Flink-05 流处理API
1. Environment
1.getExecutionEnvironment
创建一个执行环境,表示当前执行程序的上下文。 如果程序是独立调用的,则此方法返回本地执行环境;如果从命令行客户端调用程序以提交到集群,则此方法返回此集群的执行环境,也就是说,getExecutionEnvironment会根据查询运行的方式决定返回什么样的运行环境,是最常用的一种创建执行环境的方式。
ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
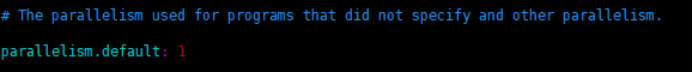
如果没有设置并行度,会以flink-conf.yaml中的配置为准,默认是1。
2.createLocalEnvironment
返回本地执行环境,需要在调用时指定默认的并行度。
LocalStreamEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironment(1);
3.createRemoteEnvironment
返回集群执行环境,将Jar提交到远程服务器。需要在调用时指定JobManager的IP和端口号,并指定要在集群中运行的Jar包。
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createRemoteEnvironment("jobmanage-hostname", 6123, "YOURPATH//WordCount.jar");
2 . Source
1.从集合读取数据
public class SourceTest1_Collection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// 1.Source:从集合读取数据
DataStream<SensorReading> sensorDataStream = env.fromCollection(
Arrays.asList(
new SensorReading("sensor_1", 1547718199L, 35.8),
new SensorReading("sensor_6", 1547718201L, 15.4),
new SensorReading("sensor_7", 1547718202L, 6.7),
new SensorReading("sensor_10", 1547718205L, 38.1)
)
);
// 2.打印
sensorDataStream.print();
// 3.执行
env.execute();
}
}
2.从文件读取数据
DataStream<String> dataStream = env.readTextFile("YOUR_FILE_PATH ");
3.以kafka消息队列的数据作为来源
pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.flink/flink-connector-kafka-0.11 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-kafka-0.11_2.12</artifactId>
<version>1.10.1</version>
</dependency>
// kafka配置项
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092");
properties.setProperty("group.id", "consumer-group");
properties.setProperty("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
properties.setProperty("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
properties.setProperty("auto.offset.reset", "latest");
// 从kafka读取数据
DataStream<String> dataStream = env.addSource( new FlinkKafkaConsumer011<String>("sensor", new SimpleStringSchema(), properties));
4.自定义Source
除了以上的source数据来源,我们还可以自定义source。需要做的,只是传入一个SourceFunction就可以。具体调用如下:
DataStream<SensorReading> dataStream = env.addSource( new MySensor());
我们希望可以随机生成传感器数据,MySensorSource具体的代码实现如下:
public static class MySensor implements SourceFunction<SensorReading>{
private boolean running = true;
public void run(SourceContext<SensorReading> ctx) throws Exception {
Random random = new Random();
HashMap<String, Double> sensorTempMap = new HashMap<String, Double>();
for( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ){
sensorTempMap.put("sensor_" + (i + 1), 60 + random.nextGaussian() * 20);
}
while (running) {
for( String sensorId: sensorTempMap.keySet() ){
Double newTemp = sensorTempMap.get(sensorId) + random.nextGaussian();
sensorTempMap.put(sensorId, newTemp);
ctx.collect( new SensorReading(sensorId, System.currentTimeMillis(), newTemp));
}
Thread.sleep(1000L);
}
}
public void cancel() {
this.running = false;
}
}
3 . Transform
1.map
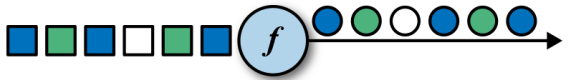
DataStream<Integer> mapStram = dataStream.map(new MapFunction<String, Integer>() {
public Integer map(String value) throws Exception {
return value.length();
}
});
2.flatmap
DataStream<String> flatMapStream = dataStream.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() {
public void flatMap(String value, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
String[] fields = value.split(",");
for( String field: fields )
out.collect(field);
}
});
3.filter
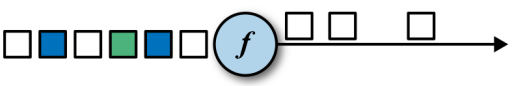
DataStream<Interger> filterStream = dataStream.filter(new FilterFunction<String>() {
public boolean filter(String value) throws Exception {
return value == 1;
}
});
4.keyby

