前课复习
File文件的操作
文件的操作比较简单,把语句看一看就行。
格式:
File f = new File(“D:\路径\abc.txt”);
//这个时候对象f就是tt.txt文件,在java中\或者/才是文件的分隔符。
基础操作
f.getName());//获取文件名
f.getPath());//获取文件或者文件夹的路径,就是new file时候写的路径
f.getAbsolutePath();//获取当前文件的绝对路径
f.getParent();//返回当前文件或者文件夹的父级路径
f.renameTo(new File(“D:\…\newname.txt”));//给文件或文件夹重命名

f.exists();//判断文件或者文件夹是否存在
f.canWrite();//判断文件是否可写
f.canRead();//判断文件是否可读
f.isFile();//判断当前的file对象是不是文件
f.isDirectory();//判断当前的file对象是不是文件夹或者目录
f.lastModified();//获取文件的最后修改时间,返回的是一个毫秒数
f.length();//返回文件的长度,单位是字节数

f.delete();//删除文件
File f = new File(“D:\newfile(文件夹)”);
f.mkdir();//创建单层目录
f.mkdirs();//这个方法是直接用来创建多层目录

File f = new File(“D:\test”);
String[ ] ff= f.list();//返回的是当前文件夹的子集的名称,包括目录和文件
遍历打印出来看看:
for(String s : ff){
System.out.println(s);
}
File[] fs = f11.listFiles();//返回的是当前文件夹的子集的file对象,包括目录和文件
for(File ff : fs){
System.out.println(ff);
}
递归遍历文件

这种代码写下去都是一样的,直接递归!
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//遍历d盘下的test文件,把test文件夹下所有的目录与文件全部遍历出来,不论层级有多深,要全部遍历出来
//这个使用递归的方式来实现
File f = new File("D:\\test");
new Test().test(f);
}
/**
* 递归遍历文件
* @param file
*/
public void test(File file){
//先确认file是文件还是文件夹
if(file.isFile()){
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath() + " 是文件");
}else{
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath() + " 是文件夹");
//如果是文件夹,这个文件夹里就可能有子文件夹或者文件
File[] fs = file.listFiles();//获取当前文件夹下的子文件夹或者文件的file对象
if(fs != null && fs.length > 0){
for(File ff : fs){
test(ff);
}
}
}
}
}
Java IO原理
Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以”流(stream)” 的方式进行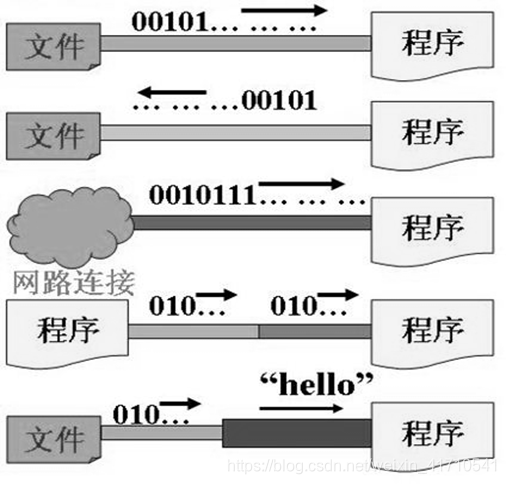
按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8 bit),字符流(16 bit)
按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流

字节流
文件字节输入流
import java.io.FileInputStream;
FileIn 键盘alt+/ 可以自动补齐
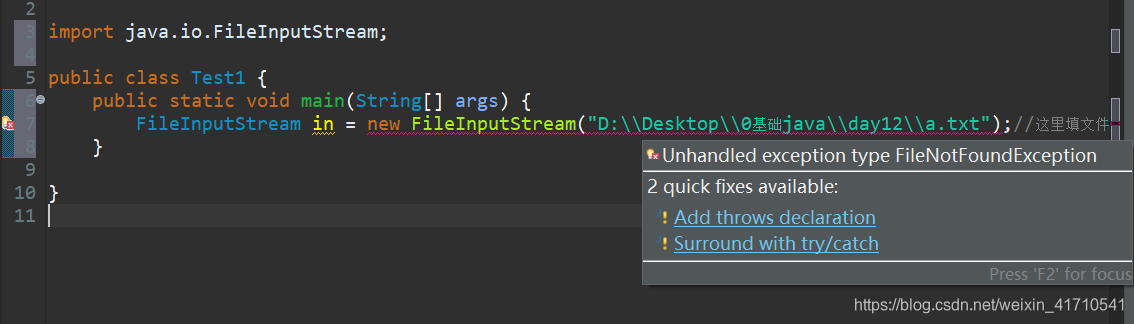
io操作可以自动添加异常,点击图片里的2.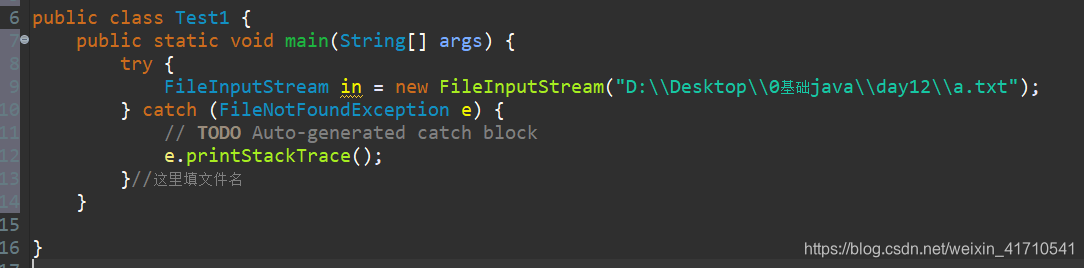
感叹!eclipse太好用了。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try {
//新建流对象
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\Desktop\\0基础java\\day12\\a.txt");//这里填文件名
//定义数组来接收数据
byte[] b = new byte[10];
in.read(b);//读数据
//转换为字符串输出
System.out.println(new String(b));
//关闭流
in.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

