1. QoS Fundamental
why we need QOS?
- Lack of Bandwidth
- Latency
- Jitter
- Packet loss
Bindwidth
- speed of the link,in bits per second(bps).
- capacity,how many bits can be sent over the link per second.
Throughput(吞吐量)
Delay
- One-way Delay:Sender send one packet and packet arriving at host destination host
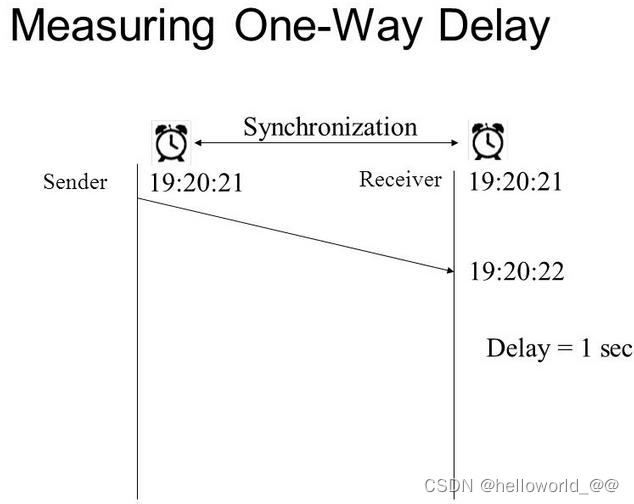
-
Two-way Delay:trip delay counts the one way delay plus the time for the receiver of the first packet to send back a packet.
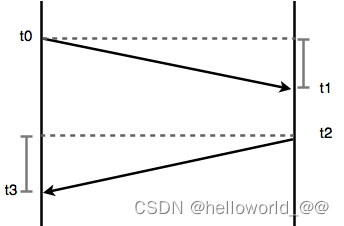
-
t2-t1的时间为 设备处理时间
sorts of Delay
-
Propagation delay
- Propagation delay is the time it takes for a packet to travel from the source to a destination at the speed of
light over a medium such as fiber optic cables or copper wires
- Propagation delay is the time it takes for a packet to travel from the source to a destination at the speed of
-
Serialization delay
- Serialization delay is the time it takes to place all the bits of a packet onto a link. It is a fixed value that
depends on the link speed; the higher the link speed, the lower the delay. The serialization delay s is equal
to the packet size in bits divided by the line speed in bits per second. For example, the serialization delay
for a 1500 byte packet over a 1 Gbps interface is 12 μs
•
s = 12,000 bits / 1000,000,000 bps = 0.000012 s
× 1000 = .012 ms × 1000 = 12 μs
- Serialization delay is the time it takes to place all the bits of a packet onto a link. It is a fixed value that
-
Processing Delay
- Processing delay is the fixed amount of time it takes for a networking device to take the packet from an
input interface and place the packet onto the output queue of the output interface
•
CPU speed
•
CPU utilization
•
IP packet switching mode (process switching, software CEF, or hardware CEF)
•
Router architecture (centralized or distributed)
•
Configured features on both input and output interfaces
- Processing delay is the fixed amount of time it takes for a networking device to take the packet from an
Jitter
- Jitter refers to the variation in one way delay between consecutive packets sent by the same application.
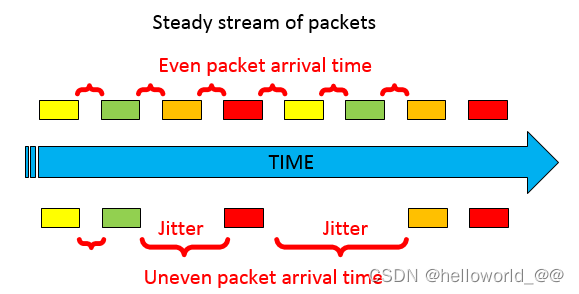
Loss
-
Loss refers to the number of lost messages, usually as a percentage of packets sent.
Loss can be caused by many factors, but often, people think of loss as something caused by faulty cabling or
poor WAN services. However, more loss happens because of the normal operation of the networking devices, in
which the devices’ queues get too full, so the device has nowhere to put new packets, and it discards the packet. -
Loss refers to the number of lost messages, usually as a percentage of packets sent.