DataStream → KeyedStream:逻辑地将一个流拆分成不相交的分区,每个分区包含具有相同key的元素,在内部以hash的形式实现的。
5.滚动聚合算子 (Rolling Aggregation)
这些算子可以针对KeyedStream的每一个支流做聚合。
sum()
min()
max()
minBy()
maxBy()
6.Reduce
KeyedStream → DataStream:一个分组数据流的聚合操作,合并当前的元素和上次聚合的结果,产生一个新的值,返回的流中包含每一次聚合的结果,而不是只返回最后一次聚合的最终结果。
DataStream<String> inputStream = env.readTextFile("sensor.txt");
// 转换成SensorReading类型
DataStream<SensorReading> dataStream = inputStream.map(new MapFunction<String, SensorReading>() {
public SensorReading map(String value) throws Exception {
String[] fileds = value.split(",");
return new SensorReading(fileds[0], new Long(fileds[1]), new Double(fileds[2]));
}
});
// 分组
KeyedStream<SensorReading, Tuple> keyedStream = dataStream.keyBy("id");
// reduce聚合,取最小的温度值,并输出当前的时间戳
DataStream<SensorReading> reduceStream = keyedStream.reduce(new ReduceFunction<SensorReading>() {
@Override
public SensorReading reduce(SensorReading value1, SensorReading value2) throws Exception {
return new SensorReading(
value1.getId(),
value2.getTimestamp(),
Math.min(value1.getTemperature(), value2.getTemperature()));
}
});
7.Split 和 Select

DataStream → SplitStream:根据某些特征把一个DataStream拆分成两个或者多个DataStream。

SplitStream→DataStream:从一个SplitStream中获取一个或者多个DataStream。
需求:传感器数据按照温度高低(以30度为界),拆分成两个流。
SplitStream<SensorReading> splitStream = dataStream.split(new OutputSelector<SensorReading>() {
@Override
public Iterable<String> select(SensorReading value) {
return (value.getTemperature() > 30) ? Collections.singletonList("high") : Collections.singletonList("low");
}
});
DataStream<SensorReading> highTempStream = splitStream.select("high");
DataStream<SensorReading> lowTempStream = splitStream.select("low");
DataStream<SensorReading> allTempStream = splitStream.select("high", "low");
8.Connect 和 CoMap

DataStream,DataStream → ConnectedStreams:连接两个保持他们类型的数据流,两个数据流被Connect之后,只是被放在了一个同一个流中,内部依然保持各自的数据和形式不发生任何变化,两个流相互独立。

ConnectedStreams → DataStream:作用于ConnectedStreams上,功能与map和flatMap一样,对ConnectedStreams中的每一个Stream分别进行map和flatMap处理。
// 合流 connect
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Double>> warningStream = highTempStream.map(new MapFunction<SensorReading, Tuple2<String, Double>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<String, Double> map(SensorReading value) throws Exception {
return new Tuple2<>(value.getId(), value.getTemperature());
}
});
ConnectedStreams<Tuple2<String, Double>, SensorReading> connectedStreams = warningStream.connect(lowTempStream);
DataStream<Object> resultStream = connectedStreams.map(new CoMapFunction<Tuple2<String,Double>, SensorReading, Object>() {
@Override
public Object map1(Tuple2<String, Double> value) throws Exception {
return new Tuple3<>(value.f0, value.f1, "warning");
}
@Override
public Object map2(SensorReading value) throws Exception {
return new Tuple2<>(value.getId(), "healthy");
}
});
9.Union

