
Ultimate Tic-Tac-Toe
一款基于 Java 的策略井字棋游戏
Preface
You can find this paper from cmd markdown.
Chapter 1 Overall overview
1.1 Tic-Tac-Toe
Tic-tac-toe (also known as noughts and crosses or Xs and Os) is a paper-and-pencil game for two players, X and O, who take turns marking the spaces in a 3×3 grid. The player who succeeds in placing three of their marks in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row wins the game.
The following example game is won by the first player, X:

Players soon discover that the best play from both parties leads to a draw. Hence, tic-tac-toe is most often played by young children.
Because of the simplicity of tic-tac-toe, it is often used as a pedagogical tool for teaching the concepts of good sportsmanship and the branch of artificial intelligence that deals with the searching of game trees. It is straightforward to write a computer program to play tic-tac-toe perfectly or to enumerate the 765 essentially different positions (the state space complexity) or the 26,830 possible games up to rotations and reflections (the game tree complexity) on this space.
The game can be generalized to an m,n,k-game in which two players alternate placing stones of their own color on an m×n board, with the goal of getting k of their own color in a row. Tic-tac-toe is the (3,3,3)-game. Harary’s generalized tic-tac-toe is an even broader generalization of tic-tac-toe. It can also be generalized as a nd game. Tic-tac-toe is the game where n equals 3 and d equals 2. If played properly, the game will end in a draw, making tic-tac-toe a futile game.
1.2 Ulltimate Tic-Tac-Toe
Ultimate tic-tac-toe also known as super tic-tac-toe, strategic tic-tac-toe, meta tic-tac-toe, or tic-tac-tic-tac-toe-toe is a board game composed of nine tic-tac-toe boards arranged in a 3-by-3 grid. Players take turns playing in the smaller tic-tac-toe boards until one of them wins in the larger tic-tac-toe board. Compared to traditional tic-tac-toe, strategy in this game is conceptually more difficult, and has proven more challenging for computers.
Each small 3-by-3 tic-tac-toe board is referred to as a local board, and the larger 3-by-3 board is referred to as the global board.
The game starts with X playing wherever they want in any of the 81 empty spots. This move ‘sends’ their opponent to its relative location. For example, if X played in the top right square of their local board, then O needs to play next in the local board at the top right of the global board. O can then play in any one of the nine available spots in that local board, each move sending X to a different local board.
If a move is played so that it is to win a local board by the rules of normal tic-tac-toe, then the entire local board is marked as a victory for the player in the global board.
Once the outcome of a local board is decided (win or draw), no more moves may be played in that board. If a player is sent to such a board, then that player may play in any other board.
Game play ends when either a player wins the global board or there are no legal moves remaining, in which case the game is a draw.
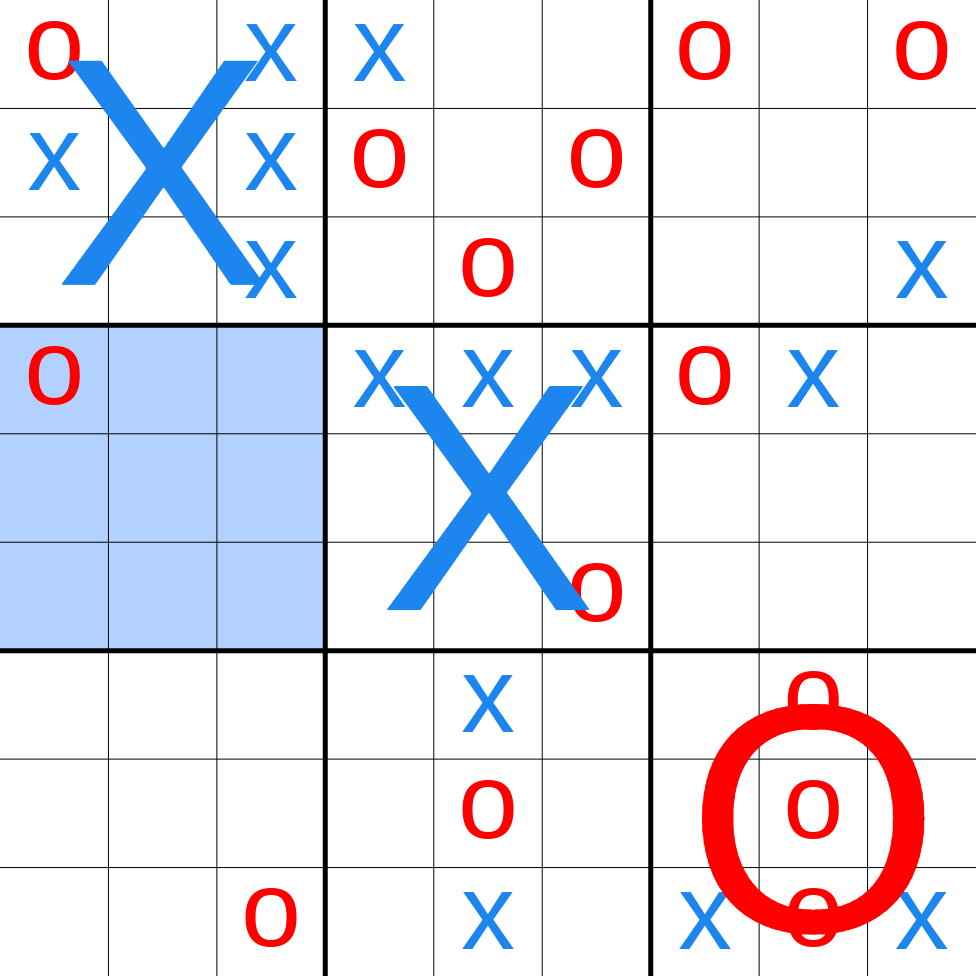
The board of an incomplete ultimate tic-tac-toe game (the large "X"s and "O"s representing local board games which have been won by that player). The most recent move was O playing in the middle-left square of the top-middle grid, forcing X to play their next move in the middle-left grid.
Ultimate tic-tac-toe is significantly more complex than most other variations of tic-tac-toe, as there is no clear strategy to playing. This is because of the complicated game branching in this game. Even though every move must be played in a local board, equivalent to a normal tic-tac-toe board, each move must take into account the global board in several ways:
-
Anticipating the next move: Each move played in a local board determines where the opponent’s next move may be played. This might make moves that may be considered bad in normal tic-tac-toe viable, since the opponent is sent to another local board, and may be unable to immediately respond to them. Therefore, players are forced to consider the larger game board instead of simply focusing on the local board.
-