-
Loss can be caused by many factors, but often, people think of loss as something caused by faulty cabling or
-
poor WAN services. However, more loss happens because of the normal operation of the networking devices, in
-
which the devices’ queues get too full, so the device has nowhere to put new packets, and it discards the
-
packet.
Types of Traffic Data Applications
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-kBhJdnwd-1686879943622)(C:\Users\16897\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230616093401896.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/44e62a9f4751487b94ba98bfbaad6d08.png)
What is the impact of bandwidth, delay, jitter, and loss on an interactive application (e.g. HTTP Web)
•
packets require a certain amount of
bandwidth capacity
•
each of those packets from the server to the client takes some amount of one
way delay with some jitter
•
packet
lost will cause TCP retransmit
What is the impact of bandwidth, delay, jitter, and loss on a noninteractive application (e.g. backup)
•
delay
and jitter do not matter much
•
enough
bandwidth , less lost is more important
Types of Traffic Voice and Video Applications
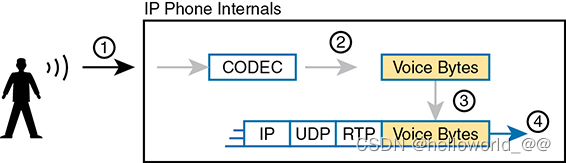
Types of Traffic Voice and Video Applications
Interactive voice does require a much better level of quality for delay, jitter, and loss
Video has a much more varied set of QoS requirements. Generally, think of video like voice, but with a much
higher bandwidth requirement than voice (per flow) and similar requirements for low delay, jitter, and loss .
QoS Tools
Classification and Marking
Queuing (Congestion management)
Shaping and Policing
Congestion Avoidance (Early dropping)
QoS Model
Best effort:
QoS is not enabled for this model. It is used for traffic that does not require any special treatment.
Integrated Services (
IntServ ): Applications signal the network to make a bandwidth reservation and to indicate that they
require special QoS treatment.
Differentiated Services (
DiffServ ): The network identifies classes that require special QoS treatment.
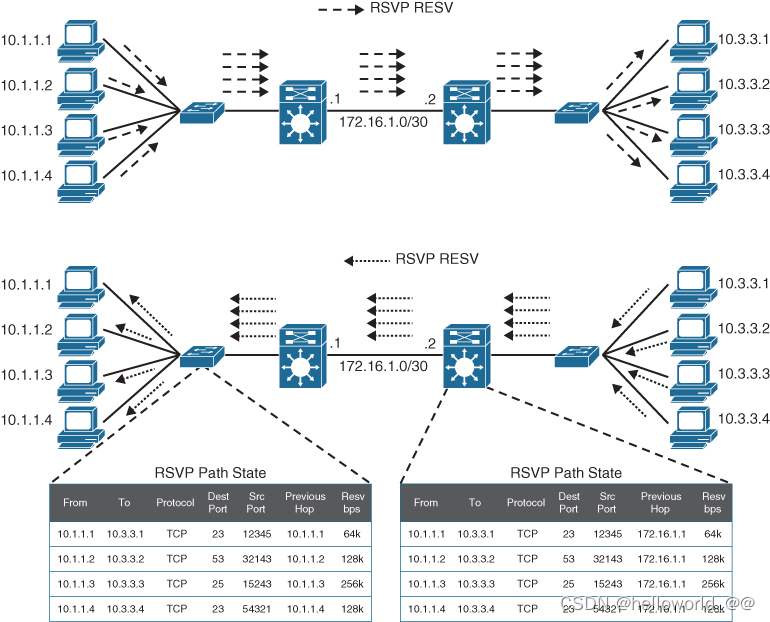
IntServ
uses Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) to reserve resources
throughout a network for a specific application and to provide call admission
control (CAC) to guarantee that no other IP traffic can use the reserved
bandwidth. The bandwidth reserved by an application that is not being used is
wasted.
IntServ
cannot scale well on large networks that might have thousands or millions
The bandwidth reserved by an application that is not being used is
wasted.
IntServ
cannot scale well on large networks that might have thousands or millions
of flows due to the large number of RSVP flows that would need to be maintained






















 312
312











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








