Table of Contents
3、在init()方法中,初始化窗口JFrame(未加载控件)时(即方法首行)调用:
一、问题描述
最近写一个java的GUI,感觉不管是awt还是swing的默认字体都是不和我意,不得不自己设置字体;但是因为组件多,如果全部都有一个个加字体(像下面这样)就感觉很麻烦,代码也很冗余,所以就想着有没有办法设置全局的字体?
// 这样
JLabel jlExcel = new JLabel("请输入表格路径:");
jlExcel.setFont(new Font("宋体", Font.BOLD, 25));
JTextField jtfExcel = new JTextField(65);
jtfExcel.setFont(new Font("宋体", Font.BOLD, 23));
// 或者是这样
Font textFont = new Font("宋体", Font.BOLD, 23);
jlExcel.setFont(textFont);
jtfExcel.setFont(textFont);
二、找资料
百度了一波,还真有!但是好像我还是不太懂怎么用……略颓丧,后面看了文档好像才弄懂了一点点。下面这是找到的相关博客:
1、Swing技巧. 设置全局字体(sun jdk)
为什么要这么做?
因为java默认的字体显示中文都很难看;
因为比如jgoodies这样的skin默认不支持中文;
因为jdk1.4中文字体mapping有严重bug,用过IDEA的人都知道;
因为大家只有sun的jdk可用,ibm的,bea的都不适合跑client。
if you are smart....//设置全局字体 public static void initGlobalFontSetting(Font fnt){ FontUIResource fontRes = new FontUIResource(fnt); for(Enumeration keys = UIManager.getDefaults().keys(); keys.hasMoreElements();){ Object key = keys.nextElement(); Object value = UIManager.get(key); if(value instanceof FontUIResource) UIManager.put(key, fontRes); } }if you aren't...
Font font = new Font("Dialog",Font.PLAIN,12); UIManager.put("ToolTip.font",font); UIManager.put("Table.font",font); UIManager.put("TableHeader.font",font); UIManager.put("TextField.font",font); UIManager.put("ComboBox.font",font); UIManager.put("TextField.font",font); UIManager.put("PasswordField.font",font); UIManager.put("TextArea.font",font); UIManager.put("TextPane.font",font); UIManager.put("EditorPane.font",font); UIManager.put("FormattedTextField.font",font); UIManager.put("Button.font",font); UIManager.put("CheckBox.font",font); UIManager.put("RadioButton.font",font); UIManager.put("ToggleButton.font",font); UIManager.put("ProgressBar.font",font); UIManager.put("DesktopIcon.font",font); UIManager.put("TitledBorder.font",font); UIManager.put("Label.font",font); UIManager.put("List.font",font); UIManager.put("TabbedPane.font",font); UIManager.put("MenuBar.font",font); UIManager.put("Menu.font",font); UIManager.put("MenuItem.font",font); UIManager.put("PopupMenu.font",font); UIManager.put("CheckBoxMenuItem.font",font); UIManager.put("RadioButtonMenuItem.font",font); UIManager.put("Spinner.font",font); UIManager.put("Tree.font",font); UIManager.put("ToolBar.font",font); UIManager.put("OptionPane.messageFont",font); UIManager.put("OptionPane.buttonFont",font);
2、java swing 界面统一设置字体样式
/** * 统一设置字体,父界面设置之后,所有由父界面进入的子界面都不需要再次设置字体 */ private static void InitGlobalFont(Font font) { FontUIResource fontRes = new FontUIResource(font); for (Enumeration<Object> keys = UIManager.getDefaults().keys(); keys.hasMoreElements();) { Object key = keys.nextElement(); Object value = UIManager.get(key); if (value instanceof FontUIResource) { UIManager.put(key, fontRes); } } }在main方法中,初始化窗口时,加入下面这句:
InitGlobalFont(new Font("alias", Font.PLAIN, 12)); //统一设置字体
就可以了。
注意:InitGlobalFont 这个方法的调用时在swing界面的入口界面里。
三、尝试解决
其实看完这两篇文章,了解到这个方法应该是可以实现我的要求的,我还是有点不太懂这个方法要放在哪个位置(InitGlobalFont 这个方法的调用时在swing界面的入口界面里???),所以就试了下:
注意下面代码中 InitGlobalFont(new Font("宋体", Font.PLAIN, 5)); //统一设置字体 的位置!
1、使用默认的字体(即不修改字体,方便对比):
package com.ys.gui;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.UIManager;
import javax.swing.plaf.FontUIResource;
public class TestGlobalFont {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jFrame = new JFrame("测试设置全局字体");
// 初始化窗口
init(jFrame);
jFrame.setBounds(800, 400, 400, 400);
jFrame.setVisible(true);
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
/**
* @Title init
* @author yansheng
* @version v1.0
* @date 2019-07-01 11:28:31
* @Description 初始化窗口
* @param jFrame
* void
*/
public static void init(JFrame jFrame) {
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT);
jFrame.setLayout(flowLayout);
JLabel jLabel = new JLabel("JLabel显示文本信息");
jFrame.add(jLabel);
JButton jButton = new JButton("JButton按钮");
jFrame.add(jButton);
}
/**
* 统一设置字体,父界面设置之后,所有由父界面进入的子界面都不需要再次设置字体
*/
private static void InitGlobalFont(Font font) {
FontUIResource fontRes = new FontUIResource(font);
for (Enumeration<Object> keys = UIManager.getDefaults().keys(); keys.hasMoreElements();) {
Object key = keys.nextElement();
Object value = UIManager.get(key);
if (value instanceof FontUIResource) {
UIManager.put(key, fontRes);
}
}
}
}
注:init()方法非必须,但是好像一般都会用来初始化窗口及组件;如果自定义一个类继承JFrame或者Frame,那么在该类中一般也会用该方法,名字可自取,为方便理解这里统一命名为init。
效果图:

2、在main()方法中,定义窗口JFrame前调用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
InitGlobalFont(new Font("宋体", Font.PLAIN, 40)); // 统一设置字体
JFrame jFrame = new JFrame("测试设置全局字体");
……效果图:

3、在init()方法中,初始化窗口JFrame(未加载控件)时(即方法首行)调用:
public static void init(JFrame jFrame) {
InitGlobalFont(new Font("宋体", Font.PLAIN, 40)); // 统一设置字体
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT);
jFrame.setLayout(flowLayout);
……在布局后面加也OK。
效果图:

4、反例,即该方法的调用位置不对,没有效果的情况:
4.1 在init()加载部分组件后调用:
public static void init(JFrame jFrame) {
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT);
jFrame.setLayout(flowLayout);
JLabel jLabel = new JLabel("JLabel显示文本信息");
jFrame.add(jLabel);
InitGlobalFont(new Font("宋体", Font.PLAIN, 40)); // 统一设置字体
JButton jButton = new JButton("JButton按钮");
jFrame.add(jButton);
}那么在它前面的加载的组件(字体设置)就会不起作用,效果如下:

4.2 在init()全部加载组件后调用(如最后一行):
public static void init(JFrame jFrame) {
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT);
jFrame.setLayout(flowLayout);
JLabel jLabel = new JLabel("JLabel显示文本信息");
jFrame.add(jLabel);
JButton jButton = new JButton("JButton按钮");
jFrame.add(jButton);
InitGlobalFont(new Font("宋体", Font.PLAIN, 40)); // 统一设置字体
}无效。
4.3 在main()的init()方面后面调用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jFrame = new JFrame("测试设置全局字体");
// 初始化窗口
init(jFrame);
InitGlobalFont(new Font("宋体", Font.PLAIN, 40)); // 统一设置字体
jFrame.setBounds(800, 400, 400, 400);
jFrame.setVisible(true);
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}由4.2在init后面加都无效可知,这种肯定也不行!
5、 总结:
虽然我不是很清楚什么时候调用比较好,但是个人喜欢3在init()方法的首行调用,(个人拙见)因为init()是用初始化窗口及组件,而字体是组件的一种属性,放在一起比较容易理解。
四、进一步理解:
分析一下该方法:打印一些信息,方便理解:
/**
* 统一设置字体,父界面设置之后,所有由父界面进入的子界面都不需要再次设置字体
*/
private static void InitGlobalFont(Font font) {
FontUIResource fontRes = new FontUIResource(font);
// 打印字体信息
System.out.println("fontRes:" + fontRes);
for (Enumeration<Object> keys = UIManager.getDefaults().keys(); keys.hasMoreElements();) {
Object key = keys.nextElement();
Object value = UIManager.get(key);
if (value instanceof FontUIResource) {
// 打印默认的所有有关字体的信息
System.out.println("\nkey:" + key + "\nvalue:" + value);
UIManager.put(key, fontRes);
// 打印更改后的相关信息
System.out.println("\nkey:" + key + "\nvalue:" + UIManager.get(key));
}
}打印的(部分)内容:

1. 类 FontUIResource 实现 UIResource 的 java.awt.Font 的子类。设置默认字体属性的 UI 类应该使用此类。
2. UIManager 管理当前外观、可用外观集合、外观更改时被通知的 PropertyChangeListeners、外观默认值以及获取各种默认值的便捷方法。UIManager.get(Object key):从默认值中返回一个对象。
3. for循环里面,初始化:将所有默认组件(类)放到枚举对象集keys中,然后遍历keys;如果是如果该组件的值(对象)是FontUIResource的实例,就进入if语句,设置该组件的font属性。(你也可以简单理解为:只要有组件是和字体有关的,就设置它的字体为我们之前的设定好的。)
这样就OK了,达到要求:设置全局的字体。
五、拓展延伸——在全局字体的基础上加一些特殊点的字体
刚弄好全局字体,假如需求变了,还想要在全局字体的基础上加一些特殊点的字体,那怎么办呢?
直接按照普通的加上字体就好了,只要不是和全局字体一样就会显示出来,因为这个时候其实是把全局字体当做默认了,你需要特殊的,直接设置就好了。
参考:(加一个不一样字体的按钮)
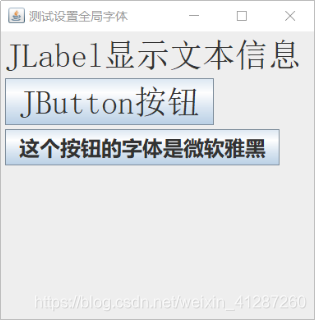
public static void init(JFrame jFrame) {
InitGlobalFont(new Font("宋体", Font.PLAIN, 40)); // 统一设置字体
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT);
jFrame.setLayout(flowLayout);
JLabel jLabel = new JLabel("JLabel显示文本信息");
jFrame.add(jLabel);
JButton jButton = new JButton("JButton按钮");
jFrame.add(jButton);
JButton jButton1 = new JButton("这个按钮的字体是微软雅黑");
jButton1.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 25));
jFrame.add(jButton1);
}效果图:
完事。
参考:设置Swing全局字体

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