Visualizing the game tree: Visualizing future branches of the game tree is more difficult than single board tic-tac-toe. Each move determines the next move, and therefore reading ahead—predicting future moves—follows a much less linear path. Future board positions are no longer interchangeable, each move leading to starkly different possible future positions. This makes the game tree difficult to visualize, possibly leaving many possible paths overlooked.
-
Winning the game: Due to the rules of ultimate tic-tac-toe, the global board is never directly affected. It is only governed by actions that occur in local boards. This means that each local move played is not intended to win the local board, but to win the global board. Local wins are not valuable if they cannot be used to win the global board—in fact, it may be strategic to sacrifice a local board to your opponent in order to win a more important local board yourself. This added layer of complexity makes it harder for humans to analyze the relative importance and significance of moves, and consequently harder to play well.
Chapter 2 Introduction of technology application
2.1 Technical overview
- object-oriented programming techniques: class, object, interface, package, encapsulation, inheritance and son on.
- The exception handling
- The input / output stream
- Collection
- The multithread technology
- The TCP client and server network programming technology
- JavaFx
- JDBC
2.2 JavaFX
JavaFX is a software platform for creating and delivering desktop applications, as well as rich Internet applications (RIAs) that can run across a wide variety of devices.
JavaFX is intended to replace Swing as the standard GUI library for Java SE, but both will be included for the foreseeable future. JavaFX has support for desktop computers and web browsers on Microsoft Windows, Linux, and macOS. JavaFX is no longer bundled with the latest Java, nor will be supported by Oracle, while it still is supported for the current long-term version Java SE 8 through March 2022.
In this project,I use some components as following:
- Label
- Button
- Text Field
- Password Field
- and some other panes and so on
2.3 JDBC
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an application programming interface (API) for the programming language Java, which defines how a client may access a database. It is a Java-based data access technology used for Java database connectivity. It is part of the Java Standard Edition platform, from Oracle Corporation. It provides methods to query and update data in a database, and is oriented towards relational databases.
JDBC allows multiple implementations to exist and be used by the same application. The API provides a mechanism for dynamically loading the correct Java packages and registering them with the JDBC Driver Manager. The Driver Manager is used as a connection factory for creating JDBC connections.
JDBC connections support creating and executing statements. These may be update statements such as SQL’s CREATE, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE, or they may be query statements such as SELECT. Additionally, stored procedures may be invoked through a JDBC connection. JDBC represents statements using one of the following classes:
Statement – the statement is sent to the database server each and every time.
PreparedStatement – the statement is cached and then the execution path is pre-determined on the database server allowing it to be executed multiple times in an efficient manner.
CallableStatement – used for executing stored procedures on the database.
Update statements such as INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE return an update count that indicates how many rows were affected in the database. These statements do not return any other information.
Query statements return a JDBC row result set. The row result set is used to walk over the result set. Individual columns in a row are retrieved either by name or by column number. There may be any number of rows in the result set. The row result set has metadata that describes the names of the columns and their types.
In this project, I manager the information of users via JDBC and MySQL.
Chapter 3 Design Analysis
3.1 Overview
There are totally 3144 lines in the src of this project.
And the structure of this project is as following:

