heroNode07 = new StudentNode(7, "7");
StudentNode heroNode08 = new StudentNode(8, "8");
StudentNode heroNode09 = new StudentNode(9, "9");
StudentNode heroNode10 = new StudentNode(10, "10");
StudentNode heroNode11 = new StudentNode(11, "11");
StudentNode heroNode12 = new StudentNode(12, "12");
StudentNode heroNode13 = new StudentNode(13, "13");
StudentNode heroNode14 = new StudentNode(14, "14");
/*
0
1 2
3 4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
*/
// 设置第一行
binaryTree.setRootStudent(heroNode00);
heroNode00.setLeft(heroNode01);
heroNode00.setRight(heroNode02);
heroNode01.setLeft(heroNode03);
heroNode01.setRight(heroNode04);
heroNode02.setLeft(heroNode05);
heroNode02.setRight(heroNode06);
heroNode03.setLeft(heroNode07);
heroNode03.setRight(heroNode08);
heroNode04.setLeft(heroNode09);
heroNode04.setRight(heroNode10);
heroNode05.setLeft(heroNode11);
heroNode05.setRight(heroNode12);
heroNode06.setLeft(heroNode13);
heroNode06.setRight(heroNode14);
System.out.println("前序遍历:");
binaryTree.preOrder();// 1 2 3 5 4
System.out.println("中序遍历:");
binaryTree.infixOrder();// 2 1 5 3 4
System.out.println("后序遍历:");
binaryTree.suffixOrder();// 2 5 4 3 1
/*System.out.println("前序查找:");
StudentNode studentNode = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(5);
System.out.println(studentNode);
System.out.println("中序查找:");
StudentNode studentNode1 = binaryTree.infixOrderSearch(5);
System.out.println(studentNode1);
System.out.println("后序查找:");
StudentNode studentNode2 = binaryTree.suffixOrderSearch(5);
System.out.println(studentNode2);
// 此处规定:如果删除的是叶子节点,直接删除即可
// 如果删除的是非叶子节点,把该非叶子节点下所有的节点都一并删除掉
System.out.println("删除节点:");
binaryTree.deleteNode(5);
System.out.println("Ivanl001");*/
}
}
class StudentBinaryTree {
StudentNode rootStudent;
public StudentNode getRootStudent() {
return rootStudent;
}
public void setRootStudent(StudentNode rootStudent) {
this.rootStudent = rootStudent;
}
// 前序查找
public StudentNode preOrderSearch(int id) {
return this.rootStudent.preOrderSearch(id);
}
// 中序查找
public StudentNode infixOrderSearch(int id) {
return this.rootStudent.infixSearch(id);
}
// 后序查找
public StudentNode suffixOrderSearch(int id) {
return this.rootStudent.suffixOrderSearch(id);
}
// 前序遍历(先遍历主节点,然后遍历左节点,最后遍历右节点)
public void preOrder() {
if (rootStudent == null) {
System.out.println("该树结构无任何元素");
} else {
this.rootStudent.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍历(先遍历左节点, 然后遍历主节点,最后遍历右节点)
public void infixOrder() {
if (rootStudent == null) {
System.out.println("该树结构无任何元素");
} else {
this.rootStudent.infixOrder();
}
}
// 后序遍历(先遍历左节点,然后遍历右节点,最后遍历主节点)
public void suffixOrder() {
if (rootStudent == null) {
System.out.println("该树结构无任何元素");
} else {
this.rootStudent.suffixOrder();
}
}
public void deleteNode(int i) {
if (this.rootStudent.getId() == i) {
System.out.println("删除的是最顶层根节点,无法删除!");
} else {
this.rootStudent.deleteNode(i);
}
}
}
// 这里是个学生类的二叉树子节点
class StudentNode {
private int id;
private String name;
private StudentNode left;
private StudentNode right;
public StudentNode(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
//删除
public void deleteNode_v1(int no) {
//这里和遍历或者查找不一样哈, 因为如果是遍历,是不会返回的
//这里就只能默认只有一个
if (this.left != null && this.left.id == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
if (this.right != null && this.right.id == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.deleteNode(no);
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.deleteNode(no);
}
}
public void deleteNode(int id) {
if (this.left != null) {
if (this.getLeft().getId() == id) {
this.setLeft(null);
return;
}
this.left.deleteNode(id);
}
if (this.right != null) {
if (this.getRight().getId() == id) {
this.setRight(null);
return;
}
this.right.deleteNode(id);
}
/*if (this.getLeft().getId() == id) {
this.setLeft(null);
return;
}
if (this.getRight().getId() == id) {
this.setRight(null);
return;
}*/
}
public StudentNode preOrderSearch(int id) {
// 1, 先找根节点
System.out.println("开始找到的id为:" + this.id);
if (this.id == id) {
return this;
}
// 2, 然后找左节点
StudentNode studentNode = null;
if (this.getLeft() != null) {
studentNode = this.getLeft().preOrderSearch(id);
}
// 这里使用studentNode进行判断是因为不能直接return this.getLeft().preOrderSearch(id). 否则右侧的判断就没法走了
if (studentNode != null) {
return studentNode;
}
// 3, 最后找右节点
// 如果studentNode 为null,说明还未找到
if (this.getRight() != null) {
studentNode = this.getRight().preOrderSearch(id);
}
// 这里为null说明为找到
return studentNode;
}
public StudentNode infixSearch(int id) {
// 1,先找左节点
StudentNode studentNode = null;
if (this.getLeft() != null) {
studentNode = this.getLeft().infixSearch(id);
}
// 这里使用studentNode进行判断是因为不能直接return this.getLeft().preOrderSearch(id). 否则右侧的判断就没法走了
// 左节点找到直接返回左节点
if (studentNode != null) {
return studentNode;
}
// 2,然后找根节点
// 左节点没找到对比根节点
System.out.println("开始找到的id为:" + this.id);
if (this.id == id) {
return this;
}
// 3,最后找右节点
// 如果根节点也没找到,找右节点
// 如果studentNode 为null,说明还未找到
if (this.getRight() != null) {
studentNode = this.getRight().infixSearch(id);
}
// 这里为null说明为找到
return studentNode;
}
public StudentNode suffixOrderSearch(int id) {
// 1,先找左节点
// 左节点找到直接返回左节点
StudentNode studentNode = null;
if (this.getLeft() != null) {
studentNode = this.getLeft().suffixOrderSearch(id);
}
// 这里使用studentNode进行判断是因为不能直接return this.getLeft().preOrderSearch(id). 否则右侧的判断就没法走了
if (studentNode != null) {
return studentNode;
}
// 2,然后找右节点
// 如果左节点没找到,找右节点
// 如果studentNode 为null,说明还未找到
if (this.getRight() != null) {
studentNode = this.getRight().suffixOrderSearch(id);
}
// 如果右侧ok了直接返回就行了
if (studentNode != null) {
return studentNode;
}
// 3,最后找根节点
// 如果左右都没找到, 再对比根节点
System.out.println("开始找到的id为:" + this.id);
if (this.id == id) {
return this;
}
// 这里为null说明为找到
return studentNode;
}
public void preOrder(){
// 先打印出当前
System.out.println(this);
if (this.left != 







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 4932
4932











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








