webhook
对kubernetes的webhook开发实例
介绍
Webhook就是一种HTTP回调,用于在某种情况下执行某些动作,Webhook不是K8S独有的,很多场景下都可以进行Webhook,比如在提交完代码后调用一个Webhook自动构建docker镜像
K8S中提供了自定义资源类型和自定义控制器来扩展功能,还提供了动态准入控制,其实就是通过Webhook来实现准入控制,分为两种:验证性质的准入 Webhook (Validating Admission Webhook) 和 修改性质的准入 Webhook (Mutating Admission Webhook)
Admission Webhook使用较多的场景如下
- 在资源持久化到ETCD之前进行修改(Mutating Webhook),比如增加init Container或者sidecar Container
- 在资源持久化到ETCD之前进行校验(Validating Webhook),不满足条件的资源直接拒绝并给出相应信息
现在非常火热的的 Service Mesh 应用istio就是通过 mutating webhooks 来自动将Envoy这个 sidecar 容器注入到 Pod 中去的:https://istio.io/docs/setup/kubernetes/sidecar-injection/。
更多详情介绍可参考:https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/extensible-admission-controllers/
Admission Webhook
上面提到K8S的动态准入控制是通过Webhook来实现的,请看下图
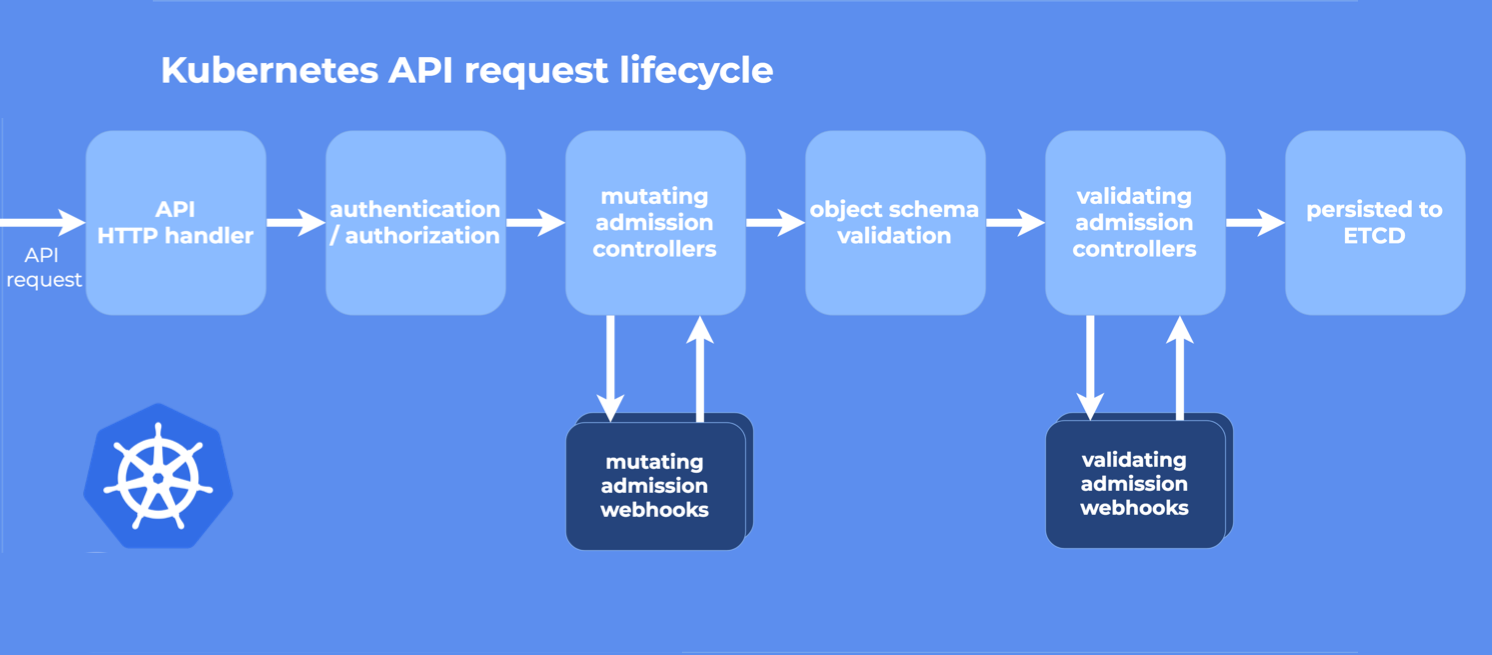
Webhook可以理解成Java Web开发中的Filter,每个请求都会经过Filter处理,从图中可以看到,先执行的是Mutating Webhook,它可以对资源进行修改,然后执行的是Validating Webhook,它可以拒绝或者接受请求,但是它不能修改请求
K8S中有已经实现了的Admission Webhook列表,详情参考每个准入控制器的作用是什么?