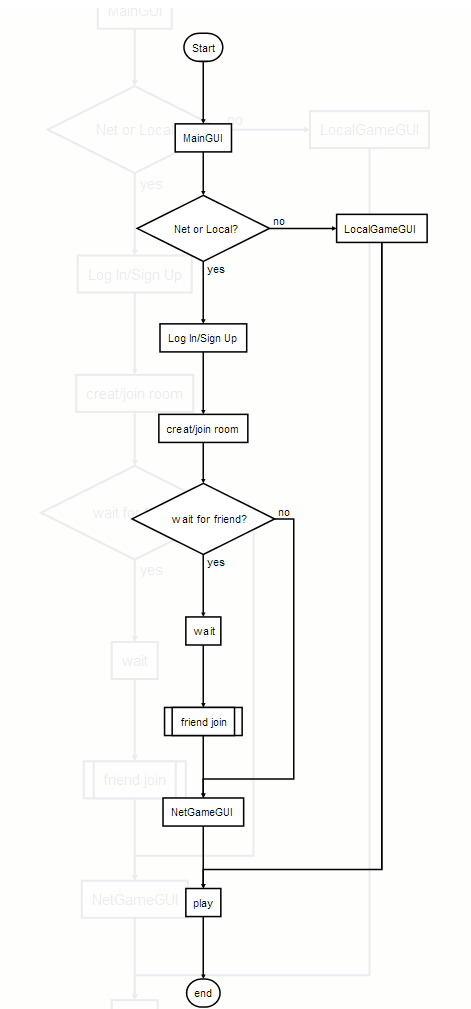
In this project, I design a server and a client to achieve the function of the game. Just as the picture shows, on the client side, there are four packages, which are windows 、dao 、style and component.
In the windows, there are the GUI of this project. These files of Java are completed via JavaFX and css.
In the dao, there are some actions of the Listeners and some classes about the players.
In the component, there are some classes, which extends some super classes.
while on the server side, there are some classes abuot net and some operation needed net, such as operations in database and so on.
In this project, there are two kinds of modes players can choose, which are online game and local game.
And the picture will show the flow of this project:
At last, I would like to show the diagram of each class.
3.2 TestServer