调整一下代码
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Test1 t = new Test1();
t.testFileInputStream();//调用方法文件字节流方法
}
/**
* 这是文件字节流方法
* @throws IOException
*/
public void testFileInputStream() throws IOException {
try {
//新建流对象
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\Desktop\\a.txt");//这里填文件名
//定义数组来接收数据
byte[] b = new byte[10];
in.read(b);//读数据
//转换为字符串输出
System.out.println(new String(b));
//关闭流
in.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件字节输出流
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Test1 t = new Test1();
t.testFileInputStream();//调用方法文件字节流方法
t.testFileOutputStream();
}
/**
* 这是文件字节流方法
* @throws IOException
*/
public void testFileInputStream() throws IOException {
try {
//新建流对象
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\Desktop\\a.txt");//这里填文件名
//定义数组来接收数据
byte[] b = new byte[10];
in.read(b);//读数据
//转换为字符串输出
System.out.println(new String(b));
//关闭流
in.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 这是文件字节流方法 输出write
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testFileOutputStream() throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Desktop\\a1.txt");
int b = 3;
out.write(b);//把数据写子啊内存中
String c = "xkfjsakfjdlsfjoshfsdl";
out.write(c.getBytes());//字符串转化为byte,,,c.getBytes()
out.flush();//把数据刷新到硬盘上
out.close();//关闭流
}
}
编写一个程序,把一个a.txt文件复制的到指定文件夹下
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Test1 t = new Test1();
t.copyfile();
}
public void copyfile() throws IOException {
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\Desktop\\a.txt");//输入流,从硬盘读取文件
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Desktop\\作业\\a.txt");//输出流,输出文件到硬盘
byte[] b = new byte[100];
in.read(b);
out.write(b);
out.flush();
out.close();
in.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
代码升级一下:
把方法改为有参方法!调用的时候更加方便!
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Test1 t = new Test1();
t.copyfile("D:\\Desktop\\a.txt","D:\\Desktop\\作业\\a.txt");
}
public void copyfile(String inPath, String outPath) throws IOException {
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(inPath);//输入流,从硬盘读取文件
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(outPath);//输出流,输出文件到硬盘
byte[] b = new byte[100];
in.read(b);
out.write(b);
out.flush();
out.close();
in.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
笔记:
文件字节流非常通用,可以用来操作字符的文档,还可以**操作任何的其他类型文件****(图片,**压缩包等等),引用字节流直接使用二进制
字符流
两个区别!!
读取文件操作步骤:
1.建立一个流对象 FileReader,将已存在的一个文件加载进流。
FileReader fr = new FileReader(“Test.txt”);
2.创建一个临时存放数据的数组。char[]
char[] ch = new char[1024];
文件字符输入流
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Test2.testFileReader("D:\\Desktop\\a.txt");
}
public static void testFileReader(String inPath) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(inPath);//fr是字符输入流对象
char[] ch = new char[10];//临时存放数据数组
fr.read(ch);//读数据
System.out.println(new String(ch));
fr.close();
}
}
文件字符输出流
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Test2.testFileWriter("jlskafsof", "D:\\Desktop\\aaaa.txt");
}
public static void testFileReader(String inPath) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(inPath);//fr是字符输入流对象
char[] ch = new char[10];//临时存放数据数组
fr.read(ch);//读数据
System.out.println(new String(ch));
fr.close();
}
public static void testFileWriter(String text, String outPath) {
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(outPath);
fw.write(text);//把数据写子啊内存中
fw.flush();//把数据刷新到硬盘上
fw.close();//关闭流
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
以上两种方法处理异常,一个是throws抛出异常,一个是try …catch 扑获异常,eclipse提示自动生成的。
读取文件时,要保证有文件存在,否则报异常,
写入文件时,会覆盖同名的源文件。























 2909
2909











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