webhook使用
检查是否开启了动态准入控制
一般k8s会默认开启,可以跳过此步骤。(如果部署后,查看kube-apiserver日志没有没有准入日志,按照下面方式开启)
查看APIServer是否开启了MutatingAdmissionWebhook和ValidatingAdmissionWebhook
# 获取apiserver pod名字
apiserver_pod_name=`kubectl get --no-headers=true po -n kube-system | grep kube-apiserver | awk '{ print $1 }'`
# 查看api server的启动参数plugin
kubectl get po $apiserver_pod_name -n kube-system -o yaml | grep plugin如果输出如下,说明已经开启
- --enable-admission-plugins=NodeRestriction,MutatingAdmissionWebhook,ValidatingAdmissionWebhook否则,需要修改启动参数,请不然直接修改Pod的参数,这样修改不会成功,请修改配置文件/etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml,加上相应的插件参数后保存,APIServer的Pod会监控该文件的变化,然后重新启动。
webhook动态准入控制说明
webhooks:
- name: webhook-example.github.com
clientConfig:
service:
name: webhook-example
namespace: default
path: "/mutate" #与代码逻辑相同
caBundle: ${CA_BUNDLE}
admissionReviewVersions: [ "v1beta1" ]
sideEffects: None
rules: # 资源拦截规则
- operations: [ "CREATE" ]
apiGroups: ["apps", ""]
apiVersions: ["v1"]
resources: ["deployments"]
namespaceSelector: # 生效的namespace
matchLabels:
webhook-example: enabled
webhook简单实例
实例说明
实例将给原服务增加label、Annotation和sidecar
下载代码:https://github.com/yuenandi/webhookExample
项目结构:
.
├── Dockerfile
├── build # 镜像构建
├── debug # debug启动脚本(认证与资源创建)
├── deploy # 部署启动脚本(认证与资源创建)
├── k8s # 服务启动前k8s资源创建(主要是认证)
│ ├── run.go
│ └── utils.go
├── main.go # 启动入口
├── options
│ └── WhsvrParameters.go # 服务启动参数
├── pki
└── webhook
└── webhook.go # 主要代码逻辑其中main.go和webhook.go是整个webhook的核心,前者用于启动Server,监听端口,后者用于实现核心业务逻辑
main.go
服务启动,监听端口
func main() {
parameters := options.Parameters
pair, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair(parameters.CertFile, parameters.KeyFile)
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("Failed to load key pair: %v", err)
}
whsvr := &webhook.WebhookServer{
Server: &http.Server{
Addr: fmt.Sprintf(":%v", parameters.Port),
TLSConfig: &tls.Config{Certificates: []tls.Certificate{pair}},
},
}
// define http server and server handler
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc(options.MutatePath, whsvr.Serve)
whsvr.Server.Handler = mux
// start webhook server in new routine
go func() {
if err := whsvr.Server.ListenAndServeTLS("", ""); err != nil {
log.Errorf("Failed to listen and serve webhook server: %v", err)
}
}()
log.Infof("Server started, Listening to the port %d", parameters.Port)
// listening OS shutdown singal
signalChan := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(signalChan, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)
<-signalChan
log.Infof("Got OS shutdown signal, shutting down webhook server gracefully...")
//whsvr.Server.Shutdown(context.Background())
}
webhook.go
其核心在serve方法,根据传进来的path mutate,然后执行相应的操作,这个path是自己在MutatingWebhookConfiguration中定义的
// Serve method for webhook server
func (whsvr *WebhookServer) Serve(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
//读取从ApiServer过来的数据放到body
var body []byte
if r.Body != nil {
if data, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body); err == nil {
body = data
}
}
....
var admissionResponse *v1beta1.AdmissionResponse
ar := v1beta1.AdmissionReview{}
if _, _, err := deserializer.Decode(body, nil, &ar); err != nil {
...
} else {
if r.URL.Path == options.MutatePath {
// mutate 业务逻辑
admissionResponse = whsvr.mutate(&ar)
admissionReview := v1beta1.AdmissionReview{}
if admissionResponse != nil {
admissionReview.Response = admissionResponse
if ar.Request != nil {
admissionReview.Response.UID = ar.Request.UID
}
}
resp, err := json.Marshal(admissionReview)
if err != nil {
...
}
if _, err := w.Write(resp); err != nil {
...