3.3 TheverThread

3.4 ServerOperation

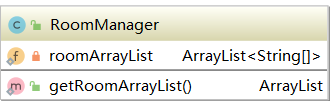
3.5 RoomManager
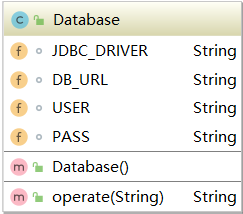
3.6 Database
3.7 BeginGUI

3.8 LanGUI

3.9 LocalGameGUI
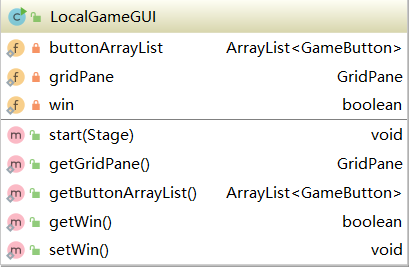
3.10 LogInGUI

3.11 MainGUI

3.12 NetGameGUI

3.13 RankGUI

3.14 RoomGUI

3.15 WaitGUI

3.16 LocalOperation
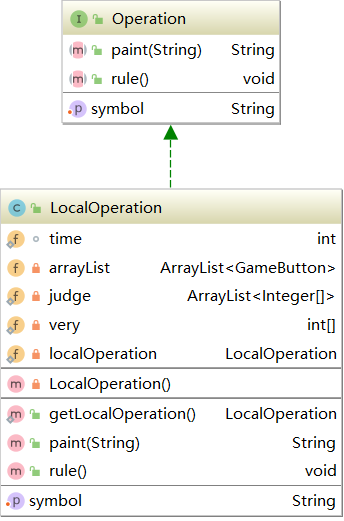
3.17 NetOperation

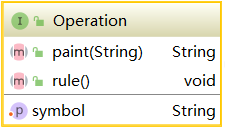
3.18 Operation
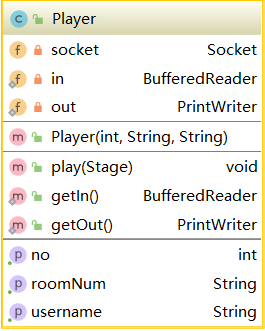
3.19 Player
3.20 PlayerNet

3.21 Rank

3.22 Receive

3.23 MyButton

3.24 GameButton

3.25 NetGameButto

Note:Because of the complexity,some relationships between these classes may not be showed.
Chapter 4 System manual
4.1 Icon

4.2 MainGUI

Just as the picture shows, there are some choices in this window.
Single: Choose to play with your friends via net;
Double: Choose to play with your friends locally;
Rule: Choose to look up the rules of the game or tips;
And some rules are as following:
Firstly, I will introduce some basic rules so that you can play the game soon ——
- Each square of the 3x3 game board contains another, smaller, 3x3 game board.
- Where you make your move in a square of any small board, you send the opponent in the respective square of the big board.
- 3 in a row in a small board wins the small board and the big square.
- 3 small boards in a row wins the game.
- Strategize your play, plan your next move, let the opponent win some small boards, while you win the game!
And then, you can look through the detailed rules to find some stratege to play the game better ———
When the game starts, the player with the O piece will move first, and can place his piece wherever he wants. To let the opponent (AI,which I will descibe it later, or friend) place the first piece, you can choose to play with O. Placing the first piece will not give the player such a big advantage as in the classic tic-tac-toe game, he still needs to create a strategy in order to defeat you.
Next, your opponent will have to play the board respective to the square that you’ve just filled.
Your next move will be in a board that your opponent sends you to, given by the square that he just made his move on.
What happens if the opponent sends you to an already won or draw board? Then you can go wherever you like.
After playing a little, you will see that, even though you could win a small board easily, the fact that if the move you make would put your opponent at an advantage, you could chose to not win that board at the time, or perhaps forfeit it, if it will give you an advantage to complete other 3 boards in a row and win the match.
A draw board will not count for either X, nor O.
4.3 LocalGameGUI
When you play the game, the red square will remind you of the area where you can only go.