DataStream → DataStream:对两个或者两个以上的DataStream进行union操作,产生一个包含所有DataStream元素的新DataStream。
DataStream<SensorReading> unionStream = highTempStream.union(lowTempStream);
Connect与 Union 区别:
1. Union之前两个流的类型必须是一样,Connect可以不一样,在之后的coMap中再去调整成为一样的。
2. Connect只能操作两个流,Union可以操作多个。
4 . 支持的数据类型
Flink使用类型信息的概念来表示数据类型,并为每个数据类型生成特定的序列化器、反序列化器和比较器。
Flink还具有一个类型提取系统,该系统分析函数的输入和返回类型,以自动获取类型信息,从而获得序列化器和反序列化器。但是,在某些情况下,例如lambda函数或泛型类型,需要显式地提供类型信息,才能使应用程序正常工作或提高其性能。
Flink支持Java和Scala中所有常见数据类型。使用最广泛的类型有以下几种。
1.基础数据类型
Flink支持所有的Java和Scala基础数据类型,Int, Double, Long, String, …
DataStream<Integer> numberStream = env.fromElements(1, 2, 3, 4);
numberStream.map(data -> data * 2);
2.Java和Scala元组(Tuples)
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> personStream = env.fromElements(
new Tuple2("Adam", 17),
new Tuple2("Sarah", 23) );
personStream.filter(p -> p.f1 > 18);
3.Scala 样例类(case class)
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
val persons: DataStream[Person] = env.fromElements(
Person("Adam", 17),
Person("Sarah", 23) )
persons.filter(p => p.age > 18)
4.Java 简单对象(POJOS)
public class Person {
public String name;
public int age;
public Person() {}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
DataStream<Person> persons = env.fromElements(
new Person("Alex", 42),
new Person("Wendy", 23));
5.其它(Arrays,Lists,Maps,Enums等等)
Flink对Java和Scala中的一些特殊目的的类型也都是支持的,比如Java的ArrayList,HashMap,Enum等等。
5. 实现UDF函数-更细粒度的控制流
1.函数类(Function Classes)
Flink暴露了所有udf函数的接口(实现方式为接口或者抽象类)。例如MapFunction, FilterFunction, ProcessFunction等等。
下面例子实现了FilterFunction接口:
DataStream<String> flinkTweets = tweets.filter(new FlinkFilter());
public static class FlinkFilter implements FilterFunction<String> {
@Override
public boolean filter(String value) throws Exception {
return value.contains("flink");
}
}
还可以将函数实现成匿名类
DataStream<String> flinkTweets = tweets.filter(new FilterFunction<String>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(String value) throws Exception {
return value.contains("flink");
}
});
我们filter的字符串"flink"还可以当作参数传进去。
DataStream<String> tweets = env.readTextFile("INPUT_FILE ");
DataStream<String> flinkTweets = tweets.filter(new KeyWordFilter("flink"));
public static class KeyWordFilter implements FilterFunction<String> {
private String keyWord;
KeyWordFilter(String keyWord) { this.keyWord = keyWord; }
@Override
public boolean filter(String value) throws Exception {
return value.contains(this.keyWord);
}
}
2.匿名函数(Lambda Functions)
DataStream<String> tweets = env.readTextFile("INPUT_FILE");
DataStream<String> flinkTweets = tweets.filter( tweet -> tweet.contains("flink") );
3.富函数(Rich Function)
“富函数”是DataStream API提供的一个函数类的接口,所有Flink函数类都有其Rich版本。它与常规函数的不同在于,可以获取运行环境的上下文,并拥有一些生命周期方法,所以可以实现更复杂的功能。
RichMapFunction
RichFlatMapFunction
RichFilterFunction
…
Rich Function有一个生命周期的概念。典型的生命周期方法有:
open()方法是rich function的初始化方法,当一个算子例如map或者filter被调用之前open()会被调用。
close()方法是生命周期中的最后一个调用的方法,做一些清理工作。
getRuntimeContext()方法提供了函数的RuntimeContext的一些信息,例如函数执行的并行度,任务的名字,以及state状态
public static class MyMapFunction extends RichMapFunction<SensorReading, Tuple2<Integer, String>> {
@Override
public Tuple2<Integer, String> map(SensorReading value) throws Exception {
return new Tuple2<>(getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask(), value.getId());
}
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
System.out.println("my map open");
// 以下可以做一些初始化工作,例如建立一个和HDFS的连接
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
System.out.println("my map close");
// 以下做一些清理工作,例如断开和HDFS的连接
}
}