}
}
}
}
mutate方法,发往apiserver的patch
func (whsvr *WebhookServer) mutate(ar *v1beta1.AdmissionReview) *v1beta1.AdmissionResponse {
req := ar.Request
var (
objectMeta *metav1.ObjectMeta
resourceNamespace, resourceName string
deployment appsv1.Deployment
)
switch req.Kind.Kind {
// 支持Deployment
case "Deployment":
if err := json.Unmarshal(req.Object.Raw, &deployment); err != nil {
log.Errorln(fmt.Sprintf("\nCould not unmarshal raw object: %v", err))
return &v1beta1.AdmissionResponse{
Result: &metav1.Status{
Message: err.Error(),
},
}
}
resourceName, resourceNamespace, objectMeta, deployment = deployment.Name, deployment.Namespace, &deployment.ObjectMeta, deployment
//其他不支持的类型
default:
msg := fmt.Sprintf("\nNot support for this Kind of resource %v", req.Kind.Kind)
log.Warnf(msg)
return &v1beta1.AdmissionResponse{
Result: &metav1.Status{
Message: msg,
},
}
}
//跳过不进行处理的情况
if !mutationRequired(ignoredNamespaces, objectMeta) {
log.Infoln(fmt.Sprintf("Skipping validation for %s/%s due to policy check", resourceNamespace, resourceName))
return &v1beta1.AdmissionResponse{
Allowed: true,
}
}
//开始处理,主要处理方法
patchBytes, err := createPatch(deployment, addAnnotations, addLabels)
...
log.Debugf(fmt.Sprintf("AdmissionResponse: patch=%v\n", string(patchBytes)))
return &v1beta1.AdmissionResponse{
Allowed: true,
Patch: patchBytes,
PatchType: func() *v1beta1.PatchType {
pt := v1beta1.PatchTypeJSONPatch
return &pt
}(),
}
}
主要业务处理createPatch
func createPatch(deployment appsv1.Deployment, addAnnotations map[string]string, addLabels map[string]string) ([]byte, error) {
...
labelsPatch := updateLabels(labels, addLabels)
annotationsPatch := updateAnnotation(annotations, addAnnotations)
containersPatch := updateContainers(addContainer, deployment)
...
}
// 手动拼接patch,简单改动可用
func updateLabels(target map[string]string, added map[string]string) (patch []patchOperation) {
values := make(map[string]string)
for key, value := range added {
if target == nil || target[key] == "" {
values[key] = value
}
}
patch = append(patch, patchOperation{
Op: "add",
Path: "/metadata/labels",
Value: values,
})
return patch
}
// 复杂的改动,可定义出新的deployment对象与原deployment做jsondiff.Compare操作
var addContainer = []corev1.Container{
{
Name: "side-car",
Image: "busybox",
Command: []string{"/bin/sleep", "infinity"},
},
}
func updateContainers(addContainer []corev1.Container, deployment appsv1.Deployment) (patch []patchOperation) {
currentDeployment := deployment.DeepCopy()
containers := currentDeployment.Spec.Template.Spec.Containers
containers = append(containers, addContainer...)
currentDeployment.Spec.Template.Spec.Containers = containers
diffPatch, err := jsondiff.Compare(deployment, currentDeployment)
if err != nil {
log.Error("")
}
for _, v := range diffPatch {
addPatch := patchOperation{
Op: v.Type,
Value: v.Value,
Path: string(v.Path),
}
patch = append(patch, addPatch)
}
return patch
}
webhook部署
脚本部署
修改install.sh脚本,如下部分,kube_config集群本地执行需修改为空kube_config=''
#集群命名空间
ns='webhook-example'
kubectl_ns='--namespace webhook-example'
#集群远程证书
kube_config='--kubeconfig config'执行脚本
脚本详情
#!/bin/bash # 修改serviceaccount的namespace字段 sed -e "s/\${namespace}/${ns}/g" rbac.yaml > current_rbac.yaml # 部署rbac kubectl apply -f current_rbac.yaml ${kubectl_ns} ${kube_config} # 认证: 或者kubernetes集群证书 ./webhook-create-signed-cert.sh ${kubectl_ns} ${kube_config} # 部署service kubectl apply -f service.yaml # 部署webhook应用 kubectl apply -f webhook-example.yaml # 部署MutatingWebhookConfiguration cat ./mutatingwebhook.yaml | ./webhook-patch-ca-bundle.sh > current_mutatingwebhook.yaml ${kube_config} && kubectl apply -f current_mutatingwebhook.yaml ${kubectl_ns} # 为namespace添加label kubectl label ns ${ns} webhook-example=enabled ${kube_config}