After you win the game in the small board or win the game finally, the window will be just like this

Besides these, you will enjoy the certain music when you play the game, which is called BGM.
4.4 SingleGameGUI
If you choose to press the button named single, you can play with your friend who is using the same WLAN with you.
But first, you need to log in a new account or sign up if you have had a account.

When you log in or sign up with some errors, there will be a dialog to show something about the erroe, like signing up without account and so on.
Signing up successfully, you will see the window, wihch show some information of you, and you can creat or join a room to play with your friend.


Before your friend join the room, you can only stay in the wait window.

Next, you can play with your friend.

While your opponent will see another picture,which indicates his name on the window.

Each time you place a chess on the chessboard, the information of turn will change.
Another thing I want to explain is that the priority belongs to those who creat the room.
If one of two players wins the game, the winner’s name will appear at the bottom of the window.
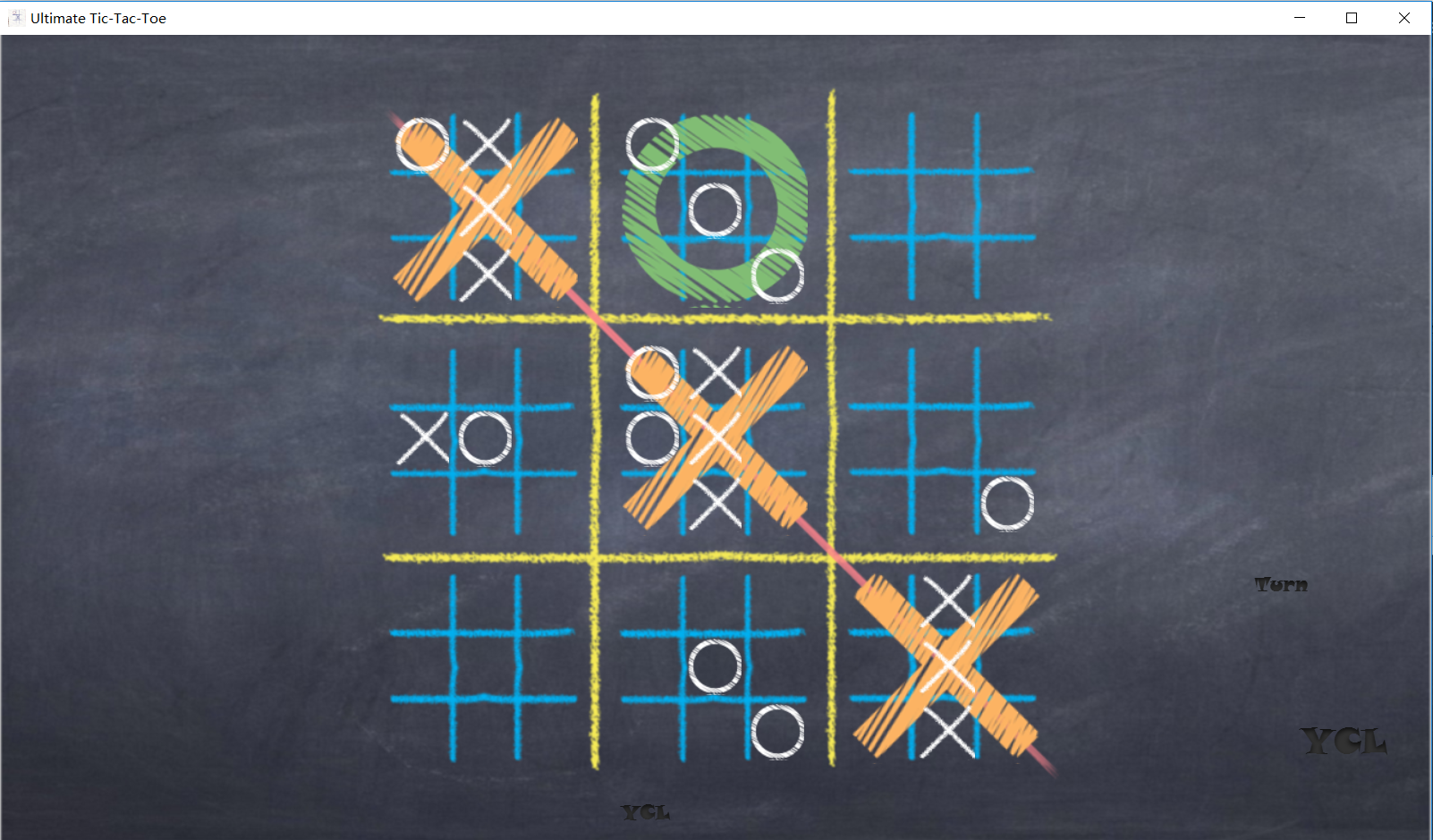