6. Sink
Flink没有类似于spark中foreach方法,让用户进行迭代的操作。虽有对外的输出操作都要利用Sink完成。最后通过类似如下方式完成整个任务最终输出操作。
stream.addSink(new MySink(xxxx))
1.Kafka
pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.flink/flink-connector-kafka-0.11 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-kafka-0.11_2.12</artifactId>
<version>1.10.1</version>
</dependency>
dataStream.addSink(new FlinkKafkaProducer011[String]("localhost:9092", "test", new SimpleStringSchema()))
2.Redis
pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.bahir/flink-connector-redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.bahir</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-redis_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
public static class MyRedisMapper implements RedisMapper<SensorReading>{
// 保存到redis的命令,存成哈希表
public RedisCommandDescription getCommandDescription() {
return new RedisCommandDescription(RedisCommand.HSET, "sensor_tempe");
}
public String getKeyFromData(SensorReading data) {
return data.getId();
}
public String getValueFromData(SensorReading data) {
return data.getTemperature().toString();
}
}
FlinkJedisPoolConfig config = new FlinkJedisPoolConfig.Builder()
.setHost("localhost")
.setPort(6379)
.build();
dataStream.addSink( new RedisSink<SensorReading>(config, new MyRedisMapper())
3.Elasticsearch
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-elasticsearch6_2.12</artifactId>
<version>1.10.1</version>
</dependency>
// es的httpHosts配置
ArrayList<HttpHost> httpHosts = new ArrayList<>();
httpHosts.add(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200));
dataStream.addSink( new ElasticsearchSink.Builder<SensorReading>(httpHosts, new MyEsSinkFunction()).build());
public static class MyEsSinkFunction implements ElasticsearchSinkFunction<SensorReading>{
@Override
public void process(SensorReading element, RuntimeContext ctx, RequestIndexer indexer) {
HashMap<String, String> dataSource = new HashMap<>();
dataSource.put("id", element.getId());
dataSource.put("ts", element.getTimestamp().toString());
dataSource.put("temp", element.getTemperature().toString());
IndexRequest indexRequest = Requests.indexRequest()
.index("sensor")
.type("readingData")
.source(dataSource);
indexer.add(indexRequest);
}
}
4.JDBC 自定义sink
pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.44</version>
</dependency>
public static class MyJdbcSink extends RichSinkFunction<SensorReading> {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement insertStmt = null;
PreparedStatement updateStmt = null;
// open 主要是创建连接
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "root", "123456");
// 创建预编译器,有占位符,可传入参数
insertStmt = conn.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO sensor_temp (id, temp) VALUES (?, ?)");
updateStmt = conn.prepareStatement("UPDATE sensor_temp SET temp = ? WHERE id = ?");
}
// 调用连接,执行sql
@Override
public void invoke(SensorReading value, Context context) throws Exception {
// 执行更新语句,注意不要留super
updateStmt.setDouble(1, value.getTemperature());
updateStmt.setString(2, value.getId());
updateStmt.execute();
// 如果刚才update语句没有更新,那么插入
if (updateStmt.getUpdateCount() == 0) {
insertStmt.setString(1, value.getId());
insertStmt.setDouble(2, value.getTemperature());
insertStmt.execute();
}
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
insertStmt.close();
updateStmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}
dataStream.addSink(new MyJdbcSink())






















 3720
3720











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