部署webhook
kubectl apply -f deploy/webhookExample.yaml不使用边车
为应用添加如下label
labels:
webhook-example.github.com/app: "false"webhook调试
远程调试,需要做本地与k8s集群的认证
主要脚本,webhook-create-signed-cert.sh
cat<<EOF >> ${tmpdir}/csr.conf
[req]
req_extensions = v3_req
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
[req_distinguished_name]
[ v3_req ]
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
#修改为Debug本机Ip
IP.1 = ${currentIp}
EOF
mutatingwebhook.yaml
webhooks:
- name: webhook-example-debug.github.com
clientConfig:
# 修改为本地ip
url: https://10.8.1.90:6444/mutate/
脚本部署
修改debug/create-debug.sh如下参数
#本机地址
currentIp=10.8.1.90
#本地服务端口
currentPort=6444
#集群命名空间
ns='webhook-example'
kubectl_ns='--namespace webhook-example'
#远程集群证书
kube_config='--kubeconfig config'运行webhook
IDEA修改启动参数,注意地址修改,如下图:
--tlsCertFile=pki/cert.pem
--tlsKeyFile=pki/key.pem
--log-v=5
--automatic-authentication=false验证
-
给webhook-example namespace添加label
kubectl label namespace webhook-example webhook-example-debug=enabled -
部署
sleep.yamlkubectl apply -f deploy/sleep.yaml
自动认证,资源创建部分
以上部署在脚本中进行认证和资源创建
也可将认证和一些资源创建,例如csr、MutatingWebhookConfiguration,在程序启动前进行创建
可扩展,做认证失效监控,进行证书自动更新
部署编排文件为deploy/all/webhookExample-all.yaml
主要代码如下
自动认证参数,DEBUG模式为了方便本地开发调试
type WhSvrParameters struct {
Port int // webhook server port
CertFile string // path to the x509 certificate for https
KeyFile string // path to the x509 private key matching `CertFile`
Logv int32 // 日志级别,默认4
AutoAuthentication bool // 是否自动认证,默认true
Service string // 服务的service,默认webhook-example
Namespace string // 命名空间
KubeConfig string // 集群证书
IsDebug bool // 是否为DEBUG模式,默认false
Url string // 本地机器URL,DEBUG模式用到
}
--tlsCertFile=pki/cert.pem
--tlsKeyFile=pki/key.pem
--log-v=5
--kubeconfig=pki/config
--namespace=webhook-example
--debug=true
--url=10.8.1.90
--automatic-authentication=true
k8s客户端认证
func NewKubernetsClient(options *options.WhSvrParameters) (k *K8s, err error) {
k = &K8s{}
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", options.KubeConfig)
if err != nil {
log.Error(err)
return nil, err
}
k.config = config
k.kubernetesClient, err = kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
if err != nil {
log.Error(err)
return nil, err
}
return k, nil
}
webhook启动前准备代码
func (k *K8s) Run() (err error) {
// 获取证书key,和CSR
csr, key, err := genKubernetesCSR()
// 创建CSR
csr, err = k.kubernetesClient.CertificatesV1beta1().CertificateSigningRequests().Create(context.Background(), csr, metav1.CreateOptions{})
// CSR审批
cert, err := k.Approve(csr)
// 写证书
keyBuf := x509.MarshalPKCS1PrivateKey(key)
err = writePki(k.parameters.KeyFile, "RSA PRIVATE KEY", keyBuf)
err = writeCert(k.parameters.CertFile, cert)
// 删除CSR
err = k.kubernetesClient.CertificatesV1beta1().CertificateSigningRequests().Delete(context.Background(), csr.Name, metav1.DeleteOptions{})
var (
path = options.MutatePath
url string
service *admissionV1.ServiceReference
)
// 判断是否为DEBUG模式
// 创建mutat
logrus.Debugf("DEBUG模式:%t", k.parameters.IsDebug)
if k.parameters.IsDebug {
url = fmt.Sprintf("https://%s:%d%s", k.parameters.Url, k.parameters.Port, path)
err = k.CreateMutationWebhook(mutationWebhookConfigurationName, mutatingWebhookName, nil, &url)
} else {
service = &admissionV1.ServiceReference{
Name: k.parameters.Service,
Namespace: k.parameters.Namespace,
Path: &path,
}
logMU, _ := yaml.Marshal(service)
logrus.Debugf(string(logMU))
err = k.CreateMutationWebhook(mutationWebhookConfigurationName, mutatingWebhookName, service, nil)
}
return err
}





















 1336
1336











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