4.5 Other Settings
I haven’t show some GUI, like GUI of logging in 、rule dialog and rank GUI.
But it maybe similar with those I have showed with you or it’s so easy to make it clear for you that I won’t explain them in detail.
Chapter 5 Innovation
Just as I said before, I use some new technologies in this project, which are JavaFX and JDBC.Of course, I may be not very familar with them and take advantages of them well. But, I learn something new and important when I learn and use them.
Something else I want to stress is that the project is finished by mysely compeletely,no copies,no reference in source code. I try my best to complete this game. Finally, the lines of the code are up to 3000+.

Of course, I need to improved it in some functions. Because of the limit of the time,a few of founctions are not implemented well and there are some modes of the game I need to implemented.
And I will write them down later.
Chapter 6 Improvement
6.1 Forget Mode
You can also play on the Forget mode, which erases your 4th oldest game piece, thus having another strategic element which you must focus on, and there won’t be any boards that end-up in ties.
6.2 Play with AI
6.2.1 Computer implementations from Wikipedia
While tic-tac-toe is elementary to solve, and can be done nearly instantly using depth-first search, ultimate tic-tac-toe cannot be reasonably solved using any brute force tactics.
Therefore, more creative computer implementations are necessary in order to play this game.
The most common artificial intelligence (AI) tactic, minimax, may be used to play ultimate tic-tac-toe, but has difficulty playing this. This is because, despite having relatively simple rules, ultimate tic-tac-toe lacks any simple heuristic evaluation function. This function is necessary in minimax, for it determines how good a specific position is. Although elementary evaluation functions can be made for ultimate tic-tac-toe by taking into account the number of local victories, these largely overlook positional advantage that is much harder to quantify. Without any efficient evaluation function, most typical computer implementations are weak, and therefore there are few computer opponents that can consistently outplay humans.
However, artificial intelligence algorithms that don’t need evaluation functions, like the Monte Carlo tree-search algorithm, have no problem in playing this game. The Monte Carlo tree-search relies on random simulations of games in order to determine how good a position is instead of a positional evaluation, and is therefore able to accurately assess how good a current position is. Therefore, computer implementations using these algorithms tend to outperform minimax solutions, and can consistently beat human opponents.
6.2.2 My design of AI
Data structure
Game tree
Each node represents a chessboard situation, and each node has a value generated by the evaluation function. Taking the current situation as the root node, a child node is generated for every possible legal operation, and a game tree is generated iteratively.
Decision tree algorithm
The minimax algorithm
The minimax algorithm will allow both sides to take turns playing chess during the game. When it’s our next turn, I will choose the state with the highest score. And the other side will choose the most unfavorable state for me. It can be said that every time I need to choose the best ( max ) from the worst ( min ) situation my opponent has chosen for me, which is the meaning of the algorithm name minimax.
The algorithm obtains the optimal solution of the current AI movement by solving it on the game tree.The time / space complexity is O ( b d ) \mathcal{O}(b^d) O(bd) , the branching factor ( number of nodes ) of each layer is B, and the search depth is D layer.
Pruning optimization
Alpha-beta pruning
A search algorithm to reduce the number of nodes in the game tree of Minimax algorithm. The algorithm will stop calculating the subsequent development of a strategy when it evaluates that the subsequent development of the strategy is worse than the score of the previous strategy. The results of the algorithm are the same as those of the minimax algorithm, but the branches that do not affect the final decision are cut out.
