线程同步:线程同步就是让多个线程按顺序访问临界区域,只有在当前线程访问临时区结束后,下一个线程才能继续访问。(临界区加锁即可)
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
int g_num = 0; // 为 g_num_mutex 所保护
mutex g_num_mutex;
void slow_increment(int id)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
g_num_mutex.lock();
++g_num;
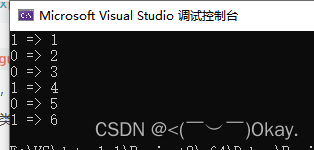
cout << id << " => " << g_num << endl;
g_num_mutex.unlock();
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));
}
}
int main()
{
thread t1(slow_increment, 0);
thread t2(slow_increment, 1);
t1.join();
t2.join();
}
lock_guard
lock_guard在使用上面提供的这个构造函数构造对象时,会自动锁定互斥量,而在退出作用域后进行析构时就会自动解锁,从而保证了互斥量的正确操作,避免忘记unlock()操作而导致线程死锁。
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
int g_num = 0; // 为 g_num_mutex 所保护
mutex g_num_mutex;
void slow_increment(int id)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
{ //这一对{}是lock_guard的作用域,
lock_guard<mutex> lock(g_num_mutex);
++g_num;
cout << id << " => " << g_num << endl;
}
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));
}
}
int main()
{
thread t1(slow_increment, 0);
thread t2(slow_increment, 1);
t1.join();
t2.join();
}























 8378
8378











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