In short, each node will determine a search and calculation range by alpha and beta values, alpha values representing the lower bound and beta values representing the upper bound. Every time a child node is searched, the scope is corrected according to the rules. The corresponding Max node can modify the lower limit alpha value of the search, and the min node can modify the upper limit beta value of the search. When the situation of b e t a ≤ a l p h a beta \leq alpha beta≤alpha appears, the search for more subtrees will be stopped, and this molecular tree that has not been searched will be ignored to achieve the pruning effect, thus optimizing the game tree and improving the efficiency.
Evaluation method
Valuation function
The valuation function can be simply recorded as
f
(
x
)
=
a
∑
A
−
b
∑
B
+
c
∑
C
−
d
∑
D
+
e
f(x) = a\sum A- b\sum B+ c\sum C- d\sum D+e
f(x)=a∑A−b∑B+c∑C−d∑D+e where A, B, C, D and e are constants to determine the proportion of each part, and a, b, c, d and e are the main influencing factors:
For a chessboard of $ 3 \ times $ 3, different inherent scores are assigned to different positions in the chessboard, as shown in the figure,
| 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 2 | 4 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 |
This score is derived from the number of winning results that can be formed at different positions.
-
A = number of pieces on our side
That is, in the current chessboard of $ 3 \ times $ 3, the number of our chessmen is multiplied and summed with the scores of the corresponding positions according to the number of our chessmen at different score positions to obtain the first part of the numerical value in the model. -
B = number of opposing pieces
That is, in the current chessboard of $ 3 \ times $ 3, the number of opponent pieces is multiplied by the score of the corresponding position according to the number of opponent pieces at different score positions and summed to obtain the second part of the numerical value in the model. -
C = number of threats from the other party
The opponent’s threat refers to the fact that the formed opponent’s two chess pieces are in the same straight line and under legal operation, the opponent can obtain the third son under the straight line and win the chessboard. The third part of the numerical value in the model is obtained by summing up the number of threats formed by the opponent in different positions. -
D = number of our advantages
Our advantage means that the two pieces of the formed opponent are in the same straight line and under the legal operation, we can get the third piece under the straight line and win the chessboard. According to the sum of the threats we have formed in different positions, we can get the fourth part of the numerical value in the model.
As follows, I’m round pieces

According to the above model, the score of the chessboard is obtained as follows
f
=
a
×
2
−
b
×
2
×
3
+
c
×
1
−
d
×
0
f = a \times 2 -b \times 2 \times 3 +c \times 1 - d \times 0
f=a×2−b×2×3+c×1−d×0
Subsequent optimization
- The parameter setting of the evaluation function can be iterated by genetic algorithm ( GA ) to optimize the evaluation function.
- Although the pruning operation is carried out, the complexity is still high, and Monte Carlo tree can be used to search for further optimization.
- More aspects can be included in the valuation function for calculation.
Chapter 7 Summary and evaluation
By the development of the Ultimate Tac-Tic-Toe, I learn some new knowledge about Java and understand some knowledge I have learned beforer better.
Besides those, I learn the importance of the design pattern and qulity manager,which will do me a favor if I can design well at first.
Therefore, I will learn to how to make my design of my project or code better and form some good habits of coding.
At last, I learn something important in testing and I am interested in testing more and more now. I think it will influence my plan of my career in the future.
Appendix and Reference
[1] Core Java Volume I–Fundamentals
[2] Core Java Volume II–Advanced Features
Postscript
You can get the source code from github “src in github”.
























 410
410

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










